Self-directed learning empowers individuals to take control of their educational journey by setting goals, identifying resources, and evaluating progress independently. This approach fosters critical thinking, resilience, and adaptability in diverse learning environments. Discover practical strategies to enhance your self-directed learning skills throughout the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
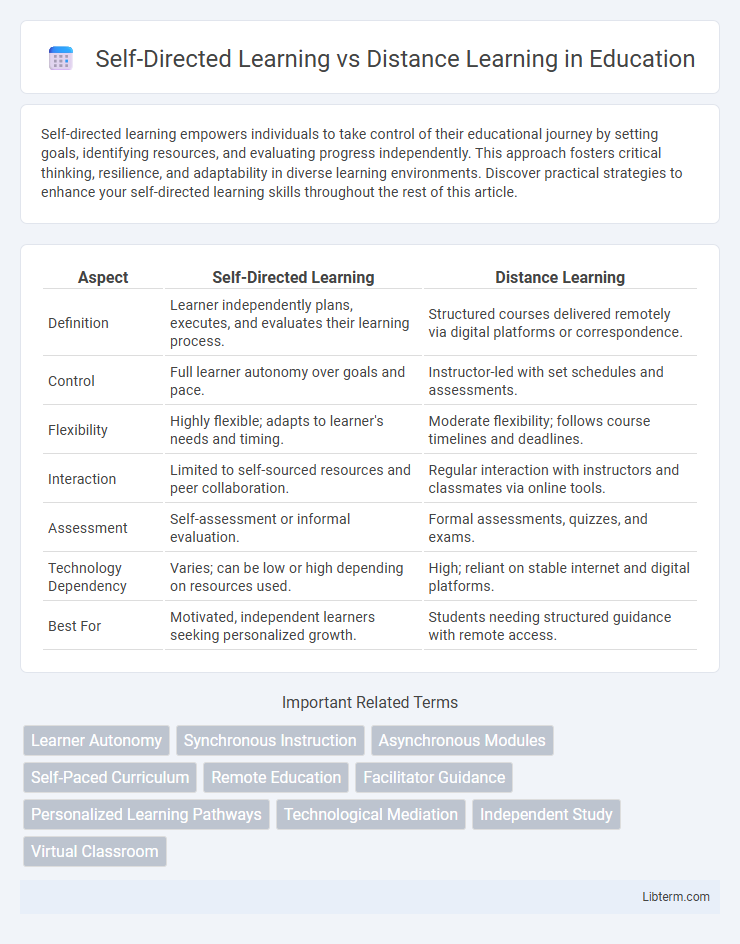
| Aspect | Self-Directed Learning | Distance Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Learner independently plans, executes, and evaluates their learning process. | Structured courses delivered remotely via digital platforms or correspondence. |
| Control | Full learner autonomy over goals and pace. | Instructor-led with set schedules and assessments. |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible; adapts to learner's needs and timing. | Moderate flexibility; follows course timelines and deadlines. |
| Interaction | Limited to self-sourced resources and peer collaboration. | Regular interaction with instructors and classmates via online tools. |
| Assessment | Self-assessment or informal evaluation. | Formal assessments, quizzes, and exams. |
| Technology Dependency | Varies; can be low or high depending on resources used. | High; reliant on stable internet and digital platforms. |
| Best For | Motivated, independent learners seeking personalized growth. | Students needing structured guidance with remote access. |
Understanding Self-Directed Learning
Self-directed learning involves individuals taking initiative, diagnosing their learning needs, setting goals, identifying resources, and evaluating outcomes independently. Unlike distance learning, which primarily refers to the geographical separation of instructor and learner, self-directed learning emphasizes intrinsic motivation and personal responsibility in the educational process. Mastery of self-directed learning skills enhances lifelong learning, critical thinking, and adaptability in diverse educational and professional environments.
Defining Distance Learning
Distance learning is an educational approach where instruction is delivered remotely, typically via online platforms, allowing students to access course materials and interact with educators without being physically present in a traditional classroom. This mode of learning leverages technology such as video lectures, discussion forums, and digital assessments to facilitate knowledge acquisition and skill development. Unlike self-directed learning, distance learning often involves structured curricula and scheduled interactions, providing a guided framework while maintaining flexibility in time and location.
Key Differences Between Self-Directed and Distance Learning
Self-directed learning emphasizes learner autonomy, allowing individuals to set their own goals, select resources, and pace their study, while distance learning typically follows a structured curriculum delivered remotely by an institution. Self-directed learners actively manage their educational journey, relying heavily on intrinsic motivation and self-discipline, whereas distance learning often provides scheduled classes, assessments, and instructor support via online platforms. The key distinction lies in self-directed learning's focus on personalized control versus distance learning's organized format designed for geographic flexibility.
Advantages of Self-Directed Learning
Self-directed learning fosters personalized education by allowing learners to set their own goals, pace, and methods, enhancing motivation and retention. It promotes critical thinking and problem-solving skills through active engagement, supporting lifelong learning habits. Unlike distance learning, which often relies on structured curriculum and schedules, self-directed learning empowers autonomy, making it adaptable to individual interests and career needs.
Benefits of Distance Learning
Distance learning offers unparalleled flexibility, enabling students to access educational content from any location at any time, which suits diverse schedules and lifestyles. It provides a wide range of courses and programs, often at reduced costs compared to traditional settings, making education more accessible and affordable. Advanced technologies and interactive platforms enhance engagement and allow personalized pacing, improving knowledge retention and skill acquisition.
Challenges Facing Self-Directed Learners
Self-directed learners often face challenges such as lack of motivation, time management difficulties, and limited access to immediate feedback. Unlike distance learning environments that provide structured schedules and instructor guidance, self-directed learning demands high levels of self-discipline and resourcefulness. Overcoming these obstacles requires strong organizational skills and effective use of learning technologies to maintain progress and engagement.
Common Obstacles in Distance Learning
Common obstacles in distance learning include limited interaction with instructors, which can hinder personalized feedback and delay clarification of doubts. Technical issues such as unreliable internet connections and inadequate access to digital devices disrupt the learning process and reduce engagement. Time management challenges and lack of self-motivation often lead to procrastination and lower course completion rates in remote education environments.
Skills Needed for Self-Directed vs Distance Learning
Self-directed learning requires strong skills in time management, self-motivation, and critical thinking to independently set goals, seek resources, and evaluate personal progress. Distance learning emphasizes digital literacy, effective communication, and adaptability to virtual environments for successful engagement with instructors and peers. Mastery of self-regulation distinguishes self-directed learners, while technical proficiency is crucial for navigating distance learning platforms.
Technology’s Role in Both Learning Models
Technology enhances self-directed learning by providing personalized resources, interactive tools, and access to vast online libraries, empowering learners to control their educational pace and focus. In distance learning, technology enables real-time virtual classrooms, video conferencing, and collaborative platforms, facilitating structured interaction despite physical separation. Both models rely on digital advancements like AI-driven analytics and adaptive learning systems to optimize engagement and improve educational outcomes.
Choosing the Right Learning Approach for Your Needs
Choosing between self-directed learning and distance learning depends on your personal goals, learning style, and discipline levels. Self-directed learning offers flexibility and autonomy, empowering you to set your own pace and explore topics deeply, while distance learning provides structured courses with access to instructors and peer support. Evaluating your need for guidance, interaction, and time management helps determine the optimal approach tailored to your educational needs.
Self-Directed Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com