Curriculum acceleration enables students to progress through educational material at a faster pace, tailored to their individual learning abilities and needs. It fosters academic growth by challenging learners beyond the standard grade level, promoting engagement and mastery of advanced concepts. Discover how curriculum acceleration can transform Your educational journey and boost academic success in the full article.
Table of Comparison
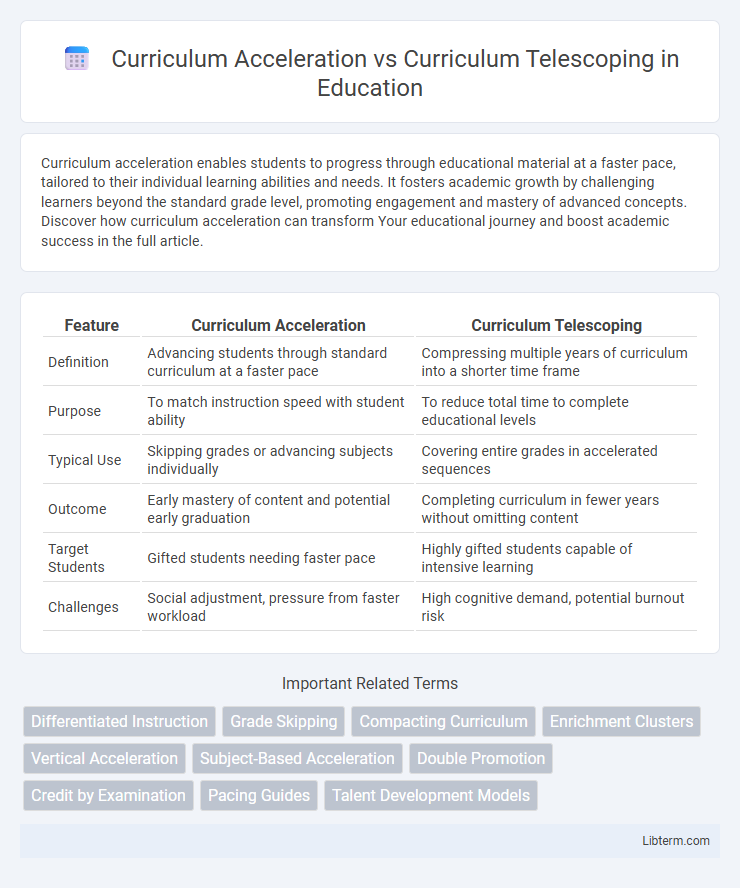
| Feature | Curriculum Acceleration | Curriculum Telescoping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Advancing students through standard curriculum at a faster pace | Compressing multiple years of curriculum into a shorter time frame |
| Purpose | To match instruction speed with student ability | To reduce total time to complete educational levels |
| Typical Use | Skipping grades or advancing subjects individually | Covering entire grades in accelerated sequences |
| Outcome | Early mastery of content and potential early graduation | Completing curriculum in fewer years without omitting content |
| Target Students | Gifted students needing faster pace | Highly gifted students capable of intensive learning |
| Challenges | Social adjustment, pressure from faster workload | High cognitive demand, potential burnout risk |
Understanding Curriculum Acceleration
Curriculum acceleration allows gifted students to progress through educational materials at a faster pace by promoting early mastery of content and grade skipping, enhancing intellectual engagement and motivation. Unlike curriculum telescoping, which compresses the standard curriculum into a shorter time frame without skipping content, acceleration emphasizes personalized learning speed aligned with student readiness and cognitive ability. Effective implementation of curriculum acceleration requires careful assessment of academic and social-emotional factors to support sustained achievement and well-being.
What is Curriculum Telescoping?
Curriculum telescoping is an educational strategy that compresses the standard curriculum into a shorter time frame by allowing students to complete multiple grade levels or courses at an accelerated pace. This approach enables gifted or advanced learners to progress more rapidly through content without the extended periods typical of regular grade progression. Unlike curriculum acceleration, which may involve skipping grades or enrichment programs, telescoping specifically condenses the curriculum's timeframe while maintaining all required learning objectives.
Key Differences Between Acceleration and Telescoping
Curriculum acceleration involves advancing students through standard grade levels at a faster pace, allowing them to complete educational milestones earlier than usual. Curriculum telescoping compresses the entire curriculum timeline by condensing content, enabling learners to finish the program in a shorter overall duration without skipping key stages. The key difference lies in acceleration promoting early grade advancement, while telescoping focuses on condensing content delivery within the same grade structure.
Benefits of Curriculum Acceleration
Curriculum acceleration enhances academic growth by allowing gifted students to progress at a faster pace, preventing disengagement and underachievement. It promotes deeper mastery of subjects by challenging students to advance beyond standard grade-level content, fostering motivation and intellectual stimulation. Research shows accelerated learning aligns with higher student satisfaction and improved long-term educational outcomes compared to traditional pacing.
Advantages of Curriculum Telescoping
Curriculum telescoping enables students to complete standard educational content in a reduced timeframe, fostering early entry into advanced studies or career paths. This approach enhances motivation and engagement by allowing learners to progress at their own accelerated pace. The condensed learning schedule frequently leads to increased academic efficiency and better alignment with gifted or high-achieving student needs.
Challenges and Drawbacks of Each Approach
Curriculum acceleration often presents challenges such as increased academic pressure and potential gaps in foundational knowledge due to the rapid pace of instruction. Curriculum telescoping may lead to content overload and diminished depth of understanding as multiple grade levels are compressed into a shorter timeframe. Both approaches can cause social-emotional stress for students who may struggle to keep up with peer interactions and developmental milestones.
Suitable Student Profiles for Acceleration vs Telescoping
Curriculum acceleration suits gifted students who demonstrate advanced cognitive abilities, rapid mastery of subject matter, and high motivation to progress beyond age-level peers. In contrast, curriculum telescoping is ideal for learners with consistent performance but strong focus and dedication, allowing them to complete standard curricula in a shorter timeframe without skipping significant content. Both approaches require ongoing assessment and readiness evaluation to ensure the student's social and emotional growth aligns with academic advancement.
Implementation Strategies in Schools
Curriculum acceleration involves advancing students through standard academic content at a faster pace, often by skipping grades or completing grade-level content in less time, while curriculum telescoping compresses multi-year curricula into shorter periods without omitting essential material. Effective implementation strategies in schools include individualized student assessments to determine readiness, flexible scheduling to accommodate accelerated learning paths, and ongoing teacher training to address differentiated instruction. Schools must also establish clear communication channels with parents and provide counseling support to ensure students adapt socially and emotionally to accelerated or telescoped programs.
Measuring Success: Assessing Outcomes
Measuring success in curriculum acceleration involves evaluating students' ability to master content at an advanced pace while maintaining comprehension and retention levels comparable to or exceeding grade-level standards. Curriculum telescoping success is assessed by examining how effectively students complete multi-year content in a shortened timeframe, emphasizing knowledge integration and application without compromising depth of understanding. Both approaches rely on formative and summative assessments, standardized test scores, and long-term academic performance to ensure educational effectiveness and student readiness for subsequent learning stages.
Choosing the Right Approach for Gifted Learners
Curriculum acceleration allows gifted learners to progress through standard educational content at a faster pace by skipping grades or advancing through subjects quickly, optimizing their intellectual growth without sacrificing content depth. Curriculum telescoping condenses the same curriculum into a shorter time frame, maintaining complete mastery while reducing time spent on repetitive material. Selecting the appropriate approach depends on the learner's cognitive readiness, emotional maturity, and the educational goals, ensuring both challenge and engagement for optimal development.
Curriculum Acceleration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com