Competency-Based Learning focuses on mastering specific skills and knowledge at your own pace, ensuring practical application in real-world scenarios. This personalized approach allows learners to progress only after demonstrating proficiency, leading to deeper understanding and long-term retention. Explore the rest of the article to discover how Competency-Based Learning can transform your educational experience.
Table of Comparison
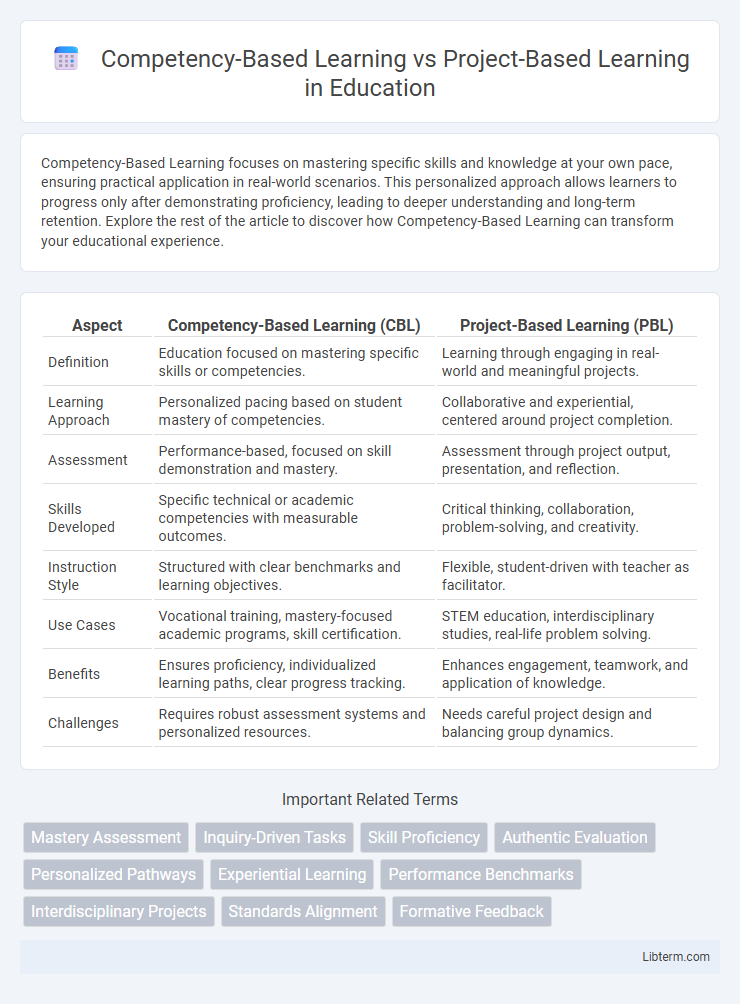
| Aspect | Competency-Based Learning (CBL) | Project-Based Learning (PBL) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Education focused on mastering specific skills or competencies. | Learning through engaging in real-world and meaningful projects. |
| Learning Approach | Personalized pacing based on student mastery of competencies. | Collaborative and experiential, centered around project completion. |
| Assessment | Performance-based, focused on skill demonstration and mastery. | Assessment through project output, presentation, and reflection. |
| Skills Developed | Specific technical or academic competencies with measurable outcomes. | Critical thinking, collaboration, problem-solving, and creativity. |
| Instruction Style | Structured with clear benchmarks and learning objectives. | Flexible, student-driven with teacher as facilitator. |
| Use Cases | Vocational training, mastery-focused academic programs, skill certification. | STEM education, interdisciplinary studies, real-life problem solving. |
| Benefits | Ensures proficiency, individualized learning paths, clear progress tracking. | Enhances engagement, teamwork, and application of knowledge. |
| Challenges | Requires robust assessment systems and personalized resources. | Needs careful project design and balancing group dynamics. |
Understanding Competency-Based Learning
Competency-Based Learning (CBL) centers on mastering specific skills or knowledge at an individual pace, ensuring learners achieve predefined competencies before advancing. Unlike traditional time-based education, CBL emphasizes personalized assessment and measurable learning outcomes aligned with industry standards. This approach enhances learner accountability and prepares students for real-world applications by focusing on skill proficiency rather than seat time.
What is Project-Based Learning?
Project-Based Learning (PBL) is an instructional methodology where students actively explore real-world problems and challenges over an extended period to acquire deeper knowledge. This approach emphasizes critical thinking, collaboration, and hands-on experience by engaging students in complex projects that require applying various skills and content. Unlike traditional learning models, PBL fosters creativity and problem-solving by integrating interdisciplinary concepts within meaningful, student-driven tasks.
Core Principles of Competency-Based Learning
Competency-Based Learning centers on mastering specific skills and knowledge through personalized pacing, ensuring learners achieve clear, measurable outcomes before progressing. It emphasizes demonstrated proficiency and real-time feedback to address individual learning gaps. This approach contrasts with Project-Based Learning, which focuses on applying knowledge through collaborative, real-world projects rather than explicit competency benchmarks.
Essential Features of Project-Based Learning
Project-Based Learning (PBL) centers on active exploration of real-world challenges through collaborative projects, fostering critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and deep content understanding. Essential features include student-driven inquiry, authentic assessments, interdisciplinary approaches, and reflection on progress. This immersive method contrasts with Competency-Based Learning's focus on mastering specific skills or knowledge at an individual pace.
Key Differences Between Competency and Project-Based Learning
Competency-Based Learning centers on mastering specific skills and knowledge demonstrated through assessments, allowing students to progress at their own pace until they achieve proficiency. Project-Based Learning emphasizes completing complex, real-world projects that integrate multiple skills and foster collaboration, critical thinking, and problem-solving over time. The key difference lies in Competency-Based Learning's focus on individual mastery of discrete competencies versus Project-Based Learning's holistic, interdisciplinary approach to applying knowledge in practical contexts.
Benefits of Competency-Based Learning
Competency-Based Learning (CBL) offers personalized progression by allowing students to advance upon mastering specific skills, ensuring a deeper understanding and retention of knowledge. This approach aligns with workforce demands by emphasizing real-world competencies and measurable outcomes that enhance employability. CBL also fosters learner autonomy, enabling tailored educational experiences that accommodate diverse learning paces and styles, resulting in improved student engagement and success rates.
Advantages of Project-Based Learning
Project-Based Learning (PBL) enhances critical thinking, collaboration, and real-world problem-solving skills by engaging students in hands-on projects directly tied to authentic contexts. This approach promotes deeper understanding and retention of knowledge through active exploration and practical application. Students develop essential 21st-century skills such as communication, teamwork, and adaptability, which are highly valued in modern workplaces.
Challenges in Implementing Each Approach
Competency-Based Learning faces challenges such as accurately assessing individual student mastery and ensuring consistent standardization across diverse learning contexts. Project-Based Learning often struggles with aligning projects to specific curriculum standards and managing varied student engagement and collaboration skills. Both approaches require substantial teacher training and resource allocation to implement effectively, impacting adoption rates in educational institutions.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Classroom
Competency-Based Learning (CBL) emphasizes mastery of specific skills and knowledge through personalized pacing and assessment, ensuring students achieve defined competencies before advancing. Project-Based Learning (PBL) engages students in real-world challenges, fostering critical thinking, collaboration, and practical application of concepts within a contextual framework. Selecting the right approach depends on classroom goals: CBL suits environments prioritizing individualized skill acquisition and measurable outcomes, while PBL benefits those aiming to develop problem-solving abilities and teamwork through experiential learning.
Integrating Competency and Project-Based Learning for Optimal Outcomes
Integrating competency-based learning with project-based learning enhances skill mastery by aligning real-world projects with clearly defined competencies, ensuring measurable progress and practical application. This approach fosters deeper understanding as learners engage in authentic, hands-on experiences while receiving targeted feedback on specific skills and knowledge areas. Educational institutions adopting this hybrid model report improved learner engagement, retention, and success in developing both cognitive and applied competencies essential for 21st-century careers.
Competency-Based Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com