Self-contained classrooms provide a focused learning environment where students with similar needs receive specialized instruction tailored to their abilities. This approach enhances individualized support, helping Your child develop core skills more effectively within a consistent setting. Discover how self-contained classrooms can benefit diverse learners in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
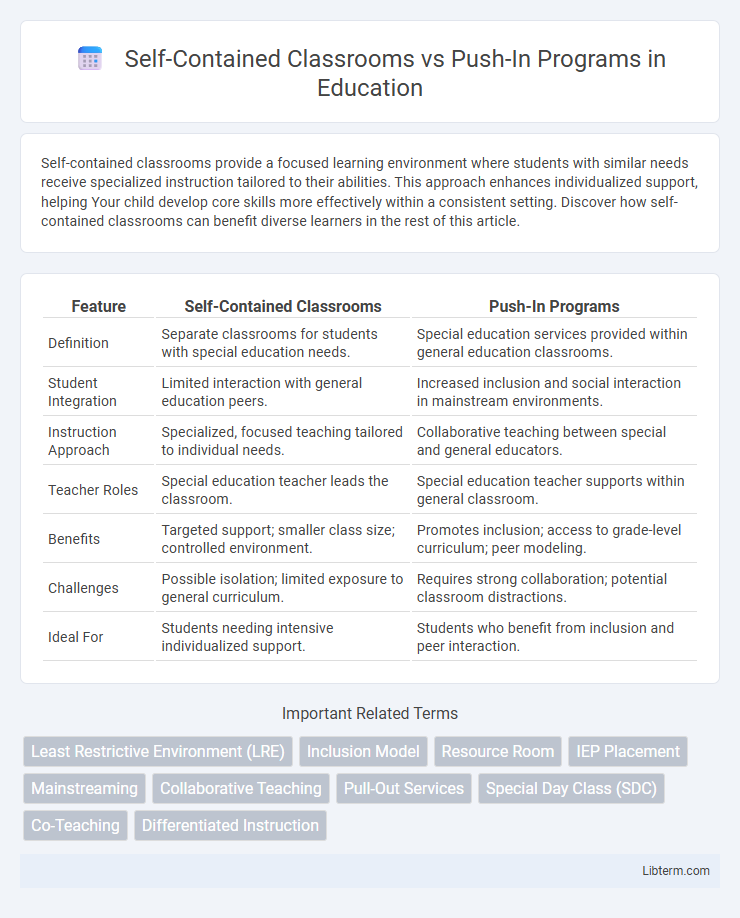
| Feature | Self-Contained Classrooms | Push-In Programs |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Separate classrooms for students with special education needs. | Special education services provided within general education classrooms. |
| Student Integration | Limited interaction with general education peers. | Increased inclusion and social interaction in mainstream environments. |
| Instruction Approach | Specialized, focused teaching tailored to individual needs. | Collaborative teaching between special and general educators. |
| Teacher Roles | Special education teacher leads the classroom. | Special education teacher supports within general classroom. |
| Benefits | Targeted support; smaller class size; controlled environment. | Promotes inclusion; access to grade-level curriculum; peer modeling. |
| Challenges | Possible isolation; limited exposure to general curriculum. | Requires strong collaboration; potential classroom distractions. |
| Ideal For | Students needing intensive individualized support. | Students who benefit from inclusion and peer interaction. |
Understanding Self-Contained Classrooms
Self-contained classrooms provide specialized instruction within a separate, dedicated environment for students with disabilities, allowing tailored teaching methods and focused support. These classrooms typically have fewer students and a higher teacher-to-student ratio, promoting individualized learning plans and consistent monitoring of academic progress. This approach prioritizes creating a structured setting that meets specific educational and behavioral needs without the distractions of a mainstream classroom.
What Are Push-In Programs?
Push-in programs involve specialized educators providing targeted support within the general education classroom, promoting inclusion and collaboration. Students receive individualized assistance without being separated from their peers, enhancing social interaction and academic engagement. This model allows for differentiated instruction while maintaining a unified learning environment.
Key Differences Between the Two Approaches
Self-contained classrooms provide specialized instruction within a separate setting, catering to students with significant disabilities by focusing on individualized curricula and intensive support services. Push-in programs integrate support personnel directly into general education classrooms, promoting inclusion by enabling students with disabilities to participate alongside their peers with assistance tailored to their needs. The key difference lies in the environment and degree of inclusion, with self-contained classrooms offering a more segregated approach and push-in programs emphasizing inclusive education within the general classroom.
Benefits of Self-Contained Classrooms
Self-contained classrooms provide specialized instruction tailored to students with significant disabilities, allowing for a focused and consistent learning environment that meets individual educational goals. These classrooms facilitate stronger teacher-student relationships and provide reduced distractions, which can enhance concentration and skill acquisition. Enhanced access to adapted materials and therapies within self-contained settings supports academic, social, and behavioral development more effectively than push-in programs.
Advantages of Push-In Programs
Push-in programs enhance inclusive education by allowing students with special needs to learn alongside their peers in general education classrooms, promoting social interaction and reducing stigma. They offer access to a broader curriculum and real-time support from specialized educators without removing students from the mainstream environment. This model fosters collaboration between general and special education teachers, improving individualized support and academic outcomes.
Challenges of Self-Contained Classrooms
Self-contained classrooms often face challenges such as limited social interaction for students with disabilities, reducing opportunities for peer modeling and inclusive experiences. These classrooms can also struggle with resource allocation, as specialized staff and materials may be insufficient to address diverse individual needs effectively. Additionally, the separation from general education settings may hinder the development of critical communication and social skills essential for broader academic and life success.
Limitations of Push-In Programs
Push-in programs often face limitations such as insufficient individualized attention due to the presence of students with diverse needs in a general education setting. Teachers may struggle to effectively balance curriculum demands while providing targeted support, leading to potential gaps in meeting specific individualized education program (IEP) goals. Furthermore, resource constraints and limited special education training can hinder seamless collaboration between special education and general education staff, reducing the overall effectiveness of push-in services.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Model
When choosing between self-contained classrooms and push-in programs, factors such as student needs, teacher expertise, and classroom dynamics are crucial. Self-contained classrooms often benefit students requiring intensive support and individualized instruction, while push-in programs promote inclusive education and social integration by having special educators collaborate within general education settings. Evaluating resource availability, desired educational outcomes, and the student's social-emotional development ensures the selected model aligns with both academic goals and well-being.
Impact on Student Outcomes and Inclusion
Self-contained classrooms provide targeted instruction tailored to students with significant learning needs, often resulting in improved academic outcomes for those requiring intensive support. Push-in programs promote inclusion by integrating special education services within general education settings, fostering social interaction and peer modeling, which positively influences both academic engagement and social development. Research indicates that balanced implementation of push-in programs can enhance inclusion without compromising individualized support, thereby improving overall student outcomes.
Best Practices for Successful Implementation
Effective implementation of self-contained classrooms and push-in programs requires clear communication and collaboration between general and special education teachers to align instructional strategies with student needs. Flexible scheduling and ongoing professional development foster an inclusive environment that supports diverse learning styles and behavioral goals. Data-driven decision-making and continuous progress monitoring ensure interventions are tailored, maximizing student engagement and academic outcomes.
Self-Contained Classrooms Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com