Interpretation involves analyzing and assigning meaning to data, events, or expressions to gain deeper understanding. It plays a crucial role in fields such as literature, law, and science, shaping how information is perceived and applied. Explore the rest of the article to uncover key techniques and tips for enhancing your interpretation skills.
Table of Comparison
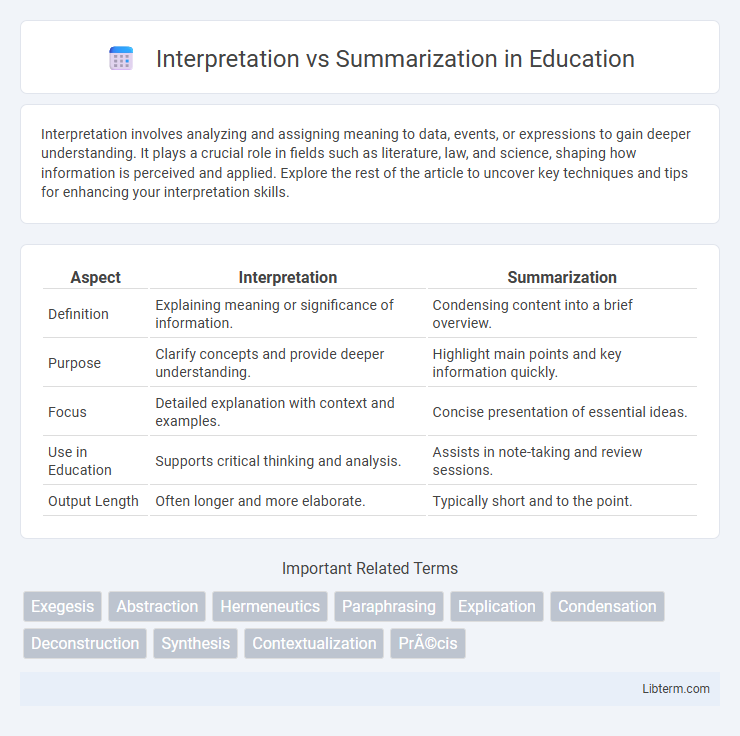
| Aspect | Interpretation | Summarization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Explaining meaning or significance of information. | Condensing content into a brief overview. |
| Purpose | Clarify concepts and provide deeper understanding. | Highlight main points and key information quickly. |
| Focus | Detailed explanation with context and examples. | Concise presentation of essential ideas. |
| Use in Education | Supports critical thinking and analysis. | Assists in note-taking and review sessions. |
| Output Length | Often longer and more elaborate. | Typically short and to the point. |
Understanding Interpretation and Summarization
Interpretation involves analyzing and explaining the meaning behind information, emphasizing context and underlying significance for deeper understanding. Summarization condenses content by highlighting key points and essential details to provide a brief overview. Both processes enhance comprehension but serve different purposes: interpretation clarifies meaning, while summarization distills content.
Key Differences Between Interpretation and Summarization
Interpretation involves explaining the meaning or significance of information by adding context and personal insight, while summarization condenses content to highlight only the main points without personal input. Interpretation requires analytical thinking and often involves subjective judgment, whereas summarization is objective, focusing on brevity and clarity. Key differences include the depth of analysis, purpose--interpretation aims to understand meaning, and summarization aims to reduce length--and the presence of personal perspective in interpretation versus the neutrality of summarization.
The Purpose of Interpretation
The purpose of interpretation is to uncover deeper meaning by analyzing context, symbolism, and underlying themes, enabling a richer understanding beyond the surface text. It seeks to connect ideas and provide insight into the author's intent, cultural significance, or emotional impact. Interpretation transforms raw information into a nuanced perspective that enhances comprehension and critical thinking.
The Role of Summarization
Summarization distills the core ideas and key points of a text, enabling efficient comprehension and retention of essential information. It serves as a foundation for interpretation by providing a concise overview, reducing complexity without losing critical meaning. Effective summarization enhances knowledge management and supports decision-making processes across academic, professional, and everyday contexts.
Techniques for Effective Interpretation
Techniques for effective interpretation include active listening, contextual analysis, and cultural awareness to accurately convey the intended meaning behind information. Employing paraphrasing and questioning clarifies ambiguous content while highlighting key themes and underlying concepts. Utilizing analogies and examples enhances comprehension by connecting new information to familiar ideas, fostering deeper understanding.
Methods for Creating Strong Summaries
Effective methods for creating strong summaries include identifying key ideas, condensing information without losing meaning, and prioritizing relevant details based on the text's purpose. Utilizing techniques such as paraphrasing, extracting main points, and structuring content logically enhances clarity and engagement. Summaries focus on conveying essential information concisely, unlike interpretation, which examines deeper meanings and subjective analysis.
When to Use Interpretation vs Summarization
Interpretation is best used when the goal is to uncover deeper meaning, analyze underlying themes, or provide insight beyond the original text, making it ideal for literature analysis, critical reviews, and academic research. Summarization is appropriate for conveying the main points quickly and concisely, useful in reporting news, creating executive briefs, or studying large volumes of information efficiently. Choosing between interpretation and summarization depends on whether the objective is detailed understanding or efficient information transfer.
Common Challenges in Interpretation and Summarization
Common challenges in interpretation and summarization include maintaining the original meaning while condensing information and avoiding distortion or loss of key details. Interpreters must navigate linguistic nuances and cultural contexts, whereas summarizers often struggle with selecting the most relevant points without oversimplifying complex content. Both processes require balancing accuracy, clarity, and brevity to effectively convey the intended message.
Examples Illustrating Interpretation and Summarization
Interpretation involves analyzing the meaning behind a text, such as explaining the symbolism in George Orwell's "1984" where the oppressive government represents totalitarian regimes. Summarization condenses content by highlighting key points, like briefly describing "1984" as a story about a dystopian society under constant surveillance. Interpretation adds depth by exploring themes and implications, while summarization provides a concise overview of the main ideas.
Enhancing Skills in Interpretation and Summarization
Enhancing skills in interpretation involves developing the ability to understand and convey the deeper meaning, context, and implications of information, while summarization focuses on distilling key points into concise and clear summaries. Mastering interpretation requires critical thinking, analytical reasoning, and the capacity to connect ideas, whereas effective summarization relies on identifying main ideas and eliminating redundant details. Improving both skills enhances communication, reading comprehension, and the ability to synthesize complex information efficiently.
Interpretation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com