A Gifted Individualized Education Plan (GIEP) is a customized program designed to meet the unique educational needs of gifted students, ensuring they receive appropriate challenges and enrichment. It outlines specific goals, services, and accommodations tailored to enhance your child's academic growth and social development. Explore the rest of the article to understand how a GIEP can maximize your gifted student's potential.
Table of Comparison
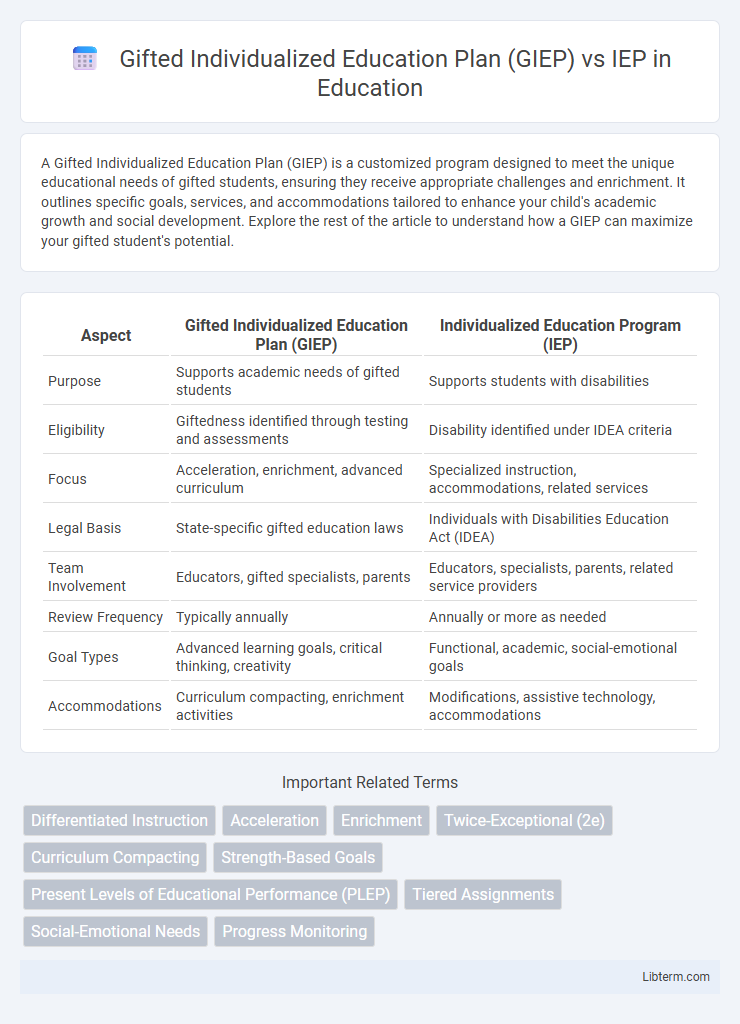
| Aspect | Gifted Individualized Education Plan (GIEP) | Individualized Education Program (IEP) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Supports academic needs of gifted students | Supports students with disabilities |
| Eligibility | Giftedness identified through testing and assessments | Disability identified under IDEA criteria |
| Focus | Acceleration, enrichment, advanced curriculum | Specialized instruction, accommodations, related services |
| Legal Basis | State-specific gifted education laws | Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) |
| Team Involvement | Educators, gifted specialists, parents | Educators, specialists, parents, related service providers |
| Review Frequency | Typically annually | Annually or more as needed |
| Goal Types | Advanced learning goals, critical thinking, creativity | Functional, academic, social-emotional goals |
| Accommodations | Curriculum compacting, enrichment activities | Modifications, assistive technology, accommodations |
Understanding Gifted Individualized Education Plans (GIEP)
Gifted Individualized Education Plans (GIEPs) are specialized plans designed to address the unique academic and social-emotional needs of gifted students, differing from Individualized Education Plans (IEPs) which cater to students with disabilities. GIEPs focus on acceleration, enrichment, and differentiation to challenge advanced learners beyond the standard curriculum, ensuring appropriate skill development and engagement. Understanding GIEPs involves recognizing their role in customizing educational goals and services to optimize the potential of gifted learners while fostering critical thinking and creativity.
What Is an Individualized Education Program (IEP)?
An Individualized Education Program (IEP) is a legally binding document designed to outline specialized educational services and supports for students with disabilities under the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA). The IEP specifies personalized goals, accommodations, and modifications tailored to meet the unique learning needs of each eligible student, ensuring access to free appropriate public education (FAPE). Unlike the Gifted Individualized Education Plan (GIEP), which targets advanced learners requiring enrichment, the IEP focuses primarily on addressing challenges related to disabilities.
Eligibility Criteria: GIEP vs. IEP
The eligibility criteria for a Gifted Individualized Education Plan (GIEP) require students to demonstrate exceptional intellectual ability, creativity, or academic achievement beyond grade-level standards, typically through assessments and teacher nominations. In contrast, an Individualized Education Plan (IEP) eligibility centers on identifying students with disabilities that adversely affect educational performance, as defined by the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA). While GIEP focuses on giftedness and advanced learning needs, IEP addresses special education services for various disabilities, making the criteria distinct in terms of cognitive capabilities and support requirements.
Legal Frameworks Governing GIEP and IEP
The Gifted Individualized Education Plan (GIEP) and Individualized Education Program (IEP) are governed by distinct legal frameworks, with IEPs mandated under the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) to support students with disabilities in public education. GIEPs, however, are not federally mandated but are developed under state laws and local policies aimed at addressing the educational needs of gifted students, often providing specialized enrichment beyond standard curricula. Compliance with IDEA ensures IEPs include specific procedural safeguards, while GIEP frameworks vary widely, influencing eligibility criteria, service delivery, and parental rights.
Key Components of a GIEP
A Gifted Individualized Education Plan (GIEP) specifically addresses the advanced academic, creative, and intellectual needs of gifted students by including key components such as differentiated instruction strategies, acceleration options, and enrichment activities tailored to their unique abilities. Unlike a standard Individualized Education Plan (IEP), which targets students with disabilities, a GIEP emphasizes advanced learning goals, assessment adjustments for giftedness, and collaboration with specialists in gifted education. The plan ensures measurable objectives, periodic progress monitoring, and services designed to foster the student's higher-order thinking skills and talent development.
Core Elements of an IEP
The Core Elements of an Individualized Education Plan (IEP) include present levels of academic achievement, measurable annual goals, specific special education services, and methods of progress monitoring tailored to a student's unique needs. In contrast, a Gifted Individualized Education Plan (GIEP) emphasizes advanced curriculum goals, enrichment opportunities, and acceleration strategies, addressing the specialized needs of gifted learners. Both plans require parent participation and regular reviews to ensure appropriate educational support, but the GIEP specifically targets the strengths and talents of gifted students beyond traditional IEP frameworks.
Educational Goals: GIEP vs. IEP
Educational goals in a Gifted Individualized Education Plan (GIEP) emphasize advanced academic challenges, critical thinking, creativity, and depth in specific subject areas tailored to the gifted student's strengths. In contrast, an Individualized Education Plan (IEP) focuses on addressing learning disabilities by setting achievable, remedial, and supportive goals to improve the student's functional and academic performance. GIEP goals aim to enrich and accelerate learning, while IEP goals primarily target skill development and overcoming educational barriers.
Team Members Involved in GIEP and IEP Development
The development of a Gifted Individualized Education Plan (GIEP) typically involves a team including gifted education specialists, general education teachers, parents, and sometimes the student, focusing on advanced learning needs and enrichment opportunities. In contrast, an Individualized Education Plan (IEP) team comprises special education teachers, general educators, parents, school psychologists, and related service providers, targeting specific disability-related accommodations and support. Both teams collaborate to create tailored educational strategies but differ in expertise and objectives based on whether the focus is on giftedness or special education needs.
Differences in Parental Involvement and Advocacy
Parental involvement in a Gifted Individualized Education Plan (GIEP) often emphasizes collaboration with educators to design advanced learning opportunities tailored to the child's exceptional intellectual abilities, while an Individualized Education Program (IEP) primarily focuses on addressing specific learning disabilities or challenges through targeted interventions. Advocacy in GIEPs tends to prioritize ensuring access to enrichment programs and accelerated curriculum, whereas IEP advocacy revolves around securing necessary supports such as speech therapy, occupational therapy, or behavioral services. Both plans require active parental engagement, but the nature of advocacy differs based on the child's unique educational needs and goals.
Evaluating Outcomes: GIEP vs. IEP Success
Evaluating outcomes of Gifted Individualized Education Plans (GIEPs) versus Individualized Education Plans (IEPs) reveals distinct success metrics tailored to student needs. GIEPs prioritize advanced cognitive and creative growth, often measured by achievement in accelerated coursework and enrichment activities, while IEPs focus on remedial progress and functional skill development based on disability-specific goals. Research indicates that success in GIEPs is linked to enhanced problem-solving abilities and critical thinking, whereas IEP success is correlated with improved adaptive behaviors and academic competencies in core subjects.
Gifted Individualized Education Plan (GIEP) Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com