Direct Instruction in science accelerates student understanding by using clear, explicit teaching methods that break down complex concepts into manageable steps. This approach emphasizes structured lessons, active student participation, and continuous assessment to ensure mastery of scientific principles and skills. Discover how Direct Instruction can transform Your science learning experience in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
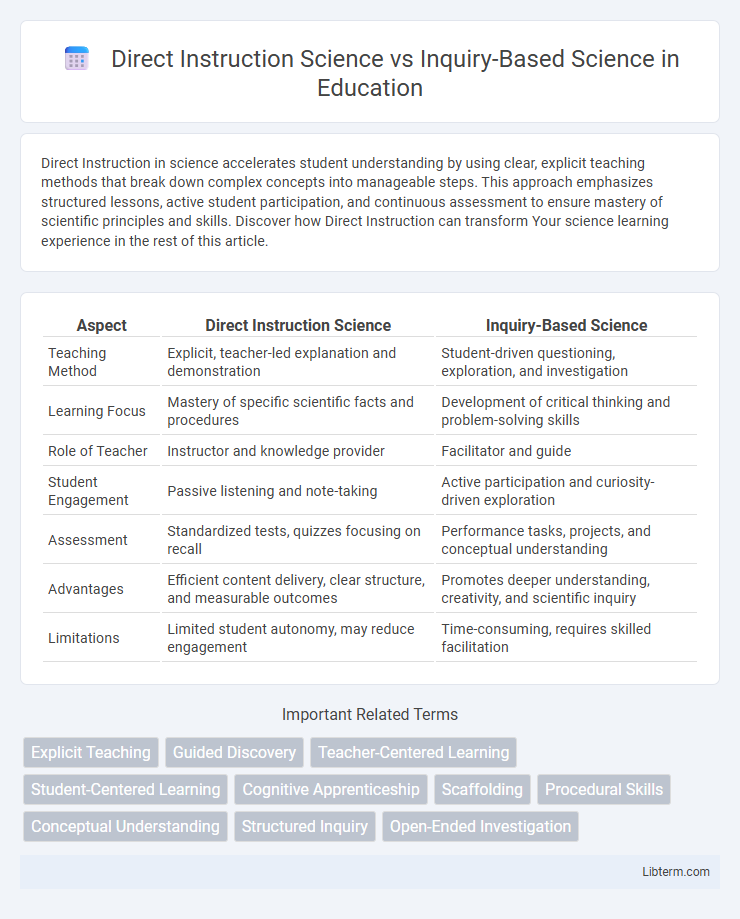
| Aspect | Direct Instruction Science | Inquiry-Based Science |
|---|---|---|
| Teaching Method | Explicit, teacher-led explanation and demonstration | Student-driven questioning, exploration, and investigation |
| Learning Focus | Mastery of specific scientific facts and procedures | Development of critical thinking and problem-solving skills |
| Role of Teacher | Instructor and knowledge provider | Facilitator and guide |
| Student Engagement | Passive listening and note-taking | Active participation and curiosity-driven exploration |
| Assessment | Standardized tests, quizzes focusing on recall | Performance tasks, projects, and conceptual understanding |
| Advantages | Efficient content delivery, clear structure, and measurable outcomes | Promotes deeper understanding, creativity, and scientific inquiry |
| Limitations | Limited student autonomy, may reduce engagement | Time-consuming, requires skilled facilitation |
Understanding Direct Instruction in Science
Direct Instruction in Science emphasizes structured, teacher-led lessons that focus on clear, specific learning objectives and explicit teaching of scientific concepts and procedures. This method prioritizes step-by-step guidance, frequent assessment, and immediate feedback to ensure student comprehension and mastery of foundational knowledge. Research shows that Direct Instruction enhances content retention and provides a solid base for students to later engage in inquiry-based learning.
Exploring Inquiry-Based Science Approaches
Inquiry-based science approaches emphasize student-led exploration, promoting critical thinking and problem-solving by encouraging learners to ask questions, investigate phenomena, and develop hypotheses. This method contrasts with Direct Instruction Science, which relies on structured, teacher-centered delivery of content and procedures. Implementing inquiry-based techniques fosters deeper conceptual understanding and engagement by allowing students to actively construct knowledge through hands-on experiments and collaborative discovery.
Core Differences Between Direct and Inquiry Science Methods
Direct Instruction Science emphasizes structured, teacher-led lessons with clear objectives and step-by-step guidance, fostering factual knowledge and procedural skills. Inquiry-Based Science encourages student-driven exploration, promoting critical thinking and hypothesis testing through hands-on experiments and open-ended questioning. Core differences lie in the degree of teacher control and the learning process, with Direct Instruction prioritizing explicit teaching and Inquiry-Based methods focusing on discovery and investigative learning.
Advantages of Direct Instruction in Science Classrooms
Direct Instruction in science classrooms offers precise, structured content delivery, ensuring students acquire core scientific concepts efficiently and consistently. This method promotes mastery through repetition and clear examples, reducing misconceptions and cognitive overload. Teachers can effectively assess understanding and provide targeted feedback, fostering higher achievement in standardized science assessments.
Benefits of Inquiry-Based Science Learning
Inquiry-Based Science Learning promotes critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and deep understanding by encouraging students to explore scientific concepts through hands-on experiments and questioning. This approach fosters curiosity and creativity, making science relevant and engaging while supporting long-term retention of knowledge. Research shows that students in inquiry-based settings demonstrate higher motivation and improved application of scientific principles in real-world contexts compared to Direct Instruction methods.
Challenges of Direct Instruction in Science Education
Direct Instruction in science education often faces challenges such as limited student engagement and reduced opportunities for critical thinking and problem-solving, which are essential for deep understanding of scientific concepts. This approach may restrict hands-on experiments and inquiry processes that promote active learning and curiosity. Educators must balance structured guidance with fostering exploration to effectively develop scientific literacy and reasoning skills.
Limitations of Inquiry-Based Science Approaches
Inquiry-Based Science approaches often face limitations such as insufficient scaffolding which can lead to student confusion and misconceptions. The reliance on student-led exploration may result in uneven coverage of essential scientific concepts and reduced acquisition of foundational knowledge. Time-intensive processes and difficulty in assessing individual contributions also hinder the effective implementation of Inquiry-Based Science in standardized educational settings.
Impact on Student Engagement and Motivation
Direct Instruction Science delivers structured lessons with clear objectives, enhancing student engagement through predictable routines and immediate feedback, which builds confidence and motivation. Inquiry-Based Science encourages active exploration and critical thinking, fostering intrinsic motivation by allowing students to pose questions and discover concepts independently. Research indicates that combining direct instruction's clarity with inquiry's autonomy can optimize engagement and sustain motivation across diverse learners.
Effectiveness in Promoting Scientific Thinking
Direct Instruction Science emphasizes structured, teacher-led lessons that deliver clear explanations and step-by-step guidance, which can enhance foundational knowledge and procedural skills. Inquiry-Based Science encourages students to explore, ask questions, and engage in hands-on experiments, fostering critical thinking, curiosity, and deeper understanding of scientific concepts. Research indicates that combining both methods often leads to the most effective promotion of scientific thinking by balancing knowledge acquisition with active exploration.
Choosing the Right Approach: Direct vs Inquiry-Based Science
Choosing the right approach between Direct Instruction Science and Inquiry-Based Science depends on educational goals and student needs. Direct Instruction Science emphasizes structured lessons, clear objectives, and step-by-step guidance to ensure mastery of foundational knowledge and skills. Inquiry-Based Science fosters critical thinking and exploration by encouraging students to ask questions, investigate phenomena, and construct their own understanding through hands-on experiments and collaborative learning.
Direct Instruction Science Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com