Curriculum modification involves tailoring educational content to meet the diverse learning needs of students, ensuring greater accessibility and engagement. This process includes adjusting the scope, sequence, and complexity of material without compromising educational standards. Discover how curriculum modification can enhance Your teaching strategies and student outcomes by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
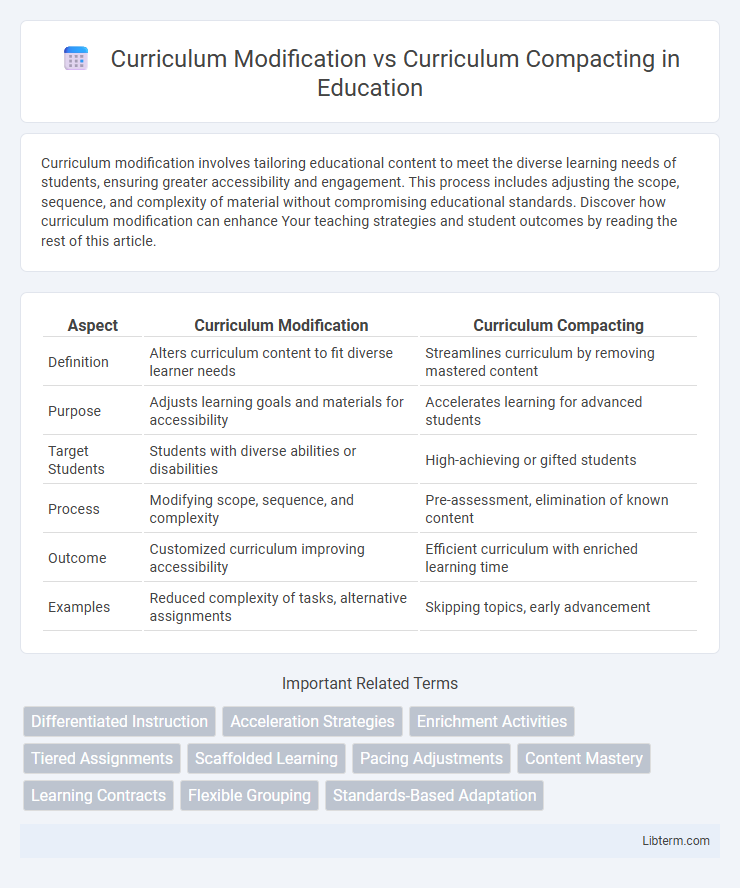
| Aspect | Curriculum Modification | Curriculum Compacting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Alters curriculum content to fit diverse learner needs | Streamlines curriculum by removing mastered content |
| Purpose | Adjusts learning goals and materials for accessibility | Accelerates learning for advanced students |
| Target Students | Students with diverse abilities or disabilities | High-achieving or gifted students |
| Process | Modifying scope, sequence, and complexity | Pre-assessment, elimination of known content |
| Outcome | Customized curriculum improving accessibility | Efficient curriculum with enriched learning time |
| Examples | Reduced complexity of tasks, alternative assignments | Skipping topics, early advancement |
Introduction to Curriculum Modification and Curriculum Compacting
Curriculum modification involves altering the content, performance expectations, or assessment methods to accommodate diverse learner needs, ensuring all students can access and engage meaningfully with the curriculum. Curriculum compacting streamlines existing curriculum by pre-assessing student mastery and eliminating redundant instruction, allowing advanced learners to progress at an accelerated pace. Both approaches aim to optimize educational outcomes by aligning curriculum design with individual student abilities and readiness levels.
Defining Curriculum Modification
Curriculum modification involves altering the content, complexity, or performance expectations to accommodate diverse learner needs, often by simplifying or reducing the material. This approach is essential for students with disabilities or significant learning challenges who require meaningful access to the curriculum at an adjusted level. Unlike curriculum compacting, which accelerates learning by reducing repetition of mastered material, modification changes the learning goals to ensure accessibility and achievement.
Understanding Curriculum Compacting
Curriculum compacting streamlines the standard curriculum by assessing and eliminating content already mastered by a student, allowing for personalized acceleration within the same instructional framework. This targeted approach enhances engagement and intellectual growth by focusing on essential, yet challenging material without redundancy. Unlike broad curriculum modification, compacting maintains core objectives while optimizing learning efficiency for advanced or gifted students.
Key Differences Between Modification and Compacting
Curriculum modification involves altering the content, objectives, or materials to meet diverse learner needs, often simplifying or reducing the complexity of the curriculum. Curriculum compacting, on the other hand, streamlines the existing curriculum by eliminating repetition and non-essential content for advanced or accelerated students, allowing faster progression through the material. The key difference lies in modification fundamentally changing curriculum expectations, while compacting maintains standards but adjusts pacing and depth.
Goals of Curriculum Modification
Curriculum modification aims to tailor educational content to meet individual student needs by adjusting learning goals, reducing complexity, and focusing on essential skills and concepts for mastery. It prioritizes achievable objectives that align with students' abilities while maintaining the integrity of core subject matter. This approach ensures personalized learning outcomes and supports diverse learners in reaching meaningful academic progress.
Objectives of Curriculum Compacting
Curriculum Compacting aims to streamline the instructional process by identifying and eliminating content that students have already mastered, thereby freeing time for enrichment and acceleration activities. The primary objective is to prevent redundancy, maintain student engagement, and challenge advanced learners with appropriately advanced material. This approach enhances educational efficiency and supports differentiated learning by tailoring curriculum pace to individual student needs.
Target Student Populations
Curriculum modification primarily targets students with diverse learning needs, including those with disabilities or English language learners, by adjusting content complexity and learning goals to enhance accessibility. Curriculum compacting is designed for gifted and talented students who already demonstrate mastery of standard curriculum, allowing them to skip redundant lessons and engage in advanced or enriched activities. Both strategies aim to optimize educational outcomes by tailoring instructional approaches to specific student populations' readiness and needs.
Practical Strategies for Implementation
Curriculum modification involves altering content complexity or learning expectations to meet diverse student needs, often by simplifying materials or extending timelines, while curriculum compacting streamlines instruction by eliminating already-mastered content to free time for enrichment activities. Practical strategies for implementing curriculum modification include differentiated assignments, tiered assessments, and scaffolding techniques that align with students' readiness levels. For curriculum compacting, teachers can use pre-assessments to identify mastered skills, then design personalized learning plans and compacted lesson units that maximize engagement without redundancy.
Benefits and Challenges of Each Approach
Curriculum modification offers tailored learning experiences by adjusting content complexity and pacing to meet diverse student needs, enhancing engagement and comprehension but requiring extensive planning and resources. Curriculum compacting streamlines content by eliminating redundancy for advanced learners, fostering motivation and deeper exploration, though it may risk gaps in foundational knowledge if not carefully balanced. Both strategies improve educational outcomes, yet they demand careful assessment and teacher expertise to align modifications or compacting with individual learner profiles.
Choosing the Right Approach for Diverse Learners
Curriculum Modification tailors the content, process, or product to meet the unique needs of diverse learners by altering objectives and expectations, while Curriculum Compacting streamlines the curriculum by eliminating already-mastered material to allow for accelerated learning. Educators must assess student readiness, learning pace, and mastery levels to determine whether modification or compacting better supports individual growth and engagement. Selecting the right approach involves careful analysis of student data and instructional goals, ensuring effective differentiation that maximizes learning outcomes.
Curriculum Modification Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com