Intended curriculum outlines the educational goals, content, and learning outcomes that guide teaching strategies and assessment methods in schools. It serves as a blueprint ensuring that students acquire essential knowledge and skills aligned with academic standards. Explore the full article to understand how your intended curriculum shapes effective learning experiences.
Table of Comparison
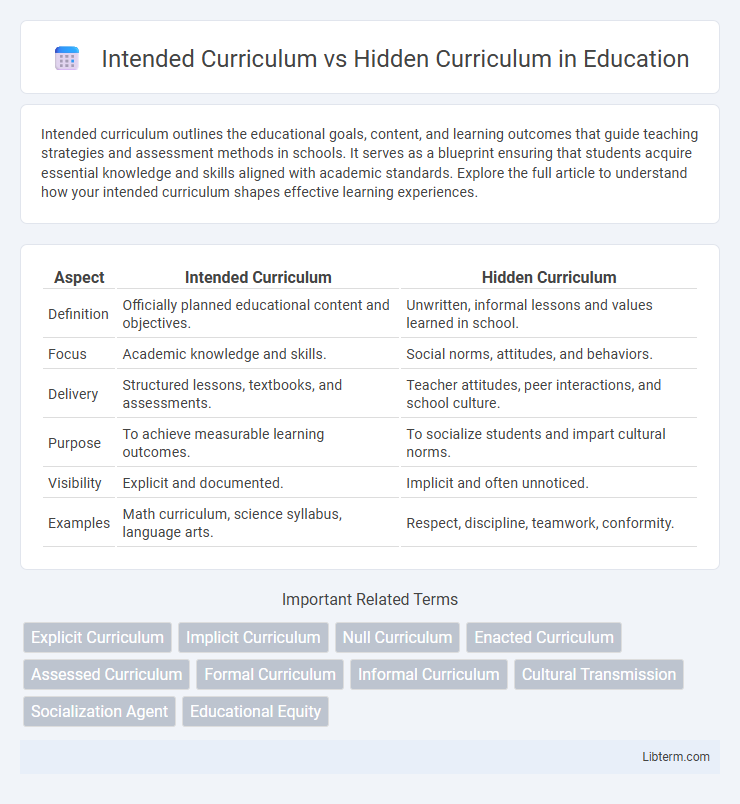
| Aspect | Intended Curriculum | Hidden Curriculum |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Officially planned educational content and objectives. | Unwritten, informal lessons and values learned in school. |
| Focus | Academic knowledge and skills. | Social norms, attitudes, and behaviors. |
| Delivery | Structured lessons, textbooks, and assessments. | Teacher attitudes, peer interactions, and school culture. |
| Purpose | To achieve measurable learning outcomes. | To socialize students and impart cultural norms. |
| Visibility | Explicit and documented. | Implicit and often unnoticed. |
| Examples | Math curriculum, science syllabus, language arts. | Respect, discipline, teamwork, conformity. |
Understanding the Intended Curriculum
The intended curriculum outlines the explicit educational goals, content, and learning outcomes designed by educators and policymakers to guide instruction and assessment. It focuses on the knowledge, skills, and competencies that students are expected to acquire through structured lesson plans and standardized materials. Understanding the intended curriculum is essential for aligning teaching strategies with educational standards and ensuring that learning objectives are systematically achieved.
Defining the Hidden Curriculum
The hidden curriculum encompasses the implicit lessons, values, and norms conveyed through the educational environment beyond the formal syllabus. It shapes student behavior, social interactions, and cultural expectations without explicit instruction, influencing attitudes and beliefs subconsciously. Understanding the hidden curriculum is crucial for educators aiming to address unintended biases and foster an inclusive learning atmosphere.
Key Differences: Intended vs Hidden Curriculum
The intended curriculum comprises explicit educational goals, lesson plans, and assessment criteria designed by educators to guide student learning outcomes. In contrast, the hidden curriculum refers to the implicit lessons, values, and norms conveyed through the school culture, teacher attitudes, and social interactions that are not formally documented. Key differences lie in the intended curriculum's explicit objectives and structured content versus the hidden curriculum's unspoken influence on student behavior and socialization.
Origins and Influences of Hidden Curriculum
The hidden curriculum originates from the implicit social norms, values, and expectations embedded within educational institutions that are not formally included in the intended curriculum. Influences of the hidden curriculum include teacher attitudes, peer interactions, school culture, and institutional policies, which collectively shape students' social behavior and reinforce societal inequalities. These unspoken lessons affect students' development of identity, conformity, and critical thinking beyond the explicit academic content.
Role of Teachers in Both Curriculums
Teachers play a pivotal role in delivering the intended curriculum by explicitly guiding students through prescribed academic content and learning objectives. In the hidden curriculum, educators influence social norms, values, and attitudes imparted implicitly through classroom interactions, discipline methods, and institutional culture. Their awareness and management of both curricula shape students' comprehensive educational experience and development.
Impact on Student Learning and Development
Intended curriculum outlines explicit educational goals and structured content designed to impart specific knowledge and skills, directly shaping student academic achievement. Hidden curriculum, consisting of implicit lessons conveyed through school culture, teacher attitudes, and peer interactions, profoundly influences socialization, values, and emotional development. The dynamic interplay between intended and hidden curricula significantly affects holistic student learning outcomes and identity formation.
Hidden Curriculum in School Culture and Environment
Hidden curriculum in school culture and environment includes the unspoken norms, values, and expectations that influence student behavior and socialization. These implicit lessons shape attitudes towards authority, peer relationships, and cultural identity, often reinforcing societal hierarchies and power dynamics. Understanding the hidden curriculum reveals how school environments contribute to shaping students beyond the formal academic content intended curriculum covers.
Addressing Bias within the Hidden Curriculum
The hidden curriculum often perpetuates implicit biases through unspoken norms and teacher behaviors, influencing students' attitudes and beliefs beyond the intended curriculum's formal content. Addressing bias within the hidden curriculum requires intentional reflection, equity-focused teacher training, and creating inclusive classroom environments that challenge stereotypes and promote diverse perspectives. Systematic evaluation of school culture and policies is essential to uncover and mitigate these underlying biases, ensuring education fosters critical thinking and social justice.
Strategies to Align Hidden and Intended Curriculums
Aligning hidden and intended curricula requires embedding core values and learning objectives into everyday classroom interactions and institutional culture. Strategies include professional development for educators to recognize and intentionally address implicit messages, alongside reflective practices that evaluate and adjust teaching methods to reinforce explicit curriculum goals. Establishing collaborative environments where student feedback shapes both visible and invisible learning experiences ensures consistency between intended outcomes and lived educational realities.
Implications for Educational Policy and Practice
Intended curriculum outlines official learning objectives and content defined by educational authorities, while hidden curriculum encompasses implicit values, behaviors, and social norms transmitted informally within school environments. Educational policy must address both curricula to ensure equitable learning outcomes, as hidden curriculum can reinforce social inequalities and cultural biases if left unexamined. Integrating teacher training on awareness of hidden curriculum and creating inclusive policies enhances holistic student development and fosters a more just educational system.
Intended Curriculum Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com