An explicit curriculum clearly outlines the specific knowledge, skills, and objectives students are expected to learn within a course or grade level. It provides a structured framework that guides teachers in delivering content and assessing student progress effectively. Discover how an explicit curriculum can enhance Your educational experience by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
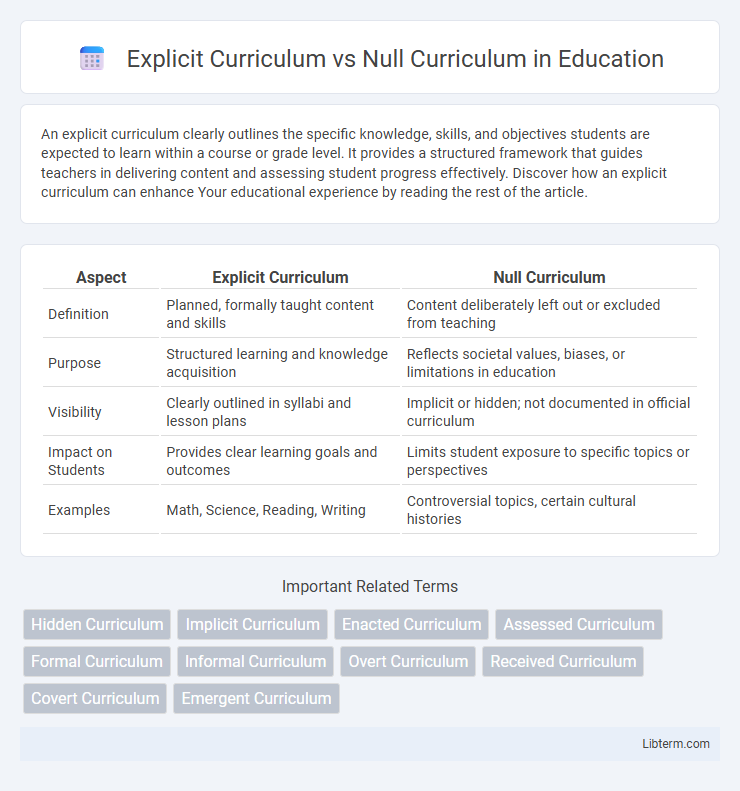
| Aspect | Explicit Curriculum | Null Curriculum |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Planned, formally taught content and skills | Content deliberately left out or excluded from teaching |
| Purpose | Structured learning and knowledge acquisition | Reflects societal values, biases, or limitations in education |
| Visibility | Clearly outlined in syllabi and lesson plans | Implicit or hidden; not documented in official curriculum |
| Impact on Students | Provides clear learning goals and outcomes | Limits student exposure to specific topics or perspectives |
| Examples | Math, Science, Reading, Writing | Controversial topics, certain cultural histories |
Introduction to Explicit and Null Curriculum
Explicit curriculum encompasses the formal, planned instructional content and learning objectives systematically delivered to students in educational settings. Null curriculum refers to the content and knowledge that educators deliberately exclude or omit from teaching, reflecting societal, cultural, or institutional priorities and constraints. Understanding the distinctions and implications of both explicit and null curricula is critical for comprehensive curriculum design and educational equity.
Defining Explicit Curriculum
Explicit curriculum refers to the formal, structured educational content and objectives intentionally designed and delivered by teachers, including lesson plans, textbooks, and assessments. It encompasses clearly defined learning goals and materials that guide classroom instruction and student achievement. Contrasting with the null curriculum, which consists of content intentionally or unintentionally omitted from instruction, the explicit curriculum represents the prioritized knowledge and skills deemed essential for student learning.
Understanding Null Curriculum
Null Curriculum refers to the content and skills intentionally or unintentionally omitted from a formal educational curriculum, often reflecting cultural values, societal norms, or institutional biases. Understanding Null Curriculum is crucial for educators and policymakers as it reveals hidden messages and gaps that affect student learning outcomes and equity. Addressing Null Curriculum helps create more inclusive, comprehensive educational experiences by ensuring marginalized perspectives and essential competencies are not excluded from instruction.
Historical Development of Curriculum Types
The explicit curriculum emerged as formal education systems evolved during the 19th century, emphasizing structured, codified knowledge and standardized learning objectives designed by educational authorities. In contrast, the null curriculum concept, identified by scholars like Philip Jackson in the 1960s, highlights the knowledge and skills intentionally omitted from official syllabi, reflecting sociopolitical values and power dynamics in educational decision-making. Understanding the historical development of these curriculum types reveals shifts in educational priorities, from rigid content transmission to critical examination of what knowledge is excluded and why.
Key Differences Between Explicit and Null Curriculum
Explicit curriculum consists of the formal, documented educational content and objectives that schools systematically teach, including lesson plans, textbooks, and assessments. Null curriculum refers to the topics and knowledge that educators intentionally or unintentionally exclude from instruction, which can influence students' understanding by omission. The key difference lies in explicit curriculum representing the planned and deliberate teaching agenda, whereas null curriculum highlights the absent or ignored content that shapes learning through what is left unsaid.
Impact of Explicit Curriculum in Education
The explicit curriculum, characterized by clearly defined learning objectives and structured content, significantly enhances student achievement by providing clear guidance and measurable goals. Its direct impact on education fosters consistency in teaching practices and ensures alignment with standardized assessments and educational standards. This targeted approach improves knowledge retention and skill acquisition, contributing to overall academic success and equity across diverse student populations.
Consequences of the Null Curriculum
The null curriculum, which comprises topics and skills deliberately left out or ignored in educational programs, can lead to significant gaps in student knowledge and critical thinking abilities. The absence of certain content may implicitly communicate societal values or biases, reinforcing stereotypes and perpetuating inequality. This omission undermines holistic education by limiting intellectual diversity and reducing students' preparedness for real-world challenges.
Examples of Explicit and Null Curriculum in Schools
Explicit curriculum in schools includes structured lessons such as math objectives, science experiments, and reading assignments that outline clear learning goals. Null curriculum refers to topics deliberately excluded, for instance, omitting discussions on controversial social issues or alternative historical perspectives. Examples of null curriculum often reveal cultural biases or societal values that influence what students do not learn.
Addressing Gaps Created by the Null Curriculum
Explicit curriculum defines the intended knowledge and skills formally taught to students, whereas the null curriculum represents what is omitted or ignored in educational content. Addressing gaps created by the null curriculum requires educators to identify overlooked topics or perspectives and intentionally integrate them into lesson plans to ensure a comprehensive learning experience. Incorporating these absent elements enhances equity, critical thinking, and diverse viewpoints essential for student development.
Future Trends in Curriculum Design
Future trends in curriculum design emphasize integrating explicit curriculum frameworks with adaptive strategies to address gaps revealed by the null curriculum, which includes unintentional omissions. Advances in artificial intelligence and data analytics facilitate personalized learning paths that expose critical but previously neglected content areas, enhancing knowledge equity. Educators increasingly prioritize transparency in curriculum objectives while incorporating interdisciplinary and culturally responsive elements to mitigate the limitations of the null curriculum.
Explicit Curriculum Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com