Disciplinary actions are essential for maintaining order and enforcing rules within organizations or institutions. Clear guidelines on acceptable behavior help prevent conflicts and ensure accountability. Discover how effective disciplinary measures can protect your environment by reading the rest of this article.
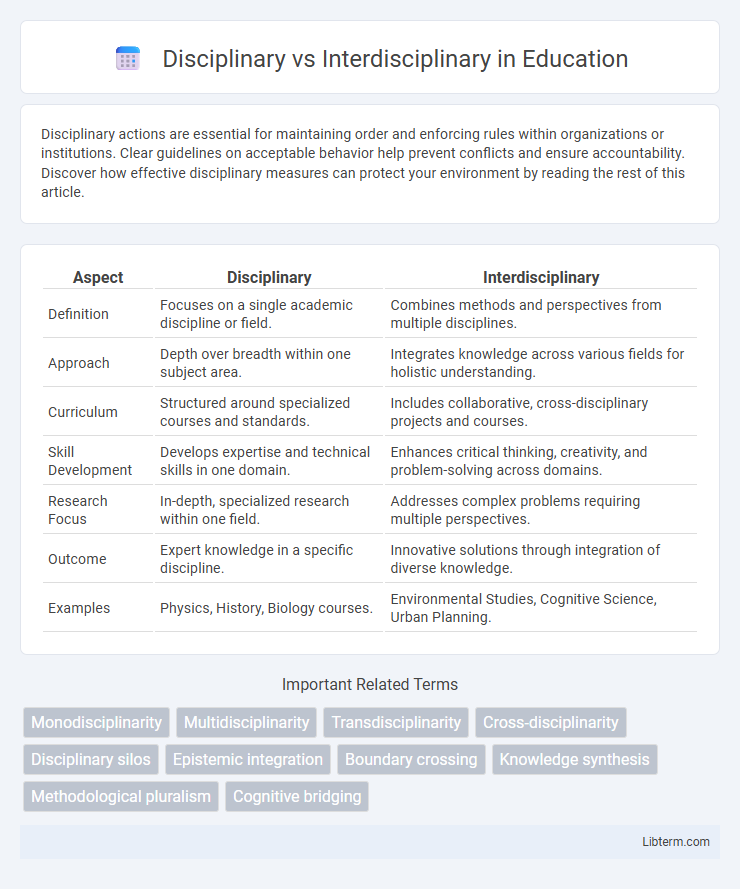
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Disciplinary | Interdisciplinary |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses on a single academic discipline or field. | Combines methods and perspectives from multiple disciplines. |
| Approach | Depth over breadth within one subject area. | Integrates knowledge across various fields for holistic understanding. |
| Curriculum | Structured around specialized courses and standards. | Includes collaborative, cross-disciplinary projects and courses. |
| Skill Development | Develops expertise and technical skills in one domain. | Enhances critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving across domains. |
| Research Focus | In-depth, specialized research within one field. | Addresses complex problems requiring multiple perspectives. |
| Outcome | Expert knowledge in a specific discipline. | Innovative solutions through integration of diverse knowledge. |
| Examples | Physics, History, Biology courses. | Environmental Studies, Cognitive Science, Urban Planning. |
Understanding Disciplinary Approaches
Disciplinary approaches concentrate on specialized knowledge within a single field, emphasizing deep expertise, methodologies, and theoretical frameworks unique to that domain. This focused perspective allows for rigorous analysis and problem-solving based on well-established criteria and terminologies specific to the discipline. Understanding disciplinary approaches is essential for grasping foundational concepts before integrating knowledge across multiple fields.
Defining Interdisciplinary Approaches
Interdisciplinary approaches integrate concepts, theories, and methods from multiple disciplines to address complex problems that cannot be solved by a single field alone. This method emphasizes collaboration and synthesis of knowledge across traditional academic boundaries, fostering innovation and comprehensive understanding. Disciplinary approaches, in contrast, rely on the depth of expertise within a single domain, often limiting the scope of analysis.
Historical Evolution of Academic Disciplines
The historical evolution of academic disciplines reveals a shift from strict disciplinary boundaries, rooted in the specialization that emerged during the Enlightenment, to the rise of interdisciplinary approaches in the late 20th century, driven by complex societal challenges requiring integrated knowledge. Early universities structured knowledge into discrete fields such as philosophy, medicine, and theology, reinforcing disciplinary silos, while contemporary academia increasingly values interdisciplinary collaboration to foster innovation across fields like environmental science and cognitive studies. This evolution reflects the dynamic interplay between traditional disciplinary foundations and the necessity for holistic perspectives in addressing multifaceted research questions.
Core Differences: Disciplinary vs Interdisciplinary
Disciplinary approaches focus on specialized knowledge within a single academic field, emphasizing depth, rigorous methodologies, and theoretical frameworks unique to that discipline. Interdisciplinary approaches integrate concepts, methods, and perspectives from multiple disciplines to address complex problems that cannot be solved by one field alone. Core differences include the scope of inquiry, with disciplinary research maintaining narrow boundaries, while interdisciplinary research promotes collaboration and synthesis across fields for holistic understanding.
Benefits of Disciplinary Research
Disciplinary research offers deep expertise by focusing on a specific field, enabling precise problem-solving and advancing specialized knowledge. It provides a structured framework for developing theories and methodologies unique to one discipline, ensuring rigor and clarity. This focused approach supports professional development and innovation within established academic and practical domains.
Advantages of Interdisciplinary Collaboration
Interdisciplinary collaboration integrates diverse expertise from multiple disciplines, fostering innovative problem-solving and comprehensive understanding that surpasses the limitations of singular fields. Combining methodologies and perspectives accelerates creativity and adaptability, enhancing research quality and practical outcomes. This approach addresses complex challenges more effectively by bridging gaps between specialized knowledge areas, promoting holistic solutions and improved decision-making.
Key Challenges in Disciplinary Studies
Disciplinary studies often face challenges such as rigid methodological frameworks and limited perspectives that hinder innovation and adaptation to complex problems. The specialization in a single discipline can lead to siloed knowledge, reducing the ability to integrate diverse insights from other fields. This confinement can restrict creativity and the development of comprehensive solutions needed in today's multifaceted research landscape.
Barriers and Solutions in Interdisciplinary Work
Interdisciplinary work faces barriers such as disciplinary jargon differences, conflicting methodologies, and institutional resistance to collaboration, which hinder effective communication and integration of diverse perspectives. Solutions include fostering mutual respect through cross-disciplinary training, implementing structured communication frameworks, and promoting institutional policies that incentivize collaborative research. Developing shared goals and creating platforms for continuous dialogue help bridge gaps and enhance interdisciplinary synergy.
Real-World Examples: Disciplinary and Interdisciplinary Projects
Disciplinary projects, such as a chemistry lab experiment or a historical archive analysis, focus on deep expertise within a single field, applying specialized methods and theories. Interdisciplinary projects combine knowledge from multiple disciplines, exemplified by urban planning integrating environmental science, sociology, and economics to create sustainable cities. Real-world examples include engineering teams developing medical devices by merging biomedical engineering, materials science, and clinical research for innovative healthcare solutions.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Research
Disciplinary research delves deeply into a specific field, leveraging specialized methodologies and theories to address focused questions. Interdisciplinary research integrates concepts and techniques from multiple disciplines, fostering innovative solutions for complex problems that span traditional boundaries. Selecting the right approach depends on your research objectives, the scope of the problem, and the need for comprehensive insights versus detailed expertise.
Disciplinary Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com