Response to Intervention (RTI) is a multi-tiered approach designed to identify and support students struggling with learning and behavior through early intervention. It emphasizes data-driven decision-making and targeted instruction to improve student outcomes efficiently. Explore the rest of the article to understand how RTI can transform your educational strategies.
Table of Comparison
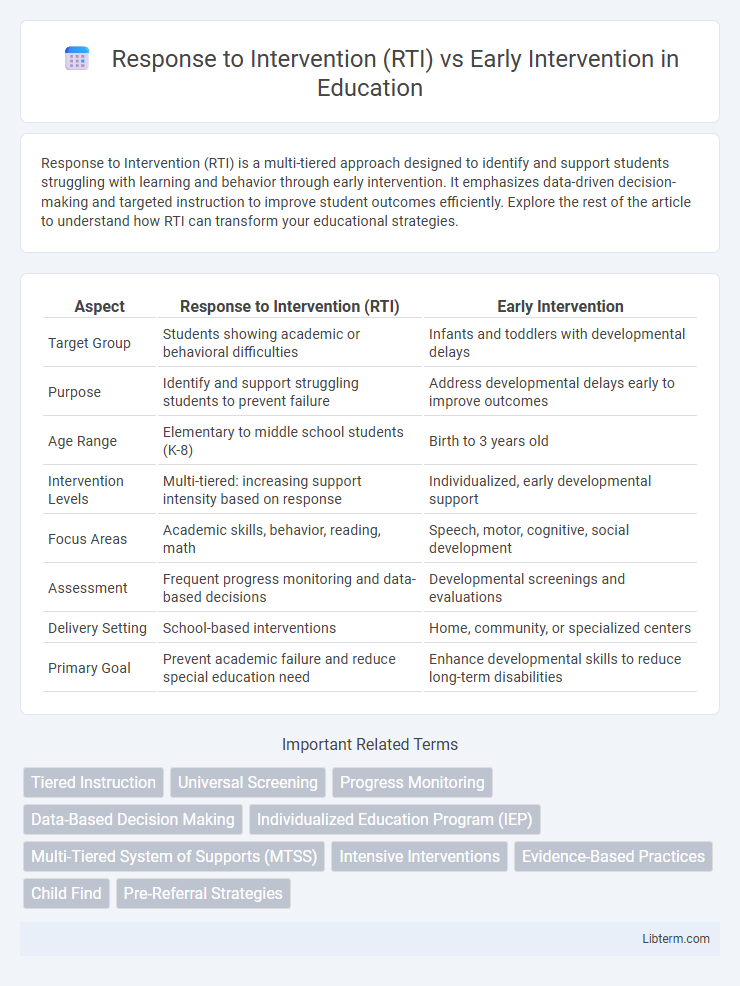
| Aspect | Response to Intervention (RTI) | Early Intervention |
|---|---|---|
| Target Group | Students showing academic or behavioral difficulties | Infants and toddlers with developmental delays |
| Purpose | Identify and support struggling students to prevent failure | Address developmental delays early to improve outcomes |
| Age Range | Elementary to middle school students (K-8) | Birth to 3 years old |
| Intervention Levels | Multi-tiered: increasing support intensity based on response | Individualized, early developmental support |
| Focus Areas | Academic skills, behavior, reading, math | Speech, motor, cognitive, social development |
| Assessment | Frequent progress monitoring and data-based decisions | Developmental screenings and evaluations |
| Delivery Setting | School-based interventions | Home, community, or specialized centers |
| Primary Goal | Prevent academic failure and reduce special education need | Enhance developmental skills to reduce long-term disabilities |
Introduction to RTI and Early Intervention
Response to Intervention (RTI) is a multi-tiered approach that identifies struggling students early and provides targeted teaching strategies to improve learning outcomes. Early Intervention focuses on addressing developmental delays and disabilities in children from birth to age five to facilitate optimal growth and reduce future challenges. Both RTI and Early Intervention prioritize timely support but differ in their application settings and target age groups, emphasizing prevention and individualized instruction.
Defining Response to Intervention (RTI)
Response to Intervention (RTI) is a multi-tiered approach designed to identify and support students with learning and behavioral challenges through increasingly intensive levels of intervention. RTI emphasizes frequent progress monitoring and data-based decision making to tailor instruction to individual student needs. This framework contrasts with Early Intervention, which generally targets younger children with developmental delays prior to formal schooling.
Understanding Early Intervention Services
Early Intervention services provide specialized support to infants and toddlers with developmental delays or disabilities, focusing on family-centered approaches to promote optimal child development during critical early years. Response to Intervention (RTI) is a tiered framework primarily used in school settings to identify and support students struggling academically or behaviorally through increasingly intensive interventions. Understanding Early Intervention services highlights the importance of timely, individualized supports designed to address developmental concerns before children enter formal education systems.
Key Objectives of RTI vs Early Intervention
Response to Intervention (RTI) focuses on providing targeted instruction and interventions based on students' academic performance to prevent learning difficulties, emphasizing progress monitoring and data-driven decision-making. Early Intervention aims to identify and support infants and young children with developmental delays or disabilities as early as possible, promoting optimal development across cognitive, social, and physical domains. Key objectives of RTI include reducing special education referrals through tiered support, while Early Intervention prioritizes early detection and enhancing developmental outcomes before school entry.
Target Populations: Who Benefits?
Response to Intervention (RTI) primarily benefits students exhibiting early signs of academic struggles by providing tiered support based on their specific learning needs within the general education setting. Early Intervention serves infants and toddlers with developmental delays or disabilities, focusing on enhancing developmental skills before they enter formal schooling. Both approaches target distinct age groups and needs, with RTI addressing emerging academic challenges in school-aged children while Early Intervention focuses on developmental support during critical early years.
Differences in Assessment and Eligibility
Response to Intervention (RTI) utilizes a tiered assessment process that involves ongoing progress monitoring and data collection to identify students struggling academically and determine responsiveness to interventions. Early Intervention focuses on screening and comprehensive developmental evaluations to diagnose eligibility for services in infants and toddlers with developmental delays or disabilities. Unlike RTI's dynamic adjustment based on student performance data within general education, Early Intervention eligibility relies on standardized developmental assessments and medical diagnostic criteria.
Implementation Strategies for RTI
Response to Intervention (RTI) focuses on a multi-tiered approach to identify and support struggling students through systematic progress monitoring and data-driven decision-making. Implementation strategies for RTI emphasize universal screening, targeted small-group instruction, and ongoing assessment to adjust interventions efficiently. Effective RTI frameworks rely on teacher collaboration, professional development, and fidelity of intervention delivery to improve student outcomes.
Core Components of Effective Early Intervention
Effective Early Intervention centers on individualized assessment, targeted instruction, and family involvement to address developmental delays promptly. Core components include comprehensive screening, evidence-based teaching strategies, and consistent progress monitoring to tailor support. Unlike RTI, which primarily targets academic difficulties through a tiered approach, Early Intervention emphasizes holistic developmental support across multiple domains from infancy through early childhood.
Comparing Outcomes: RTI vs Early Intervention
Response to Intervention (RTI) focuses on providing tiered, data-driven support within the general education setting to identify and address learning difficulties early, often improving academic outcomes by targeting interventions based on student progress monitoring. Early Intervention targets developmental delays in children typically from birth to age three, emphasizing family-centered services that enhance cognitive, motor, and communication skills, leading to better long-term developmental outcomes. Comparative studies show RTI improves reading and math proficiency in school-aged children, while Early Intervention significantly enhances overall developmental milestones and reduces the need for special education services later in life.
Conclusion: Selecting the Best Approach
Choosing between Response to Intervention (RTI) and Early Intervention depends on the specific needs and developmental stage of the child. RTI offers a structured multi-tiered framework ideal for identifying and supporting students struggling academically within the school environment, while Early Intervention targets younger children, emphasizing developmental milestones and prevention. The best approach aligns with the child's age, risk factors, and the context of their learning challenges to ensure timely and effective support.
Response to Intervention (RTI) Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com