Self-assessment is a powerful tool that helps you identify your strengths and areas for improvement, fostering personal growth and enhancing professional development. By regularly evaluating your skills and performance, you can set realistic goals and make informed decisions to achieve success. Explore the rest of this article to learn how to conduct effective self-assessments and maximize your potential.
Table of Comparison
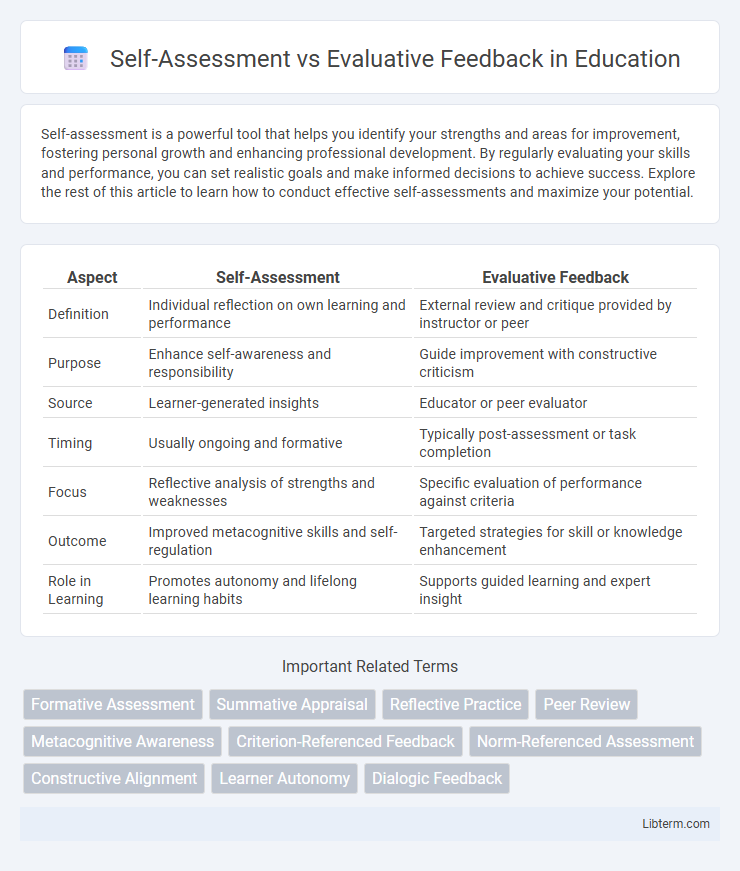
| Aspect | Self-Assessment | Evaluative Feedback |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individual reflection on own learning and performance | External review and critique provided by instructor or peer |
| Purpose | Enhance self-awareness and responsibility | Guide improvement with constructive criticism |
| Source | Learner-generated insights | Educator or peer evaluator |
| Timing | Usually ongoing and formative | Typically post-assessment or task completion |
| Focus | Reflective analysis of strengths and weaknesses | Specific evaluation of performance against criteria |
| Outcome | Improved metacognitive skills and self-regulation | Targeted strategies for skill or knowledge enhancement |
| Role in Learning | Promotes autonomy and lifelong learning habits | Supports guided learning and expert insight |
Understanding Self-Assessment
Understanding self-assessment involves recognizing it as a reflective process where individuals critically analyze their own performance, skills, and learning progress. This process encourages personal accountability and intrinsic motivation by fostering awareness of strengths and areas for improvement without relying solely on external evaluations. Effective self-assessment techniques include setting clear criteria, maintaining honest self-reflection, and regularly tracking development to enhance overall growth.
What Is Evaluative Feedback?
Evaluative feedback is a structured response provided by an external assessor that measures performance against predefined standards or criteria. It offers specific judgments on strengths and areas for improvement, often scored or rated for clear assessment. This type of feedback guides learners or employees by highlighting measurable outcomes and expectations for growth or development.
Key Differences Between Self-Assessment and Evaluative Feedback
Self-assessment involves individuals reflecting on and judging their own performance or learning progress, fostering self-regulation and personal growth. Evaluative feedback, on the other hand, is an external assessment provided by teachers, peers, or supervisors aimed at identifying strengths and areas for improvement. Key differences include the source of evaluation--internal versus external--and the purpose, with self-assessment emphasizing self-awareness and evaluative feedback focusing on guiding performance enhancement.
Benefits of Self-Assessment in Learning
Self-assessment empowers learners to take ownership of their progress by identifying strengths and areas for improvement, enhancing metacognitive skills. It fosters deeper engagement and intrinsic motivation, enabling students to set personalized goals and adapt learning strategies effectively. This proactive reflection drives long-term retention and promotes continuous, self-directed learning beyond formal evaluations.
Advantages of Receiving Evaluative Feedback
Receiving evaluative feedback provides clear, objective insights based on performance standards, enabling individuals to identify precise areas for improvement. It offers an external perspective that can uncover blind spots missed during self-assessment, fostering more accurate skill development. This form of feedback enhances motivation by setting measurable goals and promoting accountability within learning and professional environments.
Common Challenges in Self-Assessment
Common challenges in self-assessment include bias, such as overestimating or underestimating one's abilities, which affects the accuracy of self-evaluation. Lack of clear criteria or benchmarks often leads to inconsistent and subjective judgments, making it difficult to identify areas for improvement. Limited self-awareness and emotional factors also impact the effectiveness of self-assessment compared to evaluative feedback from external sources.
Limitations of Evaluative Feedback
Evaluative feedback often suffers from subjectivity and bias, limiting its accuracy and effectiveness in guiding improvement. It can undermine motivation by emphasizing shortcomings rather than growth opportunities, potentially leading to decreased engagement. The reliance on external judgment reduces learner autonomy, impeding the development of critical self-reflection skills essential for long-term personal and professional growth.
When to Use Self-Assessment vs Evaluative Feedback
Self-assessment is most effective during the learning process to foster reflection and self-regulation, enabling individuals to identify strengths and areas for improvement independently. Evaluative feedback is better suited for summative situations where objective performance measurement and external validation are required to guide further development or decision-making. Choosing between self-assessment and evaluative feedback depends on the goal: promoting learner autonomy warrants self-assessment, while ensuring accountability or providing expert judgment calls for evaluative feedback.
Integrating Both Methods for Optimal Growth
Integrating self-assessment with evaluative feedback creates a comprehensive learning environment that fosters deeper self-awareness and targeted improvement. Self-assessment encourages learners to critically reflect on their performance and set personalized goals, while evaluative feedback provides objective insights and expert guidance to refine skills. Combining these methods enhances motivation, reinforces accountability, and drives continuous growth by aligning personal perspectives with external evaluations.
Best Practices for Effective Assessment
Self-assessment encourages learners to critically analyze their own work, fostering deeper engagement and autonomous learning, while evaluative feedback provides external, objective insights crucial for skill refinement and motivation. Best practices for effective assessment integrate clear, specific criteria and timely, constructive feedback to bridge gaps between self-perception and actual performance. Incorporating reflective prompts alongside rubric-based evaluations enhances accuracy in self-assessment and ensures targeted improvements through evaluative feedback.
Self-Assessment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com