Online teaching transforms education by enabling flexible learning environments and personalized instruction tailored to your needs. Innovative digital tools and platforms foster engagement and collaboration beyond traditional classrooms. Explore the rest of this article to discover effective strategies and benefits of online teaching.
Table of Comparison
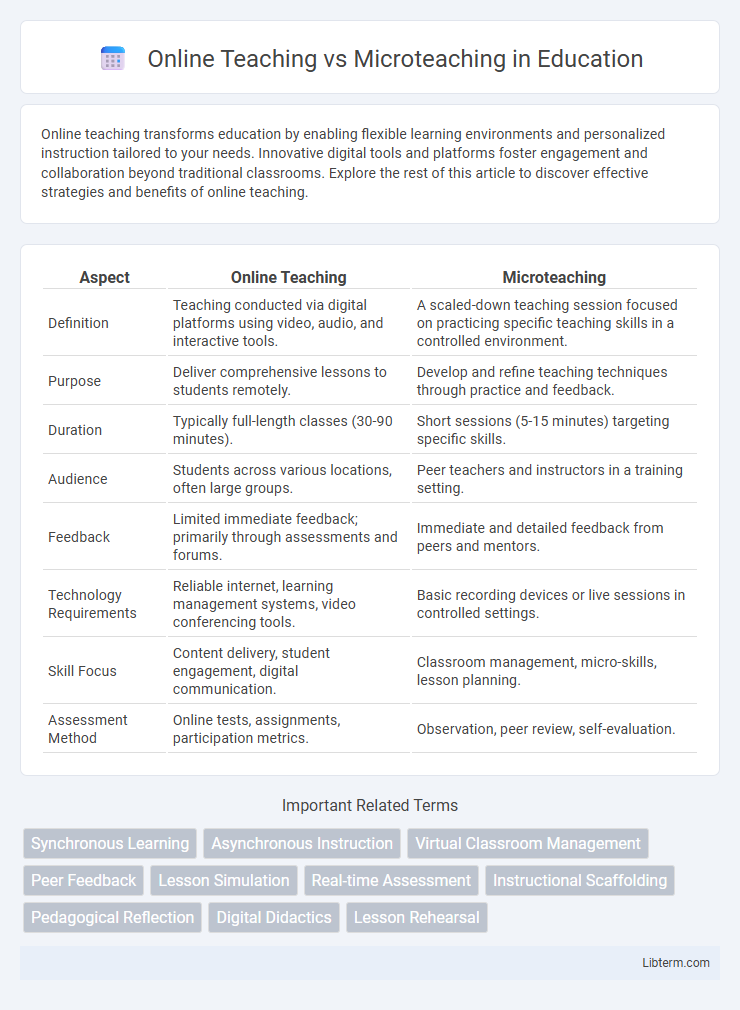
| Aspect | Online Teaching | Microteaching |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Teaching conducted via digital platforms using video, audio, and interactive tools. | A scaled-down teaching session focused on practicing specific teaching skills in a controlled environment. |
| Purpose | Deliver comprehensive lessons to students remotely. | Develop and refine teaching techniques through practice and feedback. |
| Duration | Typically full-length classes (30-90 minutes). | Short sessions (5-15 minutes) targeting specific skills. |
| Audience | Students across various locations, often large groups. | Peer teachers and instructors in a training setting. |
| Feedback | Limited immediate feedback; primarily through assessments and forums. | Immediate and detailed feedback from peers and mentors. |
| Technology Requirements | Reliable internet, learning management systems, video conferencing tools. | Basic recording devices or live sessions in controlled settings. |
| Skill Focus | Content delivery, student engagement, digital communication. | Classroom management, micro-skills, lesson planning. |
| Assessment Method | Online tests, assignments, participation metrics. | Observation, peer review, self-evaluation. |
Introduction to Online Teaching and Microteaching
Online teaching leverages digital platforms to deliver educational content, enabling real-time interaction and accessibility for diverse learners worldwide. Microteaching serves as a focused practice method where teachers conduct short, recorded lessons to refine specific teaching skills and receive targeted feedback. Combining these approaches enhances instructional effectiveness by integrating broad digital reach with precision skill development.
Core Concepts: Defining Online Teaching
Online teaching involves delivering educational content through digital platforms, enabling remote interaction between instructors and learners using tools like video conferencing, learning management systems, and multimedia resources. It emphasizes accessibility, flexibility, and the integration of technology to facilitate synchronous and asynchronous learning experiences. In contrast, microteaching is a focused, practice-based technique designed to develop specific teaching skills through short, recorded sessions and feedback, rather than delivering full-length online courses.
Microteaching Explained: Key Principles
Microteaching, a teacher training technique developed in the 1960s at Stanford University, involves delivering short, focused teaching sessions to a small group for targeted feedback and skill improvement. Key principles include controlled practice, focused skill development, and immediate constructive feedback to enhance teaching effectiveness. Unlike online teaching, microteaching emphasizes hands-on practice and peer review rather than remote content delivery and broad audience engagement.
Technological Integration in Online Teaching
Online teaching leverages advanced technological tools such as virtual whiteboards, video conferencing platforms, and interactive learning management systems to create dynamic and engaging learning experiences. These technologies enable real-time feedback, multimedia resources, and collaborative activities that enhance student understanding and participation. In contrast, microteaching primarily focuses on limited-scale teaching practice sessions without extensive use of digital tools, emphasizing skill development in controlled environments rather than full technological integration.
Classroom Environment: Virtual vs Simulated
Online teaching utilizes virtual classroom environments that enable real-time interaction and collaboration through video conferencing, chat, and digital whiteboards, fostering a dynamic and accessible learning space. Microteaching takes place in a simulated classroom setting, allowing educators to practice specific teaching techniques with a small group or peers, focusing on skill refinement and immediate feedback. Both environments offer unique benefits for teacher development, with virtual classrooms enhancing broad engagement and simulated settings supporting targeted instructional practice.
Instructor Roles: Online Platforms vs Micro Sessions
Online teaching requires instructors to manage virtual classrooms, utilize digital tools, and facilitate student engagement through multimedia content and interactive platforms like Zoom or Moodle. Microteaching focuses on brief, targeted sessions wherein instructors emphasize skill refinement, immediate feedback, and practice in a controlled, low-stakes environment often using peer review methodologies. The instructor's role in online platforms involves broader course management and technical proficiency, while microteaching prioritizes personalized coaching and micro-level pedagogical adjustments.
Assessment and Feedback Mechanisms
Online teaching utilizes digital platforms to deliver content and assess student performance through quizzes, assignments, and automated grading systems, enabling immediate feedback and data-driven insights. Microteaching focuses on brief, recorded teaching sessions reviewed by peers or instructors who provide personalized, qualitative feedback emphasizing specific teaching skills and techniques. Assessment in microteaching is formative with targeted feedback on instructional methods, while online teaching often integrates summative assessments with scalable, technology-based feedback mechanisms.
Student Engagement: Digital Tools vs Peer Interaction
Online teaching leverages digital tools such as interactive quizzes, video conferencing, and real-time polling to enhance student engagement by providing dynamic and accessible learning experiences. Microteaching emphasizes peer interaction through small-group sessions where students receive immediate feedback, fostering collaborative learning and communication skills. Combining digital tools with peer interaction can significantly boost engagement by blending technological innovation with social learning dynamics.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Method
Online teaching offers flexibility and access to diverse resources, enabling educators to reach a global audience while fostering interactive multimedia learning environments. However, it faces challenges such as limited real-time feedback, potential technical issues, and reduced personal interaction affecting student engagement. Microteaching provides targeted skill development through focused practice sessions and immediate peer or instructor feedback, enhancing teaching techniques in a controlled setting, but its scope is limited to short teaching segments and less applicable for comprehensive curriculum delivery.
Choosing the Right Method: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right method between online teaching and microteaching depends on factors such as learning objectives, audience size, and technological accessibility. Online teaching offers scalability and real-time interaction suited for diverse learners, while microteaching provides intensive skill development through focused practice and feedback in smaller settings. Consider the availability of infrastructure, learner engagement levels, and specific pedagogical goals to maximize educational outcomes.
Online Teaching Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com