Process optimization enhances efficiency by streamlining workflows and reducing waste, leading to improved productivity and cost savings. Implementing effective process management tools enables clearer communication and better resource allocation within your organization. Explore the rest of this article to discover practical strategies for refining your processes and achieving sustainable growth.
Table of Comparison
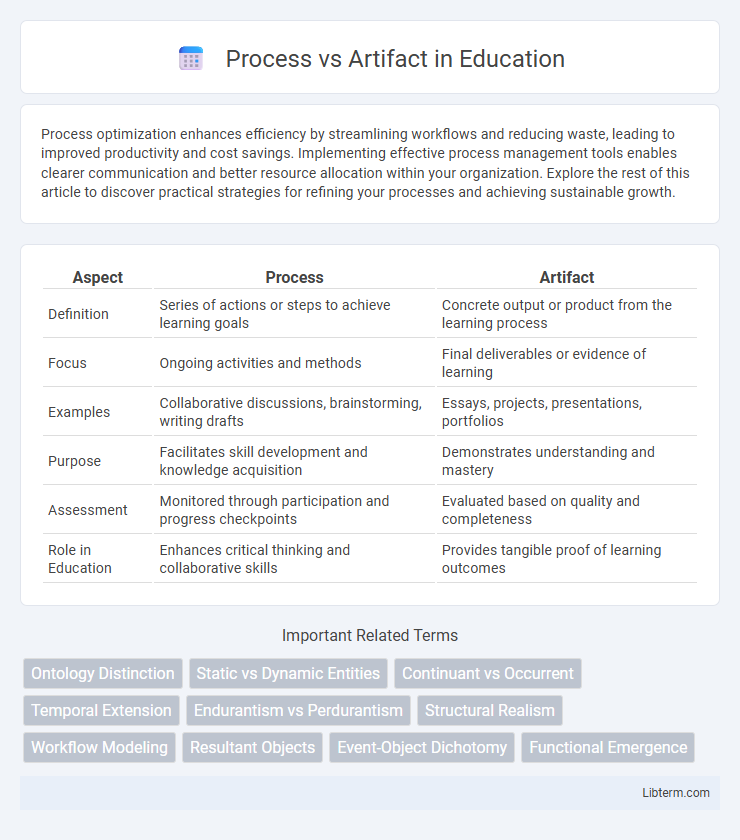
| Aspect | Process | Artifact |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Series of actions or steps to achieve learning goals | Concrete output or product from the learning process |
| Focus | Ongoing activities and methods | Final deliverables or evidence of learning |
| Examples | Collaborative discussions, brainstorming, writing drafts | Essays, projects, presentations, portfolios |
| Purpose | Facilitates skill development and knowledge acquisition | Demonstrates understanding and mastery |
| Assessment | Monitored through participation and progress checkpoints | Evaluated based on quality and completeness |
| Role in Education | Enhances critical thinking and collaborative skills | Provides tangible proof of learning outcomes |
Introduction to Process vs Artifact
A process refers to a series of actions or steps undertaken to achieve a specific goal, emphasizing workflows and methodologies. An artifact is a tangible or digital object produced as a result of a process, such as documents, models, or code. Understanding the distinction between process and artifact is essential for optimizing project management and product development strategies.
Defining Process: Key Characteristics
A process is a systematic sequence of activities designed to achieve specific outcomes by transforming inputs into outputs. Key characteristics of a process include repeatability, measurability, and defined roles or responsibilities to ensure consistent execution and continuous improvement. Emphasizing process structure and control allows organizations to optimize efficiency and maintain quality standards.
What is an Artifact? Essential Features
An artifact is a tangible byproduct or deliverable produced during a project, such as documents, diagrams, code, or models that serve as evidence of work completed. Essential features of an artifact include its reproducibility, version control capability, and its role in facilitating communication among stakeholders. Artifacts capture critical information that supports traceability, validation, and compliance within process workflows.
Process and Artifact: Core Differences
A process refers to a series of actions or steps taken to achieve a specific outcome, emphasizing activities, workflows, and methodologies. An artifact is a tangible byproduct or deliverable produced during or after the process, such as documents, models, or code. The core difference lies in processes being dynamic and ongoing while artifacts are static and concrete representations of work completed.
The Role of Process in Project Development
The role of process in project development is critical for ensuring consistent quality and efficient resource management. By defining structured workflows and standardized procedures, processes enable teams to systematically track progress, manage risks, and meet project goals within deadlines. Effective process implementation enhances collaboration and facilitates continuous improvement, directly impacting the successful delivery of project artifacts.
The Importance of Artifacts in Documentation
Artifacts play a crucial role in documentation by serving as tangible evidence of a process and its outcomes, ensuring clarity and consistency across project stages. They include diagrams, code snippets, user manuals, and meeting notes that capture detailed information, which supports knowledge transfer and facilitates auditing. Maintaining well-organized artifacts enhances collaboration, reduces errors, and accelerates decision-making within software development and business processes.
Process vs Artifact in Software Engineering
In software engineering, a process defines the structured set of activities and methodologies used to develop, maintain, and deliver software products, ensuring quality and consistency. Artifacts are the tangible by-products produced during the software development lifecycle, such as code, documentation, models, and test cases. Understanding the distinction between process and artifact enables effective project management, as processes guide the creation and refinement of artifacts that serve as deliverables or references.
Real-world Examples: Process and Artifact in Action
In software development, Agile methodology exemplifies a process emphasizing iterative progress and collaboration, while the resulting codebase serves as a tangible artifact reflecting the team's work. Manufacturing industries rely on Six Sigma processes to enhance quality, with final products acting as artifacts that demonstrate process effectiveness. In scientific research, the peer-review process ensures study validity, producing published papers as artifacts that capture verified knowledge.
Evaluating Success: Process-based vs Artifact-based Approaches
Evaluating success in process-based approaches emphasizes continuous improvement, efficiency, and adherence to predefined methodologies, often measured through key performance indicators (KPIs) and stakeholder satisfaction. Artifact-based approaches focus on the quality, completeness, and usability of the final deliverables, assessing success through metrics like defect rates, user acceptance, and alignment with requirements. Both methodologies offer complementary insights, balancing procedural rigor with tangible outcomes to provide a comprehensive evaluation framework.
Choosing Between Process and Artifact: Best Practices
Choosing between process and artifact depends on project goals, team expertise, and desired outcomes. Emphasize processes when aiming for repeatability, scalability, and continuous improvement, while artifacts serve best for delivering tangible results or documentation. Integrating feedback loops and clearly defining roles ensures alignment and maximizes value from either approach.
Process Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com