Competitive learning is a powerful neural network technique where neurons compete to become active, allowing the system to self-organize and identify patterns in input data. This method is particularly effective for tasks like clustering and feature extraction, helping your model adapt to complex datasets without explicit supervision. Explore the rest of the article to understand how competitive learning can enhance your machine learning projects.
Table of Comparison
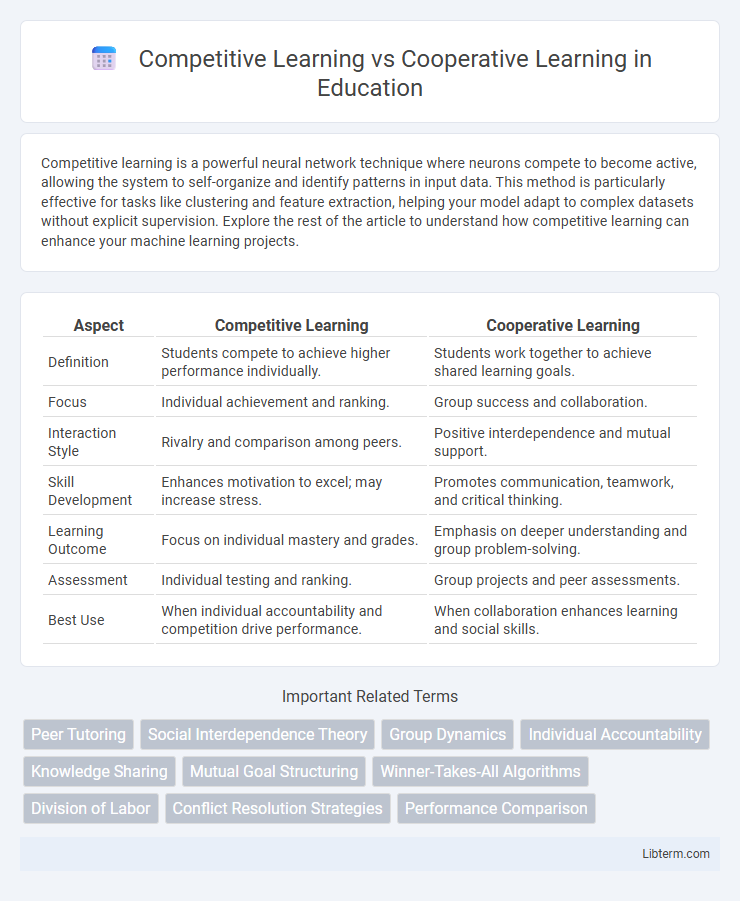
| Aspect | Competitive Learning | Cooperative Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Students compete to achieve higher performance individually. | Students work together to achieve shared learning goals. |
| Focus | Individual achievement and ranking. | Group success and collaboration. |
| Interaction Style | Rivalry and comparison among peers. | Positive interdependence and mutual support. |
| Skill Development | Enhances motivation to excel; may increase stress. | Promotes communication, teamwork, and critical thinking. |
| Learning Outcome | Focus on individual mastery and grades. | Emphasis on deeper understanding and group problem-solving. |
| Assessment | Individual testing and ranking. | Group projects and peer assessments. |
| Best Use | When individual accountability and competition drive performance. | When collaboration enhances learning and social skills. |
Introduction to Competitive and Cooperative Learning
Competitive learning emphasizes individual achievement where learners strive to outperform peers, fostering motivation through rivalry and personal success. Cooperative learning involves students working collaboratively in groups to achieve shared goals, enhancing communication, teamwork, and collective problem-solving skills. Both approaches influence educational outcomes differently, with competitive learning promoting individual accountability and cooperative learning encouraging social interaction and mutual support.
Defining Competitive Learning
Competitive learning is a machine learning paradigm where neurons or units compete to become active and represent input data, often using mechanisms like winner-takes-all to select the strongest response. This approach enhances pattern recognition by emphasizing distinct feature detection and is commonly employed in clustering algorithms and self-organizing maps. Competitive learning contrasts with cooperative learning, where units collaborate to improve data representation through joint activation and feature sharing.
Understanding Cooperative Learning
Cooperative learning involves students working together in small groups to achieve shared academic goals and develop interpersonal skills, promoting positive interdependence and individual accountability. This approach enhances critical thinking, communication, and social interaction by encouraging collaboration and mutual support among group members. Research shows that cooperative learning improves retention and motivation compared to competitive learning, which emphasizes outperforming peers.
Key Differences Between Competitive and Cooperative Learning
Competitive learning emphasizes individual achievement where learners strive to outperform peers, fostering a competitive environment that motivates personal excellence and quick problem-solving. Cooperative learning centers on collaboration, encouraging students to work together, share knowledge, and build group success through mutual support and collective goal attainment. Key differences lie in the focus on individual versus group outcomes, the level of interaction, and the type of motivation--competitive learning drives personal ambition, whereas cooperative learning enhances social skills and teamwork.
Benefits of Competitive Learning
Competitive learning enhances motivation by driving individuals to outperform peers, fostering higher levels of effort and achievement. It encourages critical thinking and problem-solving as learners strive to gain an edge, promoting skill development and innovation. This method also cultivates resilience and adaptability, preparing learners to excel in real-world situations where performance under pressure is essential.
Advantages of Cooperative Learning
Cooperative learning enhances critical thinking and communication skills by promoting group interaction and diverse perspectives. It fosters social development, increases student motivation, and improves academic achievement through shared responsibility and peer support. This collaborative approach reduces anxiety and competition-related stress, creating a positive learning environment.
Challenges in Competitive Learning Environments
Competitive learning environments often face challenges such as increased stress levels among students, which can hinder creativity and reduce intrinsic motivation. These settings may foster anxiety and fear of failure, negatively impacting collaboration and peer support. Furthermore, competitive frameworks can exacerbate inequality by favoring high-performing individuals and marginalizing those who struggle to keep up.
Obstacles in Cooperative Learning Settings
Obstacles in cooperative learning settings often include unequal participation, where some group members contribute less, and social loafing, which undermines collective effort and learning outcomes. Diverse skill levels and communication barriers can hinder effective collaboration, resulting in misunderstandings and reduced group cohesion. Addressing these challenges requires structured group roles, clear guidelines, and continuous monitoring to ensure balanced engagement and mutual support.
Choosing the Right Approach for Different Learners
Competitive learning fosters motivation through rivalry, benefiting students who thrive under pressure and seek individual recognition. Cooperative learning emphasizes collaboration and shared goals, ideal for learners who excel in social interaction and mutual support. Selecting the right approach depends on understanding each learner's personality, learning style, and the educational context to maximize engagement and achievement.
Integrating Competitive and Cooperative Strategies in Education
Integrating competitive and cooperative strategies in education enhances student engagement by balancing motivation and collaboration, fostering a dynamic learning environment. Research shows that combining these approaches improves critical thinking and social skills, as students learn to strive for personal excellence while supporting peer success. Implementing mixed methods like team competitions followed by group reflection sessions maximizes both individual accountability and collective problem-solving capabilities.
Competitive Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com