Peer review ensures the quality and credibility of scholarly work by having experts evaluate manuscripts for accuracy, originality, and relevance. This process helps identify errors, improve clarity, and validate research findings before publication. Discover how peer review enhances your understanding of academic standards by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
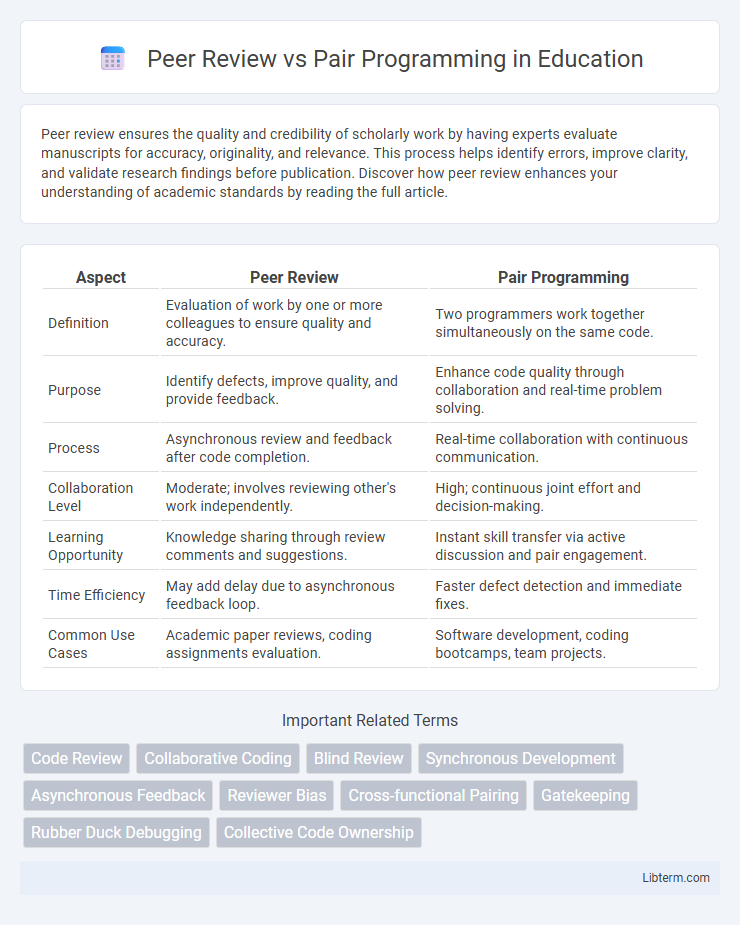
| Aspect | Peer Review | Pair Programming |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Evaluation of work by one or more colleagues to ensure quality and accuracy. | Two programmers work together simultaneously on the same code. |
| Purpose | Identify defects, improve quality, and provide feedback. | Enhance code quality through collaboration and real-time problem solving. |
| Process | Asynchronous review and feedback after code completion. | Real-time collaboration with continuous communication. |
| Collaboration Level | Moderate; involves reviewing other's work independently. | High; continuous joint effort and decision-making. |
| Learning Opportunity | Knowledge sharing through review comments and suggestions. | Instant skill transfer via active discussion and pair engagement. |
| Time Efficiency | May add delay due to asynchronous feedback loop. | Faster defect detection and immediate fixes. |
| Common Use Cases | Academic paper reviews, coding assignments evaluation. | Software development, coding bootcamps, team projects. |
Introduction to Peer Review and Pair Programming
Peer review involves systematically evaluating code by one or more developers who are not the original authors, enhancing code quality and knowledge sharing within a team. Pair programming is a collaborative approach where two developers work together at one workstation, continuously reviewing and writing code simultaneously to improve software design and reduce defects. Both practices emphasize real-time feedback and collaborative problem-solving to ensure higher code reliability and maintainability.
Core Principles of Peer Review
Peer review centers on systematic evaluation by colleagues to identify defects, ensure code quality, and enforce adherence to coding standards. It emphasizes thorough inspection, constructive feedback, and accountability to improve software reliability and maintainability. Core principles include clear documentation, iterative assessment, and collective ownership of the codebase, driving continuous improvement in development processes.
Key Concepts of Pair Programming
Pair programming involves two developers working collaboratively at one workstation, with one writing code (the driver) and the other reviewing each line in real-time (the navigator). This technique enhances code quality through continuous feedback, knowledge sharing, and immediate problem-solving, reducing errors early in the development process. Key concepts include role-switching, communication, and collective ownership of the codebase, fostering a deeply collaborative environment.
Similarities Between Peer Review and Pair Programming
Peer review and pair programming both emphasize collaborative code evaluation to improve software quality and reduce defects. Each method fosters real-time feedback and knowledge sharing between developers, enhancing team communication and collective code ownership. Both practices integrate continuous learning and cross-verification, ensuring adherence to coding standards and best practices.
Differences in Workflow and Collaboration
Peer review involves evaluating completed code independently before integration, emphasizing asynchronous feedback and quality assurance through detailed examination. Pair programming requires two developers working simultaneously on the same code in real-time, promoting continuous collaboration and immediate problem-solving. Workflow in peer review is sequential with distinct roles of author and reviewer, whereas pair programming relies on synchronous interaction with shared responsibility for coding tasks.
Benefits of Peer Review
Peer review enhances code quality by enabling multiple developers to identify bugs, improve logic, and ensure adherence to coding standards before integration. It facilitates knowledge sharing, allowing team members to learn best practices and reduce knowledge silos within the development team. This process leads to increased code maintainability and better collaboration, ultimately reducing technical debt and improving software reliability.
Advantages of Pair Programming
Pair programming enhances code quality through continuous real-time collaboration, reducing errors and improving knowledge sharing between developers. It accelerates problem-solving by combining diverse expertise and immediate feedback, which boosts productivity and fosters team cohesion. This method cultivates stronger communication skills and ensures code consistency, making it an effective practice in agile software development environments.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Peer review and pair programming both face common challenges such as communication gaps, time constraints, and inconsistent feedback quality. Effective solutions include establishing clear guidelines, fostering a collaborative culture, and integrating automated tools to ensure timely and objective evaluations. Emphasizing continuous training and open dialogue helps teams overcome these obstacles and improve code quality.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Team
Choosing the right approach between peer review and pair programming depends on your team's workflow, project complexity, and collaboration style. Peer review enhances code quality through asynchronous feedback, making it suitable for distributed teams and those needing thorough code audits. Pair programming fosters real-time collaboration and knowledge sharing, benefiting teams seeking immediate problem-solving and continuous learning during development.
Conclusion and Best Practices
Peer review enhances code quality by enabling thorough inspection and diverse feedback, while pair programming fosters real-time collaboration and immediate problem-solving. Integrating both practices maximizes software development efficiency by combining detailed analysis with continuous knowledge sharing. Best practices include scheduling regular peer reviews for critical code and pairing developers with complementary skills to optimize creativity and error detection.
Peer Review Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com