Dropout is a regularization technique used in neural networks to prevent overfitting by randomly disabling a fraction of neurons during training. This approach improves model generalization by ensuring that the network does not rely too heavily on any single feature. Discover how dropout can enhance your machine learning models and explore its practical applications in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
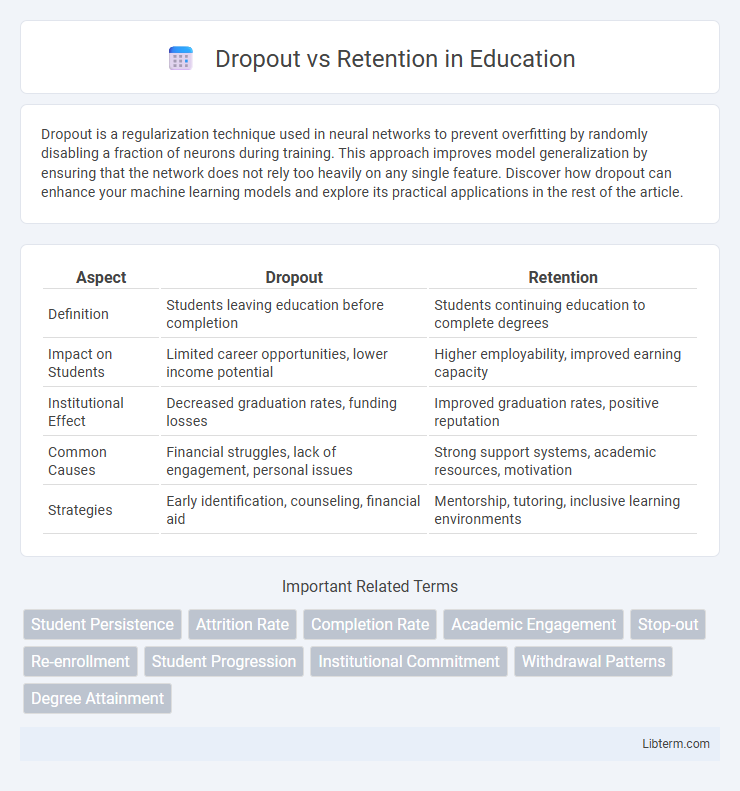
| Aspect | Dropout | Retention |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Students leaving education before completion | Students continuing education to complete degrees |
| Impact on Students | Limited career opportunities, lower income potential | Higher employability, improved earning capacity |
| Institutional Effect | Decreased graduation rates, funding losses | Improved graduation rates, positive reputation |
| Common Causes | Financial struggles, lack of engagement, personal issues | Strong support systems, academic resources, motivation |
| Strategies | Early identification, counseling, financial aid | Mentorship, tutoring, inclusive learning environments |
Understanding Dropout and Retention: Key Definitions
Dropout refers to students who discontinue their education before completing a program, while retention measures the ability of institutions to keep students enrolled until graduation. Understanding dropout requires analyzing factors like academic struggles, financial challenges, and social environment. Retention strategies focus on improving student engagement, providing support services, and creating a positive learning experience to reduce attrition rates.
Causes of Student Dropout: An Overview
Student dropout primarily results from a combination of academic difficulties, financial constraints, and lack of social integration within the educational environment. Family issues, mental health challenges, and insufficient institutional support also contribute significantly to dropout rates. Understanding these causes is essential for developing effective retention strategies that promote student success and reduce attrition.
Factors Influencing Retention Rates
Retention rates in education are influenced by factors such as student engagement, quality of instruction, and support services like counseling and tutoring. Socioeconomic status, family involvement, and school environment also play critical roles in determining whether students remain enrolled. Effective retention strategies address academic challenges, foster a sense of belonging, and provide resources to overcome external barriers.
Impact of Dropout on Individuals and Society
Dropout significantly hinders individual economic prospects by reducing lifetime earnings and increasing unemployment risk, while contributing to higher rates of poverty and social inequality. Society bears substantial costs from dropout through increased reliance on social welfare programs, higher crime rates, and diminished economic productivity. Addressing dropout rates is crucial to improving public health, workforce quality, and overall social cohesion.
Strategies for Increasing Student Retention
Effective strategies for increasing student retention include personalized academic advising, early alert systems to identify and support at-risk students, and the development of engaging, relevant curricula that meet diverse student needs. Implementing peer mentoring programs and fostering a strong campus community enhance student belonging and motivation, directly reducing dropout rates. Additionally, providing comprehensive support services such as tutoring, mental health resources, and flexible learning options significantly improves student persistence and completion rates.
Early Warning Signs of Potential Dropouts
Early warning signs of potential dropouts include a consistent decline in academic performance, frequent absenteeism, and disengagement from school activities. Behavioral indicators such as increased tardiness, lack of participation, and noticeable changes in social interactions signal the risk of student dropout. Monitoring these factors through data analytics and teacher observations enables timely interventions to improve retention rates.
Role of Family and Community in Retention
Family support significantly enhances student retention by providing emotional stability and reinforcing academic values, while active community involvement offers resources and mentorship opportunities that encourage sustained engagement in education. Strong communication between families, schools, and community organizations fosters a collaborative environment that addresses barriers to persistence and promotes student success. Research shows that integrated family and community support systems correlate with reduced dropout rates and improved long-term educational outcomes.
School Policies Affecting Dropout Rates
School policies significantly influence dropout rates by shaping student engagement and support systems. Implementing early intervention strategies, attendance monitoring, and personalized learning plans reduces dropout risk by addressing academic and social challenges. Comprehensive retention policies emphasizing counseling, family involvement, and resource allocation foster improved persistence and graduation outcomes.
Technology and Innovation in Reducing Dropout
Technology and innovation play a crucial role in reducing dropout rates by enabling personalized learning experiences through adaptive learning platforms and real-time data analytics. Digital tools such as AI-driven tutoring, interactive content, and mobile learning applications increase student engagement and provide timely academic support tailored to individual needs. Educational institutions leveraging these technologies report improved retention rates as students remain motivated and receive targeted interventions before disengaging.
Comparative Analysis: Dropout vs Retention Outcomes
Dropout rates negatively impact academic achievement and increase the likelihood of unemployment and lower lifetime earnings compared to retention, which supports improved student performance and higher graduation rates. Retention strategies, such as personalized learning interventions and early academic support, demonstrate a significant reduction in dropout incidences by addressing individual learning needs. Comparative analyses reveal that retention not only enhances educational attainment but also contributes to long-term socioeconomic benefits, while dropout perpetuates cycles of disadvantage.
Dropout Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com