Differentiated instruction tailors teaching strategies to meet diverse student needs, ensuring every learner can access and engage with the curriculum effectively. By adapting content, process, and product, educators foster a more inclusive and supportive classroom environment. Discover how implementing differentiated instruction can transform Your teaching approach in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
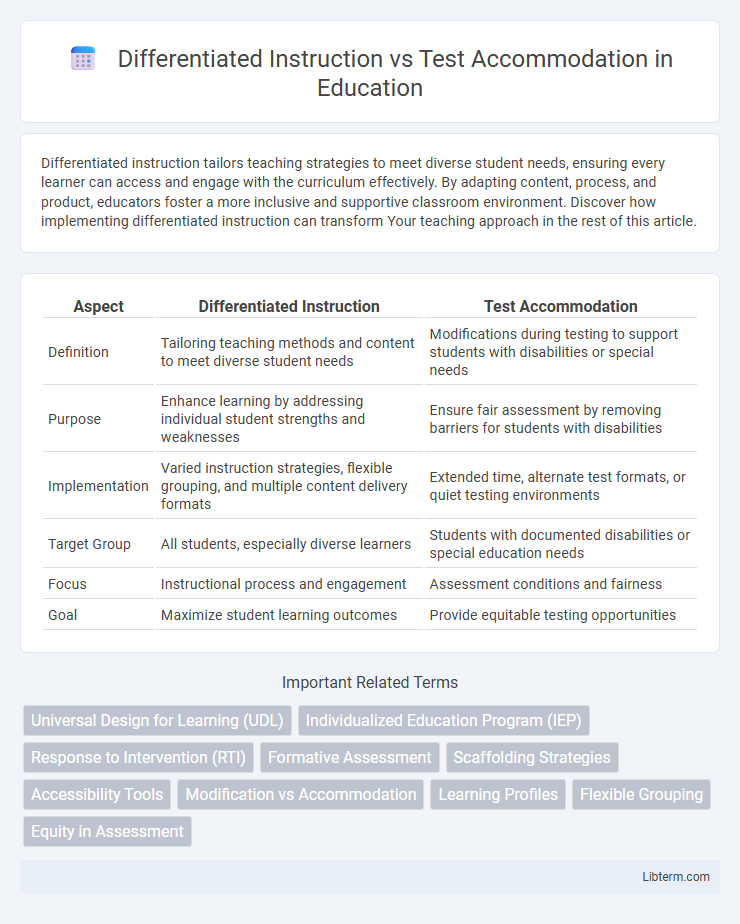
| Aspect | Differentiated Instruction | Test Accommodation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tailoring teaching methods and content to meet diverse student needs | Modifications during testing to support students with disabilities or special needs |
| Purpose | Enhance learning by addressing individual student strengths and weaknesses | Ensure fair assessment by removing barriers for students with disabilities |
| Implementation | Varied instruction strategies, flexible grouping, and multiple content delivery formats | Extended time, alternate test formats, or quiet testing environments |
| Target Group | All students, especially diverse learners | Students with documented disabilities or special education needs |
| Focus | Instructional process and engagement | Assessment conditions and fairness |
| Goal | Maximize student learning outcomes | Provide equitable testing opportunities |
Introduction to Differentiated Instruction and Test Accommodation
Differentiated Instruction tailors teaching strategies, content, and assessments to meet diverse learners' needs, promoting personalized learning experiences based on students' readiness, interests, and learning profiles. Test Accommodation modifies the testing environment or format, such as extended time or alternate settings, to reduce barriers for students with disabilities without altering the test's content or standards. Both approaches aim to support equitable education but differ fundamentally in implementation scope and target outcomes.
Defining Differentiated Instruction
Differentiated instruction refers to tailoring teaching strategies, content, and assessments to meet the diverse learning needs, readiness levels, and interests of students within a classroom. It emphasizes flexibility in lesson planning and delivery to support individual growth and maximize student engagement. This approach contrasts with test accommodation, which modifies the testing environment or procedures without altering the instructional methods.
Understanding Test Accommodation
Test accommodation refers to modifications in the testing environment or format that allow students with disabilities or special needs to demonstrate their true knowledge without altering the content or expectations of the assessment. These accommodations can include extended time, alternative test formats, or quiet testing locations to reduce barriers and provide equitable access. Effective test accommodations are legally mandated under laws such as the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) and Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act, ensuring students receive necessary supports during standardized assessments.
Key Differences between Differentiated Instruction and Test Accommodation
Differentiated instruction involves tailoring teaching methods, materials, and assessments to meet diverse student learning needs within the classroom, while test accommodation refers specifically to modifications or supports provided during assessments to help students demonstrate their knowledge without altering the test content. Differentiated instruction emphasizes proactive curriculum adaptation for varied learning styles and abilities, whereas test accommodations are reactive adjustments addressing barriers during exams, such as extended time or alternative formats. Understanding these distinctions helps educators implement effective strategies that support equitable learning and fair assessment for students with disabilities or unique learning needs.
Purposes and Goals of Each Approach
Differentiated Instruction aims to tailor teaching methods, content, and assessments to meet diverse learner needs, promoting equitable access to education and maximizing individual student growth. Test Accommodations focus on providing specific adjustments or supports during assessments to ensure that students with disabilities or learning differences can demonstrate their true knowledge without being hindered by their impairments. Both approaches seek to create fair learning environments but differ fundamentally in implementation scope, with Differentiated Instruction integrated throughout the learning process and Test Accommodations applied primarily during evaluations.
Impact on Student Outcomes
Differentiated instruction tailors teaching methods and learning activities to meet diverse student needs, enhancing engagement and academic achievement across varied skill levels. Test accommodations modify the testing environment or format to provide equitable access without altering content, supporting students with disabilities to demonstrate true proficiency. Research shows that differentiated instruction contributes to long-term growth by addressing learning differences proactively, while test accommodations primarily improve immediate assessment performance and reduce test anxiety.
Implementation Strategies in the Classroom
Differentiated instruction involves tailoring teaching methods and materials to address diverse student learning styles, readiness levels, and interests, using strategies like flexible grouping, varied assignments, and ongoing assessment. Test accommodations modify assessment conditions, such as extended time or alternative formats, to reduce barriers for students with disabilities without altering the content being tested. Effective implementation requires consistent collaboration among educators, clear documentation of student needs, and continuous monitoring to ensure instructional adaptations and accommodations align with individual learning goals and standardized testing requirements.
Legal and Policy Considerations
Differentiated instruction is grounded in educational policies promoting inclusive teaching practices, while test accommodations are legally mandated under laws such as the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) and Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act to ensure equal access during assessments. Schools must align differentiated strategies with Individualized Education Programs (IEPs) or 504 plans, adhering to federal and state regulations to provide appropriate support without compromising academic standards. Compliance with these legal frameworks ensures both equitable learning opportunities and valid assessment outcomes for students with disabilities.
Challenges and Limitations
Differentiated instruction faces challenges such as increased teacher workload, difficulty in accurately assessing diverse learner needs, and potential inconsistencies in implementation across classrooms. Test accommodations often encounter limitations including potential unfair advantages, logistical complexities in administration, and the risk of stigmatizing students who receive them. Both strategies require careful planning and ongoing evaluation to effectively support student learning without compromising educational standards.
Best Practices for Educators
Differentiated instruction involves tailoring teaching methods and materials to address diverse student learning needs, promoting engagement and mastery across varied skill levels. Test accommodations modify assessment conditions, such as extended time or alternate formats, ensuring equitable opportunities for students with disabilities to demonstrate their knowledge. Effective educators combine these strategies by understanding individual learner profiles, consistently adapting instruction, and collaborating with support specialists to optimize student achievement and access.
Differentiated Instruction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com