Distance learning offers flexible education options that allow you to study from anywhere, fitting courses into your busy schedule. It leverages technology to provide interactive lessons, personalized feedback, and access to a broad range of academic resources. Discover how distance learning can transform your educational experience by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
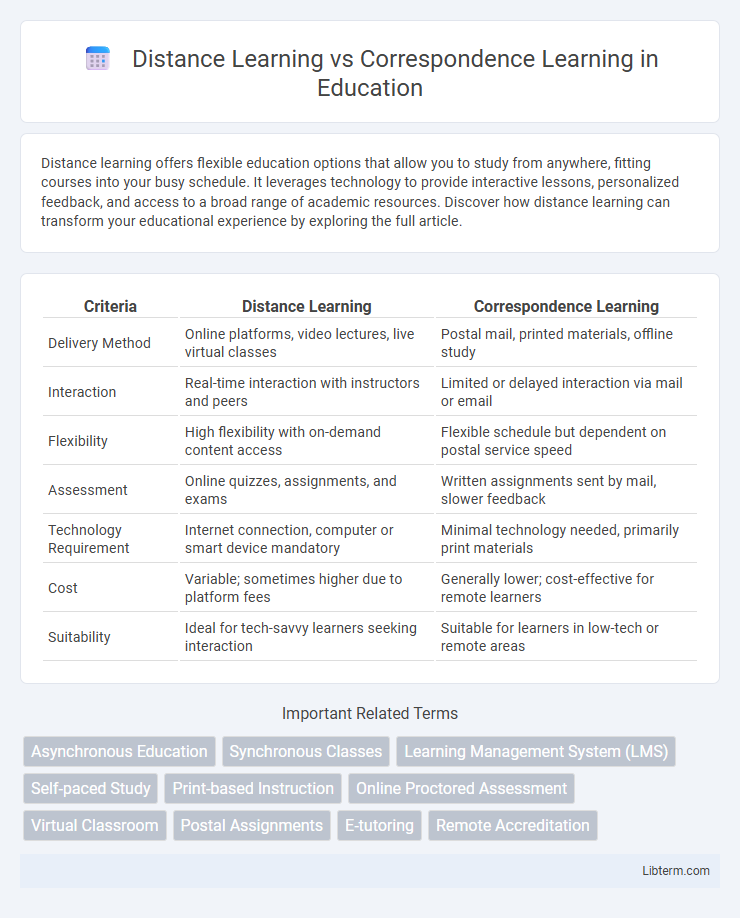
| Criteria | Distance Learning | Correspondence Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Delivery Method | Online platforms, video lectures, live virtual classes | Postal mail, printed materials, offline study |
| Interaction | Real-time interaction with instructors and peers | Limited or delayed interaction via mail or email |
| Flexibility | High flexibility with on-demand content access | Flexible schedule but dependent on postal service speed |
| Assessment | Online quizzes, assignments, and exams | Written assignments sent by mail, slower feedback |
| Technology Requirement | Internet connection, computer or smart device mandatory | Minimal technology needed, primarily print materials |
| Cost | Variable; sometimes higher due to platform fees | Generally lower; cost-effective for remote learners |
| Suitability | Ideal for tech-savvy learners seeking interaction | Suitable for learners in low-tech or remote areas |
Understanding Distance Learning: Definition and Features
Distance learning refers to an educational process where students engage with course materials and instructors remotely, often through online platforms, enabling flexible access to education regardless of geographic location. Key features include real-time or asynchronous interactions, multimedia content delivery, and the use of digital communication tools such as video conferencing, forums, and learning management systems. Unlike correspondence learning, which primarily relies on postal mail for sending assignments and study materials, distance learning integrates advanced technology to foster interactive and dynamic learning experiences.
What is Correspondence Learning? Key Characteristics
Correspondence learning is a form of distance education where instructional materials, assignments, and exams are exchanged through postal mail or online platforms, allowing students to study independently without real-time interaction. Key characteristics include asynchronous communication, self-paced progress, and minimal or no face-to-face contact with instructors. This method is often used in rural or remote areas where access to traditional classrooms is limited, emphasizing flexibility and accessibility.
Historical Evolution: Distance vs Correspondence Education
Distance learning originated in the 19th century with correspondence education, which relied on postal mail to deliver course materials to students. As technology advanced, distance learning evolved to encompass radio, television broadcasts, and eventually the internet, enabling real-time interaction and multimedia content. The historical shift from correspondence to modern distance education highlights increased accessibility and interactivity in remote learning.
Learning Platforms and Technological Integration
Distance learning leverages advanced digital platforms such as Moodle, Blackboard, and Google Classroom to facilitate real-time interaction, multimedia content delivery, and comprehensive progress tracking, enhancing student engagement and flexibility. Correspondence learning primarily relies on printed materials and postal services, limiting interactivity and immediate feedback, often lacking integration with modern educational technologies. The integration of video conferencing tools, interactive quizzes, and mobile applications in distance learning significantly improves accessibility and personalized learning experiences compared to traditional correspondence methods.
Flexibility and Accessibility Comparison
Distance learning offers greater flexibility by enabling students to access courses online anytime and anywhere, accommodating diverse schedules and time zones. Correspondence learning typically relies on mailed materials and offline assignments, which can delay feedback and limit immediacy in communication. Online distance education platforms also enhance accessibility for students with internet access, while correspondence learning serves those with limited connectivity but may pose challenges in timely engagement.
Student Interaction and Communication Methods
Distance learning employs interactive digital platforms such as video conferencing, discussion forums, and real-time chats, enabling dynamic student interaction and immediate feedback. Correspondence learning relies primarily on mailed materials and assignments, resulting in limited and delayed communication between students and instructors. The level of engagement in distance learning is significantly higher due to synchronous communication tools, whereas correspondence learning emphasizes self-paced study with asynchronous interaction.
Assessment, Assignments, and Feedback Mechanisms
Distance learning employs digital platforms to facilitate real-time assessments, instant submission of assignments, and prompt feedback through interactive tools, enhancing learner engagement and progress tracking. Correspondence learning relies on physical mail for assignment distribution and collection, often resulting in delayed assessment processing and feedback, which can impede timely learner improvement. Advanced distance learning systems utilize automated grading and multimedia feedback, whereas correspondence models face challenges in providing immediate, detailed evaluations.
Accreditation and Recognition Differences
Distance learning programs often gain accreditation from regional or national education authorities, ensuring that credits and qualifications are widely recognized by employers and institutions. Correspondence learning may lack consistent accreditation, potentially limiting the transferability of credits and acceptance of qualifications across educational or professional settings. Accreditation standards impact the credibility and recognition of credentials, making distance learning a more reliable option for students seeking officially recognized certifications.
Pros and Cons: Distance vs Correspondence Learning
Distance learning offers real-time interaction with instructors and peers via online platforms, enhancing engagement and immediate feedback, but it requires reliable internet access and technical skills. Correspondence learning provides flexibility through self-paced study using mailed materials, making it accessible in areas with limited connectivity, yet it often lacks timely feedback and interactive support. Both methods cater to different learning needs, with distance learning excelling in communication and correspondence learning in accessibility.
Which Learning Method Suits You Best?
Distance learning offers interactive, real-time classes through digital platforms, ideal for learners seeking flexibility combined with immediate instructor feedback. Correspondence learning suits self-motivated individuals who prefer studying at their own pace using mailed or downloaded course materials without scheduled sessions. Assess your learning style, discipline level, and need for interaction to determine which method aligns best with your educational goals.
Distance Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com