An internship provides hands-on experience that bridges academic learning with real-world applications, enhancing your professional skills and expanding your network. It offers opportunities to explore career paths, gain industry insights, and build a strong resume. Discover how to maximize your internship experience and unlock future career success by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
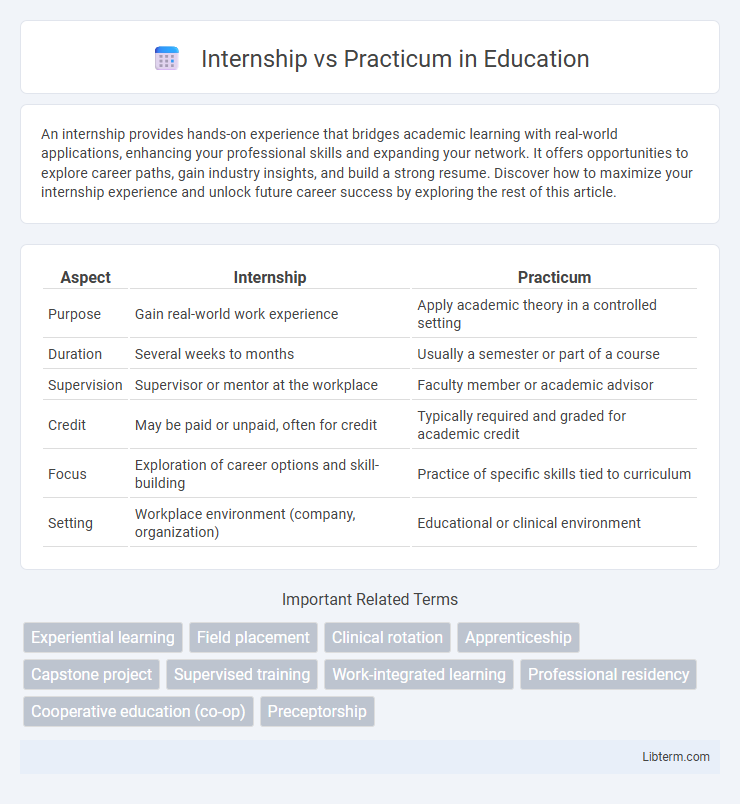
| Aspect | Internship | Practicum |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Gain real-world work experience | Apply academic theory in a controlled setting |
| Duration | Several weeks to months | Usually a semester or part of a course |
| Supervision | Supervisor or mentor at the workplace | Faculty member or academic advisor |
| Credit | May be paid or unpaid, often for credit | Typically required and graded for academic credit |
| Focus | Exploration of career options and skill-building | Practice of specific skills tied to curriculum |
| Setting | Workplace environment (company, organization) | Educational or clinical environment |
Introduction: Understanding Internship vs Practicum
Internships provide hands-on work experience within a professional environment, allowing students to apply theoretical knowledge and develop industry-specific skills. Practicums emphasize supervised, practical training closely aligned with academic coursework, often required for licensure or certification in fields like education, healthcare, or social work. Both offer valuable experiential learning but differ in structure, duration, and objectives tailored to career readiness and academic requirements.
Defining Internship: Key Features and Objectives
An internship is a structured work experience designed to provide students or recent graduates with practical, hands-on exposure to their chosen industry, often lasting several weeks to months. Key features include supervised training, skill development aligned with academic learning, and opportunities to apply theoretical knowledge in real-world settings. The primary objective is to bridge the gap between classroom education and professional practice, enhancing employability and career readiness.
Practicum Explained: Structure and Purpose
A practicum is a supervised, hands-on learning experience designed to integrate academic knowledge with practical skills in a real-world setting, often lasting a set duration within an academic program. It typically involves direct observation, application of theories, and reflection under the guidance of a professional mentor to enhance competency in a specific field. The structure of a practicum includes defined objectives, regular evaluations, and a combination of classroom instruction and fieldwork to prepare students for professional roles.
Primary Differences Between Internship and Practicum
Internships provide hands-on work experience in a professional environment, often unpaid or for academic credit, emphasizing practical skills and career exposure. Practicums are typically part of academic programs, focusing on supervised, structured training related to specific coursework, with a stronger emphasis on learning objectives and reflective practice. The primary differences lie in the level of supervision, purpose, and integration with academic requirements.
Duration and Time Commitment Comparison
Internships typically span from a few weeks to several months, with flexible time commitments that can range from part-time to full-time schedules, depending on the organization's needs and the intern's availability. Practicums generally have a more fixed duration aligned with academic semesters, requiring a regular time commitment often integrated into coursework, ensuring consistent weekly hours over the entire period. The structured timeframe of practicums contrasts with the variable length of internships, influencing the depth of hands-on experience gained in each.
Supervisors and Mentorship Roles
Internship supervisors provide structured guidance and performance evaluations to develop professional skills within a workplace setting, emphasizing real-world experience and career readiness. Practicum supervisors focus on direct mentorship and skill acquisition in educational or clinical environments, ensuring students apply theoretical knowledge under close observation. Both roles are critical for student growth, with internships oriented toward industry exposure and practicums centered on hands-on learning and skill mastery.
Academic Credit and Assessment Methods
Internships often provide academic credit based on the completion of work-hour requirements and supervisor evaluations, integrating practical experience with course objectives. Practicums emphasize direct assessment through performance evaluations, reflective journals, and skill demonstrations, aligning closely with specific academic competencies. Both methods contribute to experiential learning but differ in their structured assessment and credit allocation processes within academic programs.
Skills Gained: Internship vs Practicum Outcomes
Internships primarily develop practical, job-specific skills such as project management, communication, and industry tools, enhancing employability through real-world experience. Practicums emphasize hands-on application of academic theories, refining professional competencies like clinical assessment, educational techniques, or social work interventions. Both internships and practicums foster critical thinking and problem-solving but differ in skill focus: internships lean toward workplace readiness, while practicums target discipline-specific proficiency.
Choosing the Right Option for Your Career Goals
Internships offer hands-on experience in a professional work environment, ideal for building industry connections and gaining practical skills directly related to your career field. Practicums, typically part of academic programs, emphasize supervised, structured learning with a focus on applying theoretical knowledge through guided practice. Selecting the right option depends on your career goals, whether you prioritize networking and workplace immersion through an internship or deepening expertise and meeting educational requirements via a practicum.
Conclusion: Internship or Practicum—Which Is Better?
Internships offer hands-on industry experience and networking opportunities, ideal for students seeking practical skills and professional connections. Practicums emphasize academic learning and supervised application, best suited for fields requiring direct skill evaluation and reflection. Choosing between an internship or practicum depends on career goals, desired level of supervision, and the balance between theoretical knowledge and real-world experience.
Internship Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com