Structured instruction enhances learning by organizing content into clear, logical sequences that promote comprehension and retention. It involves breaking down complex information into manageable steps, making it easier for learners to grasp and apply new concepts effectively. Explore the rest of the article to discover practical strategies for implementing structured instruction in your teaching or training sessions.
Table of Comparison
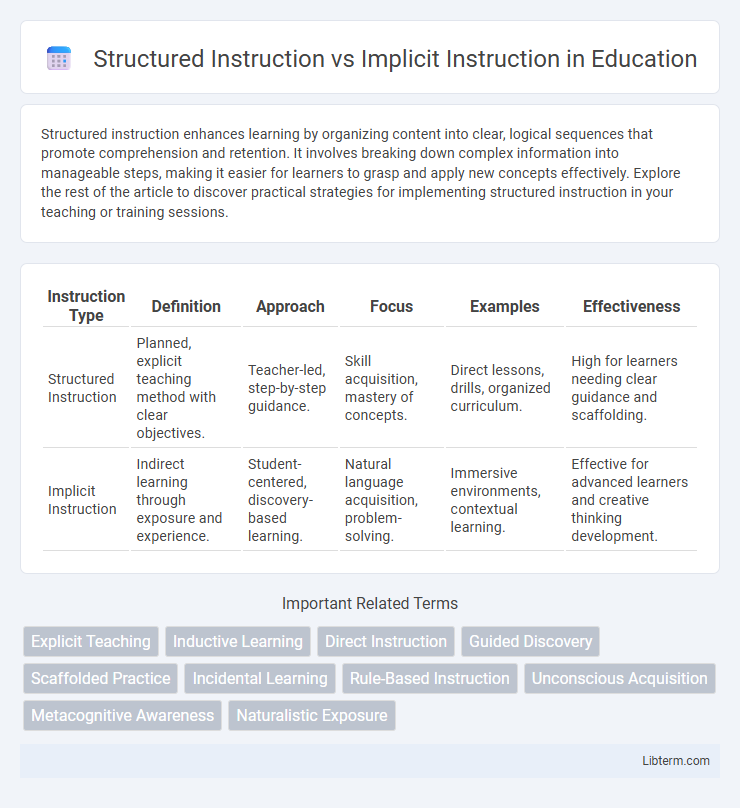
| Instruction Type | Definition | Approach | Focus | Examples | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Structured Instruction | Planned, explicit teaching method with clear objectives. | Teacher-led, step-by-step guidance. | Skill acquisition, mastery of concepts. | Direct lessons, drills, organized curriculum. | High for learners needing clear guidance and scaffolding. |
| Implicit Instruction | Indirect learning through exposure and experience. | Student-centered, discovery-based learning. | Natural language acquisition, problem-solving. | Immersive environments, contextual learning. | Effective for advanced learners and creative thinking development. |
Introduction to Structured vs Implicit Instruction
Structured instruction involves deliberate, clear, and systematic teaching methods designed to enhance comprehension and retention, particularly benefiting learners who thrive on explicit guidance. Implicit instruction relies on indirect, immersive learning experiences where individuals acquire skills or knowledge through exposure and practice without overt explanations. Understanding the differences between these approaches is essential for tailoring educational strategies to diverse learner needs and optimizing instructional outcomes.
Defining Structured Instruction
Structured Instruction refers to a systematic teaching approach that uses clear, explicit, and sequential steps to guide learners through new concepts, ensuring consistent delivery and measurable outcomes. It emphasizes breaking down complex skills into smaller, manageable components with targeted practice and immediate feedback. This method contrasts with implicit instruction, which relies on indirect learning through exposure without overt explanations or structured guidance.
Defining Implicit Instruction
Implicit instruction refers to a teaching method where learners acquire knowledge and skills naturally through exposure, observation, and experience without explicit explanations or direct teaching of rules. This approach relies heavily on context, immersive learning environments, and repeated interactions, enabling learners to internalize information subconsciously. Unlike structured instruction, implicit instruction emphasizes intuition and discovery, often used in language acquisition and skill development where explicit grammar rules or step-by-step guidance are minimized.
Key Differences between Structured and Implicit Approaches
Structured instruction emphasizes explicit teaching through clear objectives, sequential steps, and repetitive practice, targeting skill mastery and measurable outcomes. Implicit instruction relies on indirect learning via exposure, context, and natural interaction without overt explanations, promoting intuitive understanding and adaptability. Key differences lie in clarity of guidance, intentionality of learning, and methods of feedback, with structured approaches favoring systematic delivery while implicit methods prioritize experiential discovery.
Benefits of Structured Instruction
Structured Instruction enhances learning efficiency by providing clear, systematic guidance that reduces cognitive load and supports skill acquisition through repetitive practice. It benefits students with diverse learning needs by breaking complex tasks into manageable steps, ensuring consistent mastery and minimizing confusion. Research indicates that structured approaches improve academic outcomes, especially for learners with disabilities or language barriers, by fostering explicit understanding and retention.
Advantages of Implicit Instruction
Implicit instruction enhances language acquisition by promoting natural, context-driven learning, which improves retention and fluency without overt grammatical explanations. It supports learner autonomy and motivation by encouraging exploration and real-life communication, which can lead to deeper cognitive engagement and practical language use. This approach also reduces learner anxiety, fostering a more immersive and intuitive learning environment that closely mirrors first-language acquisition processes.
When to Use Structured Instruction
Structured instruction is most effective for learners who benefit from clear, explicit guidance, such as those with learning disabilities or limited prior knowledge in a subject. It provides step-by-step directions and consistent routines, enhancing comprehension and skill acquisition through repetition and scaffolding. Best used in foundational learning phases, structured instruction ensures mastery before transitioning to more autonomous, implicit learning methods.
When to Use Implicit Instruction
Implicit instruction is most effective in naturalistic learning environments where learners benefit from immersion and contextual cues, such as language acquisition or social skills development. It supports incidental learning through exposure, making it ideal for learners who struggle with explicit rules or prefer experiential learning. Use implicit instruction when fostering creativity, flexibility, and adaptive problem-solving is a priority over rigid mastery of structured content.
Impact on Student Learning Outcomes
Structured instruction, characterized by explicit teaching methods and clear, systematic guidance, significantly enhances student learning outcomes by reducing cognitive load and promoting mastery of foundational skills. Implicit instruction relies on indirect learning through exploration and discovery, often resulting in slower skill acquisition and varied comprehension levels among students. Research indicates that structured instruction leads to higher retention rates, improved academic performance, and better support for diverse learners compared to implicit approaches.
Choosing the Right Instructional Method
Choosing the right instructional method depends on learner needs and context; structured instruction offers clear, step-by-step guidance ideal for novices or complex tasks, enhancing comprehension and retention. Implicit instruction suits advanced learners by promoting discovery and critical thinking through immersive, less directed experiences. Evaluating learner readiness, content complexity, and learning goals ensures effective alignment between instructional approach and desired outcomes.
Structured Instruction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com