Competitive learning is a neural network training technique where neurons compete to become active, allowing the network to self-organize and identify distinct patterns in input data. This approach enhances feature extraction and pattern recognition without requiring labeled datasets, making it valuable for unsupervised learning tasks. Explore the rest of this article to understand how competitive learning can optimize your machine learning projects.
Table of Comparison
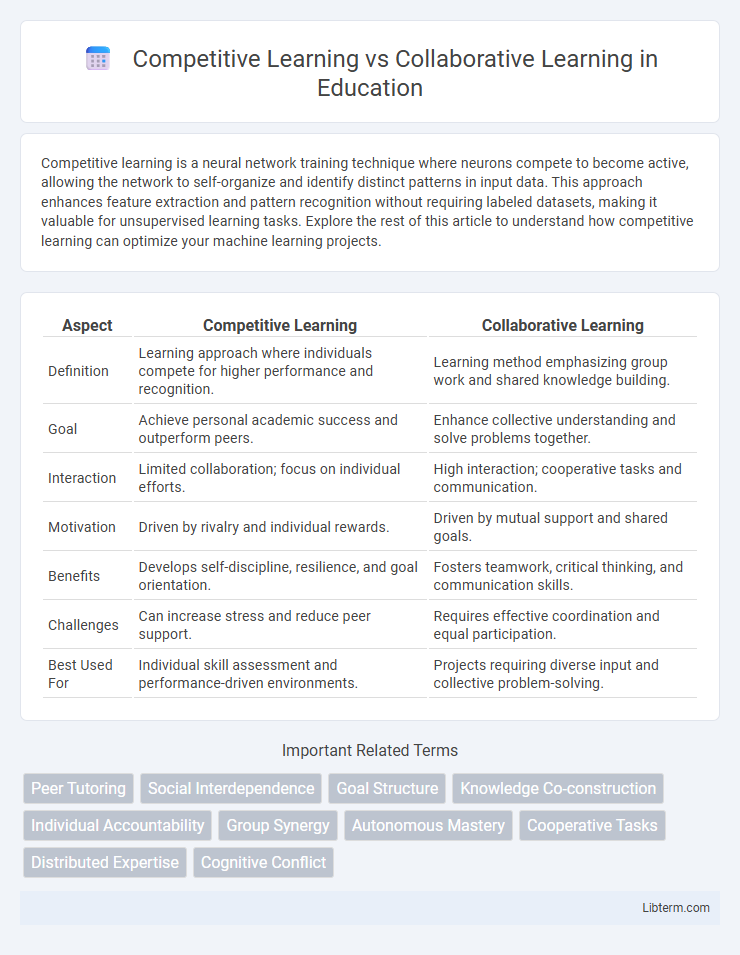
| Aspect | Competitive Learning | Collaborative Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Learning approach where individuals compete for higher performance and recognition. | Learning method emphasizing group work and shared knowledge building. |
| Goal | Achieve personal academic success and outperform peers. | Enhance collective understanding and solve problems together. |
| Interaction | Limited collaboration; focus on individual efforts. | High interaction; cooperative tasks and communication. |
| Motivation | Driven by rivalry and individual rewards. | Driven by mutual support and shared goals. |
| Benefits | Develops self-discipline, resilience, and goal orientation. | Fosters teamwork, critical thinking, and communication skills. |
| Challenges | Can increase stress and reduce peer support. | Requires effective coordination and equal participation. |
| Best Used For | Individual skill assessment and performance-driven environments. | Projects requiring diverse input and collective problem-solving. |
Introduction to Competitive and Collaborative Learning
Competitive learning emphasizes individual performance where learners compete to achieve the highest scores or ranks, fostering motivation through rivalry and self-improvement. Collaborative learning centers on group interaction and teamwork, encouraging students to share knowledge and solve problems collectively to enhance understanding and skill development. Both approaches aim to optimize educational outcomes but differ fundamentally in social dynamics and instructional strategies.
Defining Competitive Learning
Competitive learning is a machine learning paradigm where models or agents vie to be the most accurate or efficient in solving a problem, often involving winner-takes-all mechanisms to enhance pattern recognition and data clustering. This approach emphasizes individual performance improvement through rivalry, leading to distinct prototype formation in neural networks or classifiers. Competitive learning contrasts with collaborative learning by prioritizing individual success over group cooperation, driving innovation through competition and refinement.
Defining Collaborative Learning
Collaborative learning is an educational approach where students work together actively to solve problems, complete tasks, or understand new concepts, emphasizing group interaction and shared responsibility. Unlike competitive learning, which motivates individuals through rivalry and personal achievement, collaborative learning fosters cooperation, communication, and mutual support to achieve common academic goals. This method enhances critical thinking and interpersonal skills by leveraging diverse perspectives within a learning community.
Key Differences between Competitive and Collaborative Approaches
Competitive learning promotes individual achievement through rivalry and comparison, emphasizing personal success and rank within a group. Collaborative learning fosters teamwork and shared goals, encouraging students to work together, communicate, and build collective knowledge. The key difference lies in competitive learning's focus on outperforming peers, whereas collaborative learning prioritizes cooperative problem-solving and mutual support.
Cognitive Benefits of Competitive Learning
Competitive learning enhances cognitive abilities by promoting critical thinking and problem-solving skills through challenging scenarios that require quick decision-making. It fosters higher levels of motivation and engagement, driving learners to outperform peers and refine their knowledge. This learning model also improves memory retention by encouraging active participation and immediate feedback in competitive contexts.
Social Advantages of Collaborative Learning
Collaborative learning fosters social skills such as communication, teamwork, and conflict resolution by encouraging students to work together toward common goals, enhancing peer interaction and mutual understanding. It promotes a sense of community and belonging, which increases motivation and engagement, leading to improved academic outcomes and emotional well-being. Unlike competitive learning, collaborative environments reduce social anxiety and create a supportive atmosphere where diverse perspectives are valued and collective problem-solving thrives.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Learning Model
Competitive learning often leads to increased stress and anxiety among students due to constant comparison and ranking, which can hinder intrinsic motivation and create a hostile classroom environment. Collaborative learning faces challenges such as unequal participation, dominance of certain members, and potential social loafing, which can reduce individual accountability and limit the effectiveness of group outcomes. Both models require careful facilitation and structured frameworks to mitigate these limitations and foster a productive and inclusive learning experience.
Impact on Student Motivation and Engagement
Competitive learning often increases student motivation by leveraging rivalry to boost individual performance, yet it may induce anxiety and reduce collaboration. Collaborative learning enhances student engagement through shared goals and peer interaction, fostering intrinsic motivation and deeper understanding. Research indicates that cooperative environments generally yield higher sustained motivation and positive attitudes towards learning compared to competitive settings.
Best Practices for Implementing Both Strategies
Effective competitive learning strategies include setting clear goals, providing immediate feedback, and encouraging healthy rivalry to motivate students while maintaining a supportive environment. Collaborative learning thrives when instructors design diverse group tasks, promote open communication, and establish shared accountability to enhance teamwork and knowledge construction. Combining both approaches requires balancing individual achievement with group interdependence, using mixed assessment methods and fostering a classroom culture that values both competition and cooperation.
Choosing the Right Approach: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right approach between competitive learning and collaborative learning depends on factors such as learner motivation, group dynamics, and educational goals. Competitive learning suits environments where individual performance and quick decision-making are prioritized, fostering personal accountability and excellence. Collaborative learning, on the other hand, enhances critical thinking, communication skills, and teamwork by encouraging shared knowledge construction and peer support.
Competitive Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com