Solo teaching demands a unique blend of adaptability, creativity, and strong classroom management skills to effectively engage students and foster a productive learning environment. Tailoring lessons to meet diverse student needs while maintaining clear objectives ensures your teaching resonates and promotes academic growth. Discover practical strategies and tips to excel in solo teaching by exploring the rest of this article.
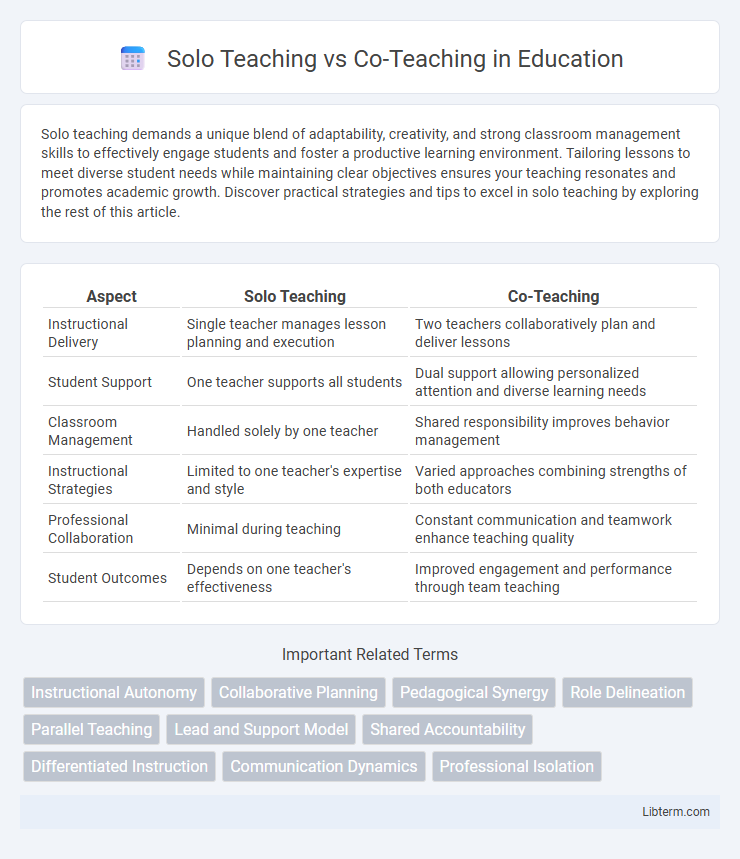
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Solo Teaching | Co-Teaching |
|---|---|---|
| Instructional Delivery | Single teacher manages lesson planning and execution | Two teachers collaboratively plan and deliver lessons |
| Student Support | One teacher supports all students | Dual support allowing personalized attention and diverse learning needs |
| Classroom Management | Handled solely by one teacher | Shared responsibility improves behavior management |
| Instructional Strategies | Limited to one teacher's expertise and style | Varied approaches combining strengths of both educators |
| Professional Collaboration | Minimal during teaching | Constant communication and teamwork enhance teaching quality |
| Student Outcomes | Depends on one teacher's effectiveness | Improved engagement and performance through team teaching |
Understanding Solo Teaching: Definition and Core Features
Solo teaching involves a single educator delivering instruction, managing classroom activities, and assessing student progress independently. Core features include sole responsibility for lesson planning, classroom management, and personalized student support, allowing for streamlined decision-making and instructional consistency. This approach fosters direct teacher-student interactions but may limit collaborative teaching strategies and diverse instructional perspectives.
What is Co-Teaching? Models and Approaches
Co-teaching involves two educators collaboratively delivering instruction within the same classroom, enhancing student engagement and learning outcomes through shared expertise. Common models include Team Teaching, where both teachers simultaneously lead lessons; One Teach, One Assist, where one leads while the other supports students; and Station Teaching, where the class is divided into groups rotating between teachers. These approaches foster differentiated instruction and accommodate diverse learning needs more effectively than solo teaching.
Benefits of Solo Teaching: Flexibility and Autonomy
Solo teaching offers unparalleled flexibility in lesson planning and classroom management, allowing educators to tailor instruction to their students' unique needs without external constraints. This autonomy empowers teachers to implement innovative strategies, adjust pacing spontaneously, and maintain consistent classroom routines, enhancing overall student engagement. Furthermore, solo teaching fosters strong teacher-student relationships by enabling personalized attention and immediate feedback.
Advantages of Co-Teaching: Collaboration and Support
Co-teaching enhances classroom dynamics through collaboration, allowing teachers to combine expertise and address diverse learning needs more effectively. Shared responsibility reduces individual workload and provides continuous peer support, improving instructional quality and student outcomes. This collaborative model fosters professional growth and creates a more inclusive learning environment for all students.
Challenges Faced in Solo Teaching Environments
Solo teaching environments often present challenges such as increased workload, limited collaboration, and difficulty in meeting diverse student needs. Teachers must independently design lesson plans, manage classroom behavior, and assess student progress without peer support. This isolation can lead to burnout and hinder professional growth compared to co-teaching settings.
Common Obstacles in Co-Teaching Classrooms
Co-teaching classrooms commonly face obstacles such as unclear roles and responsibilities between educators, leading to inconsistent instructional delivery. Conflicting teaching styles and communication breakdowns can hinder collaboration and negatively impact student engagement. Time constraints for planning and lack of professional development further challenge the effectiveness of co-teaching models.
Impact on Student Learning: Solo vs. Co-Teaching
Solo teaching allows for personalized instructional control and direct feedback, often tailoring lessons to individual student needs, which can enhance focused skill development. Co-teaching leverages diverse expertise and collaborative strategies, promoting differentiated instruction and inclusive learning environments that support varied student abilities. Research indicates that co-teaching models generally lead to improved academic outcomes and higher student engagement, especially in diverse or special education settings.
Teacher Workload Comparison: Efficiency and Burnout Risks
Solo teaching often results in a higher workload for educators due to full responsibility for lesson planning, classroom management, and student assessments. Co-teaching distributes these tasks between two or more teachers, improving efficiency and reducing individual burnout risks by sharing instructional and administrative duties. Research indicates that collaborative teaching models enhance teacher well-being and sustainability by fostering support and workload balance.
Choosing the Right Approach: Key Considerations for Schools
Choosing the right approach between solo teaching and co-teaching depends on factors such as class size, student needs, and teacher expertise. Solo teaching offers direct control and tailored instruction, while co-teaching promotes collaboration and diverse teaching strategies to support inclusive classrooms. Schools must assess resource availability, professional development opportunities, and desired student outcomes to determine the most effective model.
Future Trends in Classroom Instruction: Blending Solo and Co-Teaching
Future classroom instruction emphasizes a blended model combining solo teaching's individualized focus with co-teaching's collaborative strengths to maximize student engagement and learning outcomes. Advances in educational technology facilitate seamless integration of solo instructional methods and co-teaching frameworks, enabling personalized learning paths and diverse instructional strategies within inclusive classroom environments. Data-driven approaches guide real-time adjustments, promoting adaptive teaching models that respond to varied student needs while fostering professional collaboration among educators.
Solo Teaching Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com