Apprenticeships provide hands-on training that bridges the gap between education and real-world work experience, equipping you with practical skills in a specific trade or profession. They often combine paid work with classroom learning, allowing you to earn while you learn and build a strong foundation for your career. Explore the rest of this article to discover how apprenticeships can jumpstart your professional journey.
Table of Comparison
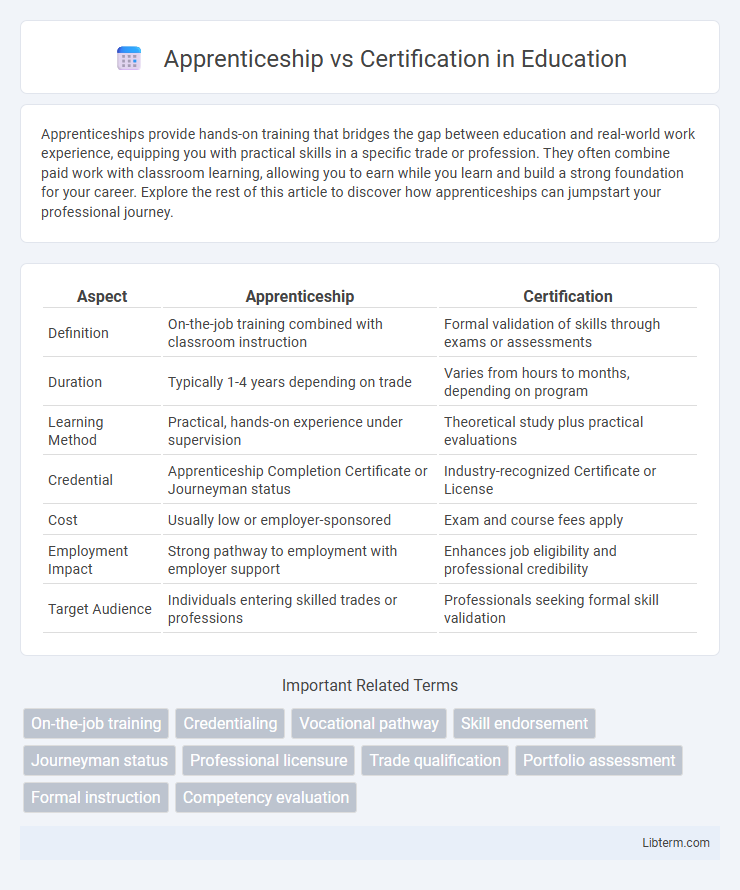
| Aspect | Apprenticeship | Certification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | On-the-job training combined with classroom instruction | Formal validation of skills through exams or assessments |
| Duration | Typically 1-4 years depending on trade | Varies from hours to months, depending on program |
| Learning Method | Practical, hands-on experience under supervision | Theoretical study plus practical evaluations |
| Credential | Apprenticeship Completion Certificate or Journeyman status | Industry-recognized Certificate or License |
| Cost | Usually low or employer-sponsored | Exam and course fees apply |
| Employment Impact | Strong pathway to employment with employer support | Enhances job eligibility and professional credibility |
| Target Audience | Individuals entering skilled trades or professions | Professionals seeking formal skill validation |
Understanding Apprenticeships and Certifications
Apprenticeships provide hands-on training combined with paid work experience, allowing individuals to develop practical skills under the guidance of experienced professionals. Certifications validate specific knowledge or expertise through exams, demonstrating competency and often enhancing job marketability. Understanding the differences helps learners choose between immersive skill-building through apprenticeships or formal recognition via certifications.
Key Differences Between Apprenticeship and Certification
Apprenticeship involves hands-on training combined with classroom instruction, emphasizing practical experience over an extended period, while certification validates specific skills or knowledge through examinations without requiring direct work experience. Apprenticeships often lead to a recognized credential and job placement, whereas certifications serve as proof of proficiency that can enhance employment opportunities and professional credibility. The key difference lies in the learning approach: apprenticeships are immersive and work-based, whereas certifications are assessment-based and knowledge-focused.
Advantages of Pursuing an Apprenticeship
Apprenticeships offer hands-on experience that bridges the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical skills, enhancing job readiness and employability. They provide earning opportunities while learning, reducing the financial burden compared to traditional education paths. The structured mentorship and industry connections gained during apprenticeships foster career advancement and long-term professional growth.
Benefits of Earning a Professional Certification
Earning a professional certification enhances career credibility by validating specialized skills and knowledge, leading to higher earning potential and job security. Certifications often provide access to exclusive industry networks and continuing education opportunities, fostering professional growth and updated expertise. Employers prioritize certified candidates for their proven competency, increasing chances for promotions and leadership roles.
Career Opportunities: Apprenticeship vs Certification
Apprenticeships offer hands-on experience and direct industry connections that often lead to immediate employment opportunities in trades and technical fields. Certifications demonstrate verified skills and knowledge, enhancing credibility and broadening job prospects across multiple industries, particularly in technology and healthcare. Combining apprenticeship experience with certifications can maximize career advancement by showcasing practical expertise alongside formal qualifications.
Duration and Structure: How They Compare
Apprenticeships typically span 1 to 6 years, combining on-the-job training with classroom instruction, offering hands-on experience and skill development in a real work environment. Certifications usually require shorter durations, from a few days to several months, focusing on exam-based validation of specific skills or knowledge through structured coursework. The structured, immersive nature of apprenticeships contrasts with the flexible, often self-paced preparation for certifications, making each suitable for different career objectives and learning preferences.
Costs Involved: Financial Considerations
Apprenticeships typically involve lower upfront costs as they combine paid on-the-job training with classroom instruction, minimizing tuition fees and income loss. Certifications often require candidates to bear exam fees, study materials, and sometimes costly preparatory courses without a guaranteed income during the process. Evaluating these financial commitments is crucial for individuals balancing budget constraints and career advancement timelines.
Industry Recognition and Value
Apprenticeships provide hands-on experience and are highly valued by employers for practical skill development and industry-specific training. Certifications demonstrate verified knowledge and competencies, often recognized globally, enhancing a professional's credibility across various sectors. Both pathways hold significant industry recognition, but apprenticeships emphasize real-world application while certifications focus on standardized expertise validation.
Choosing the Right Path for Your Career Goals
Apprenticeships offer hands-on experience and industry mentorship, ideal for those seeking practical skills in trades or technical fields. Certifications validate specific expertise through standardized exams, making them suitable for professionals aiming to demonstrate competency quickly and enhance their resumes. Evaluating your career goals, preferred learning style, and industry demands helps determine whether an apprenticeship's immersive training or a certification's focused credential aligns best with your professional growth.
Future Trends in Apprenticeship and Certification
Apprenticeships are evolving with increased integration of digital technologies and industry-specific skills to meet future workforce demands, emphasizing hands-on experience combined with formal training. Certification programs are becoming more adaptive and modular, offering micro-credentials and stackable certificates that align with rapidly changing job market requirements. Both approaches are increasingly leveraging online platforms and AI-driven assessments to enhance accessibility, personalization, and real-time skill validation.
Apprenticeship Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com