Improving reading comprehension enhances your ability to understand, interpret, and analyze written texts effectively. Techniques such as identifying main ideas, summarizing content, and making inferences strengthen critical thinking skills. Explore the rest of this article to discover practical strategies for boosting your reading comprehension.
Table of Comparison
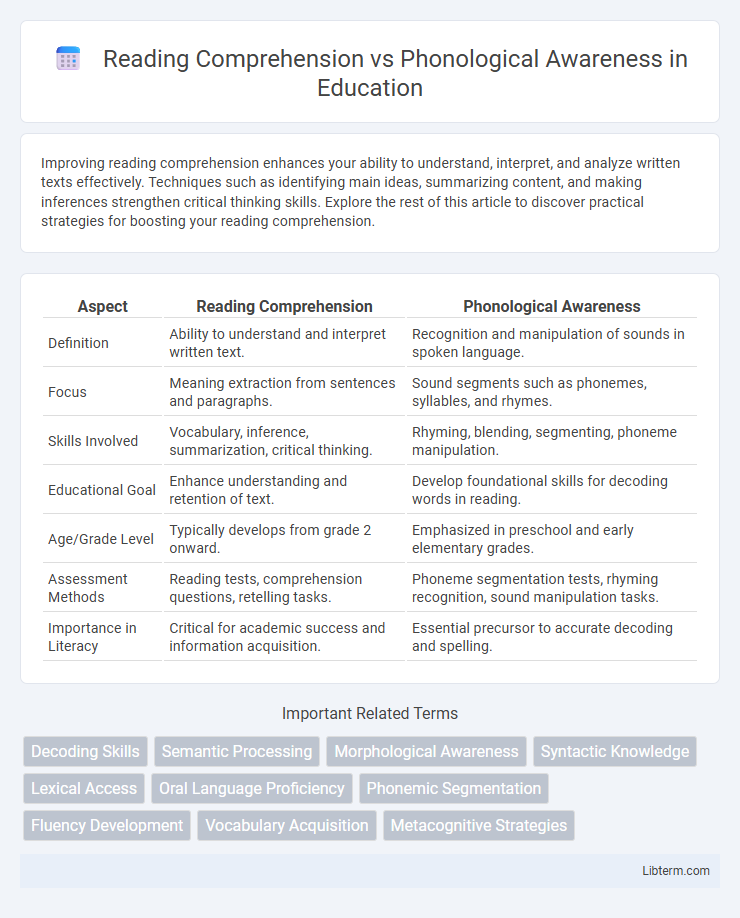
| Aspect | Reading Comprehension | Phonological Awareness |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to understand and interpret written text. | Recognition and manipulation of sounds in spoken language. |
| Focus | Meaning extraction from sentences and paragraphs. | Sound segments such as phonemes, syllables, and rhymes. |
| Skills Involved | Vocabulary, inference, summarization, critical thinking. | Rhyming, blending, segmenting, phoneme manipulation. |
| Educational Goal | Enhance understanding and retention of text. | Develop foundational skills for decoding words in reading. |
| Age/Grade Level | Typically develops from grade 2 onward. | Emphasized in preschool and early elementary grades. |
| Assessment Methods | Reading tests, comprehension questions, retelling tasks. | Phoneme segmentation tests, rhyming recognition, sound manipulation tasks. |
| Importance in Literacy | Critical for academic success and information acquisition. | Essential precursor to accurate decoding and spelling. |
Understanding Reading Comprehension
Reading comprehension involves the ability to understand, interpret, and analyze text by integrating vocabulary, background knowledge, and context clues. It requires higher-order cognitive skills such as inferencing, summarizing, and critical thinking, distinguishing it from phonological awareness, which focuses on recognizing and manipulating sounds in spoken language. Mastery of reading comprehension enables readers to extract meaning from complex texts and supports academic success across subjects.
Defining Phonological Awareness
Phonological awareness refers to the ability to recognize and manipulate sound structures in spoken language, such as phonemes, syllables, and rhymes. This foundational skill is crucial for decoding words and developing strong reading comprehension, as it enables learners to connect sounds with letters. Effective reading programs emphasize phonological awareness to improve overall literacy and support successful reading development.
Key Differences Between Reading Comprehension and Phonological Awareness
Reading comprehension involves understanding and interpreting text by integrating vocabulary, syntax, and context, whereas phonological awareness refers to the ability to recognize and manipulate sounds within spoken words. Phonological awareness is a foundational skill that supports decoding and word recognition, while reading comprehension relies on higher-level cognitive processes such as inference and background knowledge. Effective literacy instruction addresses both phonological awareness and reading comprehension to develop proficient readers.
The Role of Reading Comprehension in Literacy
Reading comprehension plays a crucial role in literacy by enabling individuals to construct meaning from text, which is fundamental for effective communication and learning. Unlike phonological awareness, which involves recognizing and manipulating sounds in spoken language, reading comprehension integrates vocabulary knowledge, background information, and cognitive strategies to understand and interpret written content. Research shows that strong reading comprehension skills significantly enhance academic performance and lifelong literacy development.
Importance of Phonological Awareness in Early Reading
Phonological awareness is crucial in early reading development as it enables children to recognize and manipulate sounds in spoken language, forming the foundation for decoding words. Mastery of phonological skills directly supports reading comprehension by facilitating word recognition and fluency, which are essential for understanding text. Research consistently shows that children with strong phonological awareness demonstrate better reading outcomes and are less likely to experience reading difficulties.
How Phonological Awareness Influences Reading Skills
Phonological awareness is crucial for developing strong reading comprehension because it enables children to recognize and manipulate sounds in spoken language, forming the foundation for decoding words. Skills such as phoneme segmentation and blending directly improve word recognition speed and accuracy, which are essential for understanding text. Research shows that early phonological awareness interventions significantly enhance reading fluency, vocabulary acquisition, and overall literacy outcomes.
Common Challenges in Reading Comprehension
Common challenges in reading comprehension include difficulties with vocabulary knowledge, inferencing skills, and the ability to connect text to prior knowledge, which are distinct from phonological awareness focused on sound recognition and manipulation. Students struggling with comprehension often face obstacles in understanding complex sentence structures and extracting main ideas, whereas phonological awareness primarily involves decoding skills essential for early reading development. Addressing these challenges requires targeted instructional strategies that enhance semantic processing and critical thinking beyond phonological decoding.
Strategies to Improve Phonological Awareness
Effective strategies to improve phonological awareness include explicit instruction in phoneme segmentation, blending, and manipulation, which help learners recognize and handle sounds within words. Incorporating multisensory approaches, such as using visual aids, gestures, and tactile activities, enhances the connection between sounds and symbols. Regular practice with rhyming games, syllable counting, and sound matching strengthens foundational skills necessary for successful reading comprehension.
Integrating Both Skills for Effective Reading Instruction
Integrating reading comprehension and phonological awareness enhances literacy development by addressing both understanding of text and decoding abilities. Effective reading instruction incorporates phonological awareness exercises to build sound recognition skills while simultaneously fostering comprehension strategies such as inference and summarization. Combining these skills ensures a balanced approach that supports fluent, meaningful reading.
Assessing and Supporting Student Progress
Reading comprehension assessment involves evaluating a student's ability to understand and interpret text by analyzing their responses to questions about key ideas, details, and inference. Phonological awareness assessment focuses on measuring a student's skill in recognizing and manipulating sounds in spoken language, such as rhymes, syllables, and phonemes. Supporting student progress requires targeted interventions, including explicit instruction in decoding skills to enhance phonological awareness and strategies like summarization and questioning to improve reading comprehension.
Reading Comprehension Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com