Inquiry-Based Learning engages students actively in the learning process by encouraging questioning, exploration, and critical thinking. This approach fosters deeper understanding and retention by connecting new knowledge to real-world contexts. Discover how Inquiry-Based Learning can transform Your educational experience throughout this article.
Table of Comparison
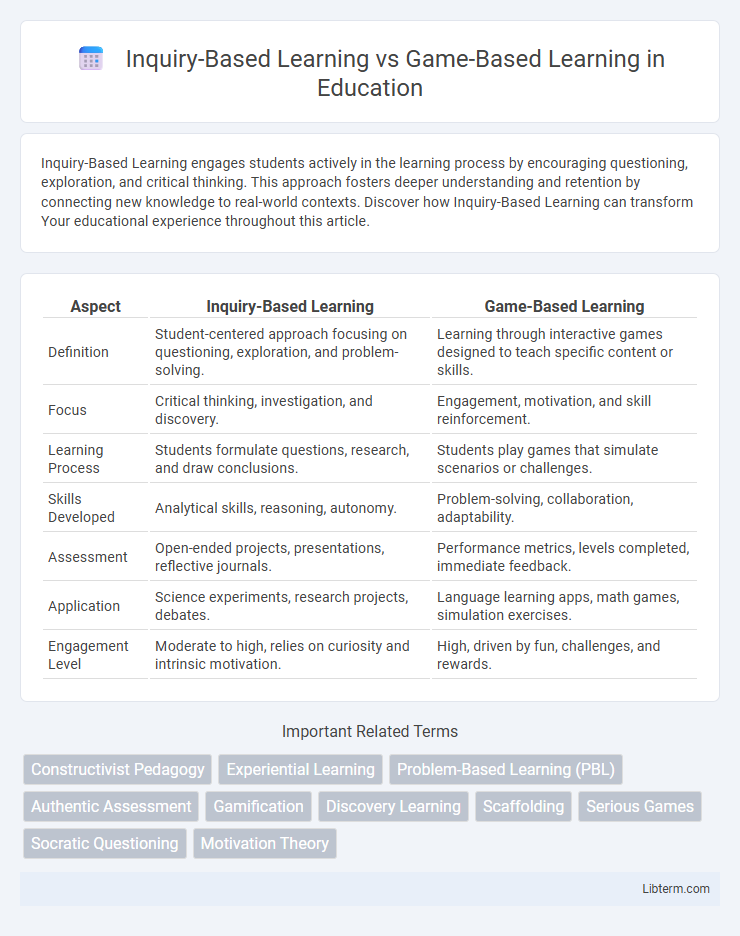
| Aspect | Inquiry-Based Learning | Game-Based Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Student-centered approach focusing on questioning, exploration, and problem-solving. | Learning through interactive games designed to teach specific content or skills. |
| Focus | Critical thinking, investigation, and discovery. | Engagement, motivation, and skill reinforcement. |
| Learning Process | Students formulate questions, research, and draw conclusions. | Students play games that simulate scenarios or challenges. |
| Skills Developed | Analytical skills, reasoning, autonomy. | Problem-solving, collaboration, adaptability. |
| Assessment | Open-ended projects, presentations, reflective journals. | Performance metrics, levels completed, immediate feedback. |
| Application | Science experiments, research projects, debates. | Language learning apps, math games, simulation exercises. |
| Engagement Level | Moderate to high, relies on curiosity and intrinsic motivation. | High, driven by fun, challenges, and rewards. |
Introduction to Inquiry-Based and Game-Based Learning
Inquiry-Based Learning emphasizes active exploration and critical thinking by encouraging students to ask questions, investigate problems, and develop solutions through hands-on experiences. Game-Based Learning integrates educational content into interactive games designed to enhance engagement, motivation, and retention by leveraging challenges and rewards. Both approaches foster student-centered environments but target different cognitive processes and learning dynamics.
Defining Inquiry-Based Learning
Inquiry-Based Learning is a student-centered educational approach that emphasizes questioning, exploration, and critical thinking to foster deeper understanding and knowledge construction. This method encourages learners to investigate real-world problems and develop solutions through active engagement and reflection. It contrasts with Game-Based Learning, which uses interactive games as a medium to motivate and enhance learning outcomes.
Defining Game-Based Learning
Game-Based Learning (GBL) involves the use of interactive games designed to facilitate educational outcomes by engaging students in problem-solving and critical thinking within a simulated environment. Unlike Inquiry-Based Learning, which emphasizes student-driven questioning and exploration, GBL integrates game mechanics such as challenges, rewards, and feedback to motivate active participation and reinforce learning objectives. This method leverages game dynamics to create immersive experiences that enhance knowledge retention and skill development in various subject areas.
Core Principles of Inquiry-Based Learning
Inquiry-Based Learning centers on student-driven exploration where learners formulate questions, investigate solutions, and reflect on their findings to build deep understanding. Core principles include fostering curiosity, promoting critical thinking, and encouraging active engagement through hands-on experiences and problem-solving. This approach emphasizes learner autonomy and the iterative process of inquiry to develop skills vital for independent learning and real-world application.
Core Principles of Game-Based Learning
Game-Based Learning centers on immersive interactive experiences that leverage game mechanics such as challenges, rewards, and feedback loops to enhance motivation and engagement. Core principles include active participation, problem-solving within a safe environment, and immediate feedback to support knowledge retention and skill development. Unlike Inquiry-Based Learning, which emphasizes exploration and questioning, Game-Based Learning uses structured gameplay to drive learning outcomes through motivation and repetitive practice.
Key Differences Between Inquiry-Based and Game-Based Learning
Inquiry-Based Learning emphasizes critical thinking and problem-solving through questioning and investigation, fostering deep understanding by engaging students in real-world scenarios. Game-Based Learning leverages interactive games to motivate and enhance skill acquisition, focusing on immediate feedback and gamified progression to maintain student engagement. The key difference lies in Inquiry-Based Learning's focus on exploration and conceptual understanding versus Game-Based Learning's focus on motivation and skill mastery through gameplay mechanics.
Advantages of Inquiry-Based Learning
Inquiry-Based Learning fosters critical thinking and deep understanding by encouraging students to ask questions and explore concepts independently. It promotes active engagement and empowers learners to develop problem-solving skills through hands-on investigations. This approach also enhances retention of knowledge by connecting new information to prior experiences and real-world applications.
Advantages of Game-Based Learning
Game-Based Learning enhances student engagement by incorporating interactive and immersive experiences that stimulate motivation and sustained attention. The approach fosters critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and immediate feedback through gameplay mechanics, making complex concepts more accessible and memorable. Research shows that learners in Game-Based Learning environments demonstrate higher retention rates and improved collaborative skills compared to traditional Inquiry-Based Learning methods.
Challenges and Limitations of Both Approaches
Inquiry-Based Learning faces challenges such as requiring significant student motivation and critical thinking skills, which can hinder engagement and understanding if not adequately supported. Game-Based Learning may encounter limitations related to the design quality of educational games, where poorly developed games can distract from learning objectives and reduce effectiveness. Both approaches demand substantial time and resource investment from educators to implement effectively, often posing difficulties in diverse or resource-constrained classroom environments.
Choosing the Right Approach for Diverse Learners
Inquiry-Based Learning fosters critical thinking and problem-solving by encouraging students to explore questions and engage deeply with content, ideal for learners who thrive on curiosity and self-directed discovery. Game-Based Learning leverages interactive, immersive experiences that enhance motivation and retention, particularly effective for students who respond well to competition and immediate feedback. Selecting the right approach depends on understanding individual learner preferences, cognitive styles, and engagement levels to maximize educational outcomes across diverse classrooms.
Inquiry-Based Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com