Private schools offer tailored educational experiences with smaller class sizes and specialized curricula, fostering personalized learning environments. These institutions often provide enhanced extracurricular opportunities and advanced resources to support student development. Explore the rest of the article to discover how private schools can benefit your child's academic journey.
Table of Comparison
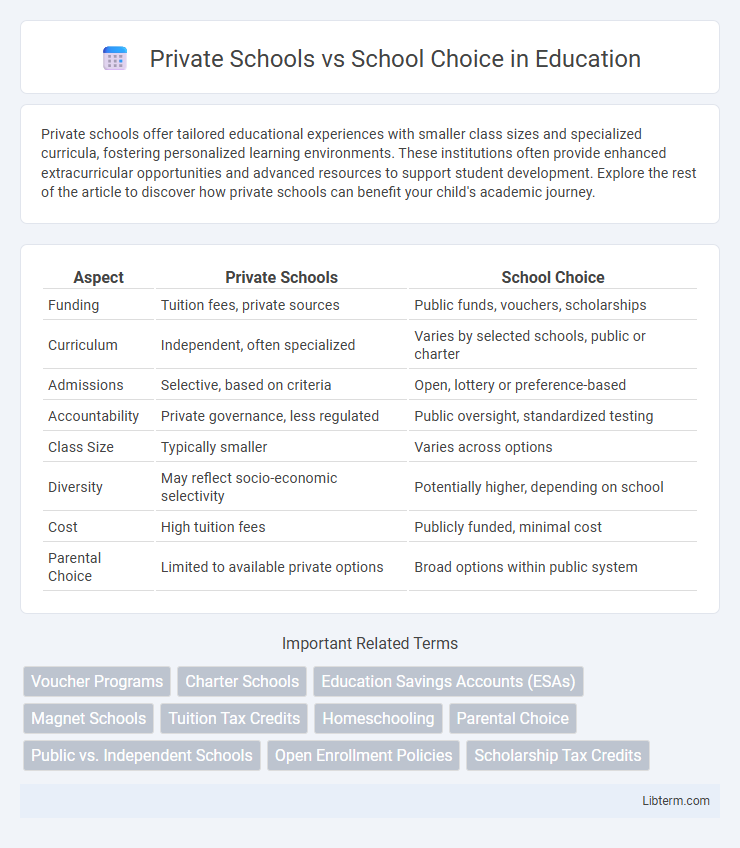
| Aspect | Private Schools | School Choice |
|---|---|---|
| Funding | Tuition fees, private sources | Public funds, vouchers, scholarships |
| Curriculum | Independent, often specialized | Varies by selected schools, public or charter |
| Admissions | Selective, based on criteria | Open, lottery or preference-based |
| Accountability | Private governance, less regulated | Public oversight, standardized testing |
| Class Size | Typically smaller | Varies across options |
| Diversity | May reflect socio-economic selectivity | Potentially higher, depending on school |
| Cost | High tuition fees | Publicly funded, minimal cost |
| Parental Choice | Limited to available private options | Broad options within public system |
Understanding Private Schools and School Choice
Private schools operate independently from public school systems, offering specialized curricula, smaller class sizes, and often religious or pedagogical affiliations, which attract families seeking tailored educational experiences. School choice policies empower parents to select educational options beyond district-assigned schools, including private institutions, charter schools, and voucher programs designed to increase access and competition. Understanding the distinctions between private schools and school choice mechanisms is crucial for evaluating educational outcomes, equity, and funding implications within diverse communities.
Key Differences Between Private Schools and School Choice
Private schools operate independently of government funding and curriculum control, offering specialized educational programs, smaller class sizes, and often religious or pedagogical orientations. School choice programs, including vouchers and charter schools, allow public funding to follow students to a variety of public or private educational settings, aiming to increase access and competition within the public education system. Key differences lie in funding sources, regulatory oversight, accessibility, and accountability standards, with private schools maintaining greater autonomy and school choice initiatives promoting broader student options within the public framework.
Enrollment Processes: Private vs. School Choice
Private school enrollment typically involves a selective application process including interviews, entrance exams, and proof of tuition payment, which can limit accessibility for some families. In contrast, school choice programs often use lottery systems or decentralized application platforms designed to provide more equitable access to public charter or magnet schools. Both methods aim to place students effectively, but private schools prioritize individual assessment while school choice emphasizes broader access and diversity.
Funding and Tuition Considerations
Private schools primarily rely on tuition payments and private funding, with limited public financial support, which often leads to higher out-of-pocket costs for families compared to public schools. School choice programs, including vouchers and education savings accounts, aim to redirect public funds to enable access to private education, although the effectiveness and equity of funding allocation remain debated. The disparity in funding mechanisms influences access, affordability, and the overall financial sustainability of private education options within school choice frameworks.
Curriculum and Educational Approaches
Private schools often implement specialized curricula tailored to specific educational philosophies, such as Montessori, Waldorf, or religious instruction, allowing for a more customized learning experience. School choice programs enable families to select from a diverse range of public, charter, and private schools, each offering varied educational approaches including STEM-focused, arts-integrated, and project-based learning models. The flexibility in curriculum design and pedagogical strategies across both private schools and school choice options fosters personalized education aligned with student needs and family preferences.
Academic Performance and Outcomes
Private schools consistently demonstrate higher academic performance with standardized test scores and graduation rates surpassing public school averages. School choice policies enable families to select educational institutions that align with students' needs, often leading to improved student outcomes and increased competitiveness. Research indicates that greater school choice contributes to enhanced academic achievement, especially in underserved communities.
Accessibility and Equity Issues
Private schools often have selective admissions and higher tuition fees, limiting access for low-income families and raising equity concerns. School choice policies aim to increase educational options through vouchers and charter schools but can exacerbate disparities if under-resourced public schools lose funding. Ensuring equitable access requires targeted support for disadvantaged students and rigorous accountability measures across all school types.
Parental Involvement and Satisfaction
Parental involvement in private schools often exceeds that in public schools due to smaller class sizes and more direct communication between parents and educators, leading to higher satisfaction rates among families. School choice programs empower parents to select educational options aligned with their values and children's needs, fostering greater engagement and customized learning experiences. Studies indicate that increased parental participation correlates with improved student performance and overall family contentment within both private schools and diverse school choice settings.
Regulatory Standards and Accountability
Private schools operate under varying regulatory standards depending on state laws, often enjoying greater autonomy compared to public schools. School choice programs enable parents to select private schools, but accountability measures differ widely, with some states imposing standardized testing and reporting requirements, while others maintain minimal oversight. Ensuring consistent regulatory standards and accountability across both private schools and school choice initiatives remains a critical challenge for policymakers aiming to balance educational quality and parental freedom.
Future Trends in Private Schools and School Choice
Emerging trends in private schools highlight increased adoption of technology-enhanced learning and personalized education models to meet diverse student needs. School choice policies continue to expand, with voucher programs and charter schools gaining momentum, influencing enrollment patterns and funding allocations. Future growth in private schools depends on their ability to innovate curriculum offerings and adapt to policy changes promoting educational equity and access.
Private Schools Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com