Diagnostic assessment identifies students' current knowledge and skill levels to tailor instruction effectively. This evaluation helps instructors pinpoint learning gaps and adapt teaching strategies for better outcomes. Discover how diagnostic assessments can transform your educational approach by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
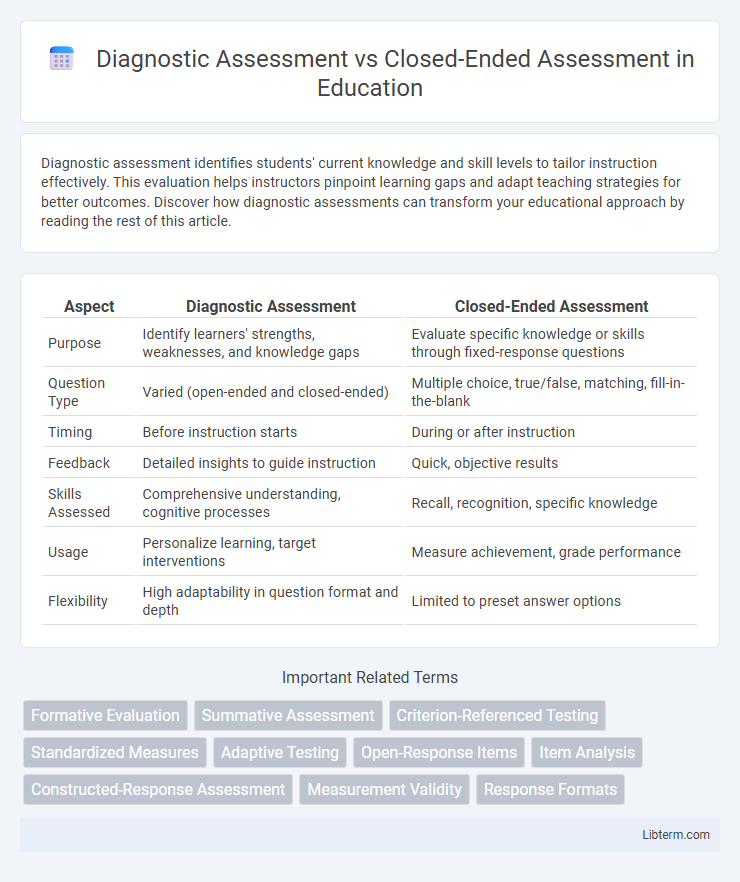
| Aspect | Diagnostic Assessment | Closed-Ended Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Identify learners' strengths, weaknesses, and knowledge gaps | Evaluate specific knowledge or skills through fixed-response questions |
| Question Type | Varied (open-ended and closed-ended) | Multiple choice, true/false, matching, fill-in-the-blank |
| Timing | Before instruction starts | During or after instruction |
| Feedback | Detailed insights to guide instruction | Quick, objective results |
| Skills Assessed | Comprehensive understanding, cognitive processes | Recall, recognition, specific knowledge |
| Usage | Personalize learning, target interventions | Measure achievement, grade performance |
| Flexibility | High adaptability in question format and depth | Limited to preset answer options |
Introduction to Assessment Types
Diagnostic assessment identifies students' existing knowledge and learning gaps through open-ended questions, enabling personalized instruction. Closed-ended assessments, such as multiple-choice or true/false tests, measure specific learned content efficiently and provide quantifiable results. Both assessment types play distinct roles in evaluating student understanding and guiding instructional strategies.
Defining Diagnostic Assessment
Diagnostic assessment is a formative evaluation method aimed at identifying students' pre-existing knowledge, skills, and learning gaps before instruction begins. It provides detailed insights into specific strengths and weaknesses, enabling tailored teaching strategies to address individual learner needs effectively. Unlike closed-ended assessments, which typically offer limited responses and focus on right or wrong answers, diagnostic assessments employ varied formats to uncover deeper understanding and misconceptions.
Understanding Closed-Ended Assessment
Closed-ended assessment involves questions with predetermined answers, such as multiple-choice or true/false formats, allowing for quick and objective evaluation of knowledge or skills. This type of assessment facilitates efficient data collection and scoring, making it ideal for standardized testing environments and large-scale evaluations. Its structured nature limits the depth of response but enhances reliability and ease of analysis compared to open-ended formats.
Key Differences Between Diagnostic and Closed-Ended Assessments
Diagnostic assessments identify students' existing knowledge gaps, skills, and learning needs through flexible, open-ended questions that allow detailed responses. Closed-ended assessments use predetermined answer choices like multiple-choice or true/false, focusing on quickly measuring specific knowledge or skill acquisition. The key difference lies in diagnostic assessments' emphasis on depth and individualized feedback, while closed-ended assessments prioritize efficiency and standardized scoring.
Purposes and Objectives of Diagnostic Assessment
Diagnostic assessment aims to identify students' existing knowledge, skills, and learning gaps to tailor instruction effectively and improve educational outcomes. It provides detailed insights into strengths and weaknesses, enabling targeted interventions and personalized learning plans. Unlike closed-ended assessments that primarily measure correct answers, diagnostic assessments uncover the root causes of errors to inform instructional strategies.
Uses and Applications of Closed-Ended Assessment
Closed-ended assessments are primarily used for measuring specific knowledge areas through objective questions such as multiple-choice, true/false, or matching items, enabling efficient scoring and data analysis. They are widely applied in standardized testing, certification exams, and classroom quizzes to quickly evaluate learner comprehension and retention. These assessments support large-scale testing environments by providing consistent, quantifiable results that facilitate comparison across different populations.
Advantages of Diagnostic Assessment
Diagnostic assessment provides detailed insights into a learner's strengths and weaknesses by identifying specific gaps in knowledge and skills. This targeted evaluation enables personalized instruction and intervention strategies, improving overall learning outcomes. Unlike closed-ended assessments, it facilitates a deeper understanding of student needs through qualitative data rather than solely quantitative scores.
Benefits of Closed-Ended Assessment
Closed-ended assessments provide clear, quantifiable results that simplify data analysis and comparison across large groups, enhancing consistency in evaluation. Their structured format minimizes subjective interpretation, making them ideal for standardized testing and large-scale benchmarking. Efficient scoring methods reduce time and resource expenditure, allowing educators to quickly identify knowledge gaps and track student progress.
Choosing the Right Assessment Method
Diagnostic assessment identifies learners' strengths and weaknesses through open-ended questions that allow detailed responses and insight into thought processes. Closed-ended assessments provide quick, objective data with standardized questions but may miss nuanced understanding. Choosing the right assessment method depends on whether in-depth diagnostic information or efficient, easily quantifiable results are the priority for instructional decision-making.
Conclusion: Selecting Effective Assessment Strategies
Choosing between diagnostic assessment and closed-ended assessment depends on the goal of gathering detailed insights versus measuring specific knowledge points. Diagnostic assessments provide comprehensive feedback on learners' strengths and weaknesses, enabling personalized instruction. Closed-ended assessments offer efficient, objective data ideal for benchmarking and standardized evaluation.
Diagnostic Assessment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com