Experiential learning engages you directly in hands-on activities, allowing knowledge to be gained through real-world experiences rather than passive listening. This method enhances retention and deepens understanding by involving active participation, reflection, and practical application. Explore the rest of the article to discover how experiential learning can transform your educational journey.
Table of Comparison
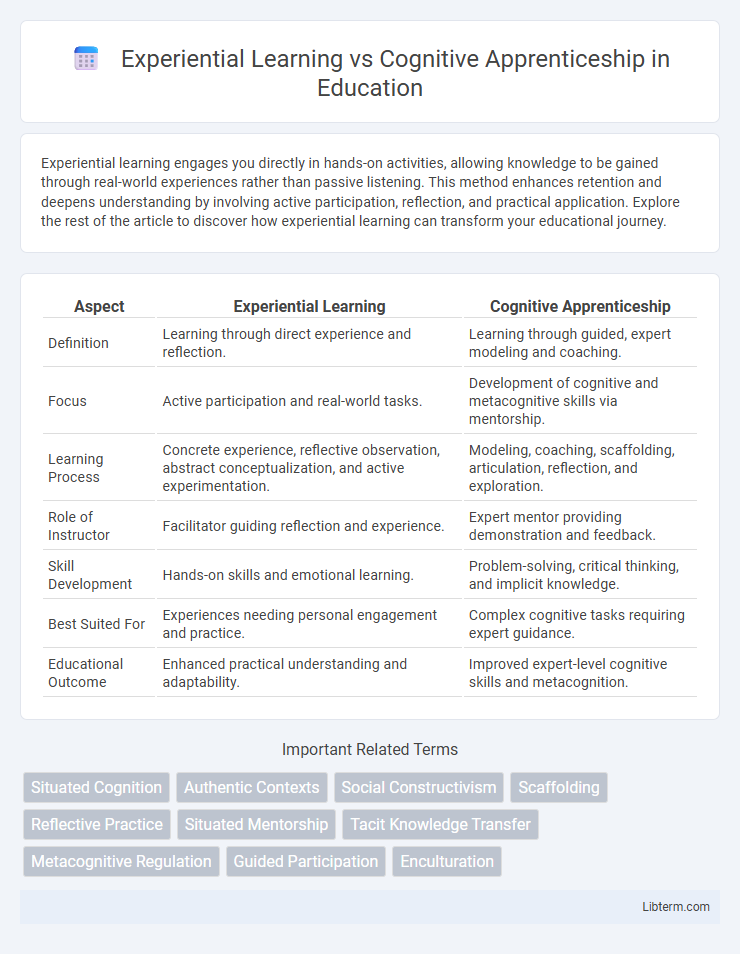
| Aspect | Experiential Learning | Cognitive Apprenticeship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Learning through direct experience and reflection. | Learning through guided, expert modeling and coaching. |
| Focus | Active participation and real-world tasks. | Development of cognitive and metacognitive skills via mentorship. |
| Learning Process | Concrete experience, reflective observation, abstract conceptualization, and active experimentation. | Modeling, coaching, scaffolding, articulation, reflection, and exploration. |
| Role of Instructor | Facilitator guiding reflection and experience. | Expert mentor providing demonstration and feedback. |
| Skill Development | Hands-on skills and emotional learning. | Problem-solving, critical thinking, and implicit knowledge. |
| Best Suited For | Experiences needing personal engagement and practice. | Complex cognitive tasks requiring expert guidance. |
| Educational Outcome | Enhanced practical understanding and adaptability. | Improved expert-level cognitive skills and metacognition. |
Introduction to Experiential Learning and Cognitive Apprenticeship
Experiential Learning emphasizes hands-on experiences where learners engage directly with tasks to construct knowledge through reflection and active participation. Cognitive Apprenticeship integrates this approach by embedding expert guidance in authentic contexts, making invisible cognitive processes explicit for learners. Both frameworks prioritize situated learning but diverge in the role of mentorship and structured scaffolding to develop practical and metacognitive skills.
Defining Experiential Learning
Experiential Learning is defined as a hands-on, immersive process where learners acquire knowledge through direct experience, reflection, and active engagement in real-world tasks. This approach emphasizes learning by doing, allowing individuals to construct understanding through practical application rather than passive instruction. Unlike traditional cognitive apprenticeship, which integrates guided expert modeling and scaffolding, Experiential Learning centers on personal discovery and self-driven problem solving within authentic environments.
Defining Cognitive Apprenticeship
Cognitive apprenticeship is an educational model that emphasizes learning through guided experiences and social interaction, where experts reveal their thought processes while performing complex tasks. This approach integrates explicit teaching of cognitive and metacognitive strategies within authentic, real-world contexts to enhance learners' practical problem-solving skills. It contrasts with experiential learning by focusing more on the mentorship and scaffolding necessary to internalize expert thinking patterns systematically.
Core Principles of Experiential Learning
Experiential learning centers on active participation, reflection, and applying knowledge through direct experience, emphasizing Kolb's learning cycle stages: concrete experience, reflective observation, abstract conceptualization, and active experimentation. This approach prioritizes learner engagement in real-world tasks to foster deeper understanding and skill acquisition. In contrast, cognitive apprenticeship integrates guided experience with expert modeling and scaffolding, focusing on developing cognitive and metacognitive skills within authentic contexts.
Key Components of Cognitive Apprenticeship
Cognitive apprenticeship centers on modeling, coaching, scaffolding, articulation, reflection, and exploration to facilitate skill acquisition in authentic contexts. Unlike experiential learning, which emphasizes learning through direct experience, cognitive apprenticeship integrates expert guidance with social interaction to develop cognitive and metacognitive abilities. Key components include the expert demonstrating tasks (modeling), providing tailored feedback (coaching), gradually reducing support (scaffolding), encouraging learners to verbalize reasoning (articulation), promoting self-assessment (reflection), and fostering problem-solving in varied situations (exploration).
Comparative Analysis: Similarities and Differences
Experiential learning and cognitive apprenticeship both emphasize hands-on engagement and real-world problem-solving to enhance skill acquisition and knowledge retention. Experiential learning focuses on the learner's direct experience and reflection cycle, while cognitive apprenticeship incorporates guided expert modeling, coaching, and scaffolding within authentic contexts. Both approaches foster deep understanding, but cognitive apprenticeship explicitly highlights social interaction and mentorship as key components in mastering cognitive processes.
Benefits of Experiential Learning in Modern Education
Experiential learning enhances student engagement by promoting active participation and real-world problem-solving, which leads to deeper understanding and retention of knowledge. It fosters critical thinking and adaptability, essential skills for the rapidly changing job market, by immersing learners in hands-on experiences. This learning approach supports collaboration and reflective practice, making it highly effective in modern education settings.
Advantages of Cognitive Apprenticeship for Skill Mastery
Cognitive apprenticeship offers distinct advantages for skill mastery by integrating real-world tasks with expert mentorship, enhancing learners' ability to apply knowledge in practical settings. This method promotes deep understanding through guided practice, reflection, and modeling of cognitive processes that scaffold complex skills incrementally. The situated learning approach inherent in cognitive apprenticeship accelerates skill acquisition and retention compared to traditional experiential learning by emphasizing contextual problem-solving and active cognitive engagement.
Choosing the Right Approach: Educational Contexts and Goals
Experiential learning emphasizes hands-on activities and reflection, ideal for developing practical skills and personal growth in dynamic educational environments. Cognitive apprenticeship focuses on modeling expert thinking processes and scaffolding, making it suitable for complex problem-solving and mastering cognitive tasks in professional or academic settings. Selecting the right approach depends on whether the goal is to enhance experiential skill acquisition or deepen cognitive understanding through guided practice and mentorship.
Future Trends in Learning Methodologies
Experiential learning emphasizes hands-on, real-world experiences that foster deeper understanding and skill acquisition through active participation. Cognitive apprenticeship integrates modeling, coaching, and scaffolding within authentic contexts to develop cognitive and metacognitive skills alongside practical abilities. Future trends point toward blending these methodologies with advanced technologies like AI and virtual reality to create immersive, adaptive learning environments that enhance personalized skill development and cognitive mastery.
Experiential Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com