Phantom curriculum refers to the unwritten, unofficial lessons and values that students absorb in school environments beyond the standard syllabus. This hidden educational layer shapes attitudes, social norms, and behaviors without formal instruction, significantly impacting student development. Explore the rest of the article to understand how the phantom curriculum influences your learning experience and educational outcomes.
Table of Comparison
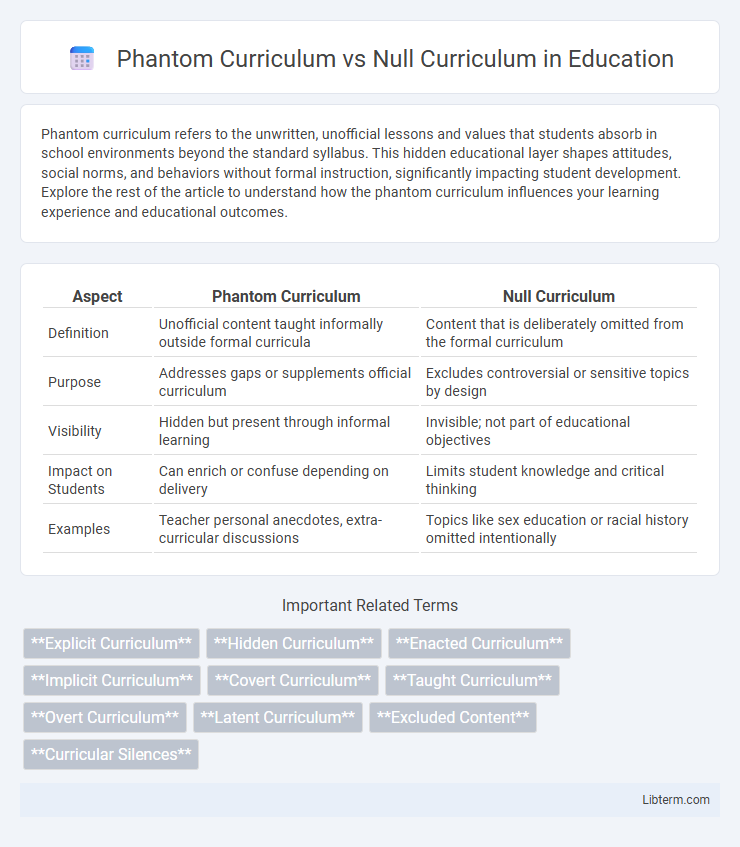
| Aspect | Phantom Curriculum | Null Curriculum |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unofficial content taught informally outside formal curricula | Content that is deliberately omitted from the formal curriculum |
| Purpose | Addresses gaps or supplements official curriculum | Excludes controversial or sensitive topics by design |
| Visibility | Hidden but present through informal learning | Invisible; not part of educational objectives |
| Impact on Students | Can enrich or confuse depending on delivery | Limits student knowledge and critical thinking |
| Examples | Teacher personal anecdotes, extra-curricular discussions | Topics like sex education or racial history omitted intentionally |
Understanding Phantom Curriculum: An Overview
Phantom Curriculum refers to the implicit, unofficial lessons students learn that are not included in formal syllabi, such as social norms and institutional values, which influence behavior and attitudes within educational environments. In contrast, Null Curriculum represents content deliberately excluded from the official curriculum, highlighting societal or political choices about what is deemed unimportant or inappropriate for instruction. Understanding Phantom Curriculum emphasizes uncovering these hidden lessons to better address their impact on student development and educational equity.
Defining the Null Curriculum in Education
The null curriculum in education refers to the content and topics intentionally or unintentionally omitted from the formal curriculum, shaping what students do not learn. Unlike the phantom curriculum, which represents implicit lessons conveyed indirectly, the null curriculum highlights critical knowledge gaps that influence students' educational experiences and societal understanding. Understanding the null curriculum helps educators recognize biases and address neglected areas to create a more comprehensive and inclusive learning environment.
Key Differences Between Phantom and Null Curricula
Phantom Curriculum refers to the unofficial, hidden lessons students learn through school culture or teacher behaviors, while Null Curriculum denotes content deliberately omitted from the formal syllabus. Key differences include the Phantom Curriculum's indirect impact on student values and attitudes versus the Null Curriculum's intentional exclusion shaping what students do not learn. Understanding these distinctions highlights how implicit messages and selective content both influence educational outcomes and student development.
The Hidden Messages of Phantom Curriculum
Phantom Curriculum conveys implicit messages and values that students absorb through what is emphasized or neglected in teaching, shaping attitudes beyond formal lessons. It differs from the Null Curriculum, which involves content deliberately left out of the educational experience, signaling what is deemed unimportant or inappropriate. Understanding Phantom Curriculum reveals how unseen biases and institutional priorities influence student perceptions and learning outcomes.
What’s Left Out: The Impact of Null Curriculum
The Null Curriculum refers to the content intentionally or unintentionally omitted from educational programs, shaping students' knowledge by what is left untaught. Its impact can reinforce cultural biases, limit critical thinking, and perpetuate systemic inequities by excluding diverse perspectives and essential skills. Understanding the Null Curriculum highlights the importance of critically examining not only what is included but also what is excluded to foster a more inclusive and comprehensive education.
Examples of Phantom Curriculum in the Classroom
Phantom Curriculum in the classroom emerges when teachers unintentionally convey biases or stereotypes through subtle cues such as preferential treatment or exclusion during group activities. For example, a teacher might consistently call on male students more often than female students, reinforcing gender disparities. Another instance is when cultural holidays or perspectives are overlooked, implicitly sending a message that certain backgrounds are less valued, which contrasts with the explicit content of the official curriculum.
Real-World Consequences of Null Curriculum Choices
Null Curriculum choices, which represent what is deliberately excluded from educational programs, can have significant real-world consequences by limiting students' exposure to critical knowledge, skills, and perspectives necessary for informed citizenship and career readiness. When important topics such as climate change, social justice, or digital literacy are omitted, learners may develop gaps in understanding that affect their ability to navigate complex societal issues and participate fully in democratic processes. This contrasts with the Phantom Curriculum, which consists of implicit messages and values conveyed through hidden or unintended curriculum elements, impacting student attitudes and beliefs without explicit instruction.
Addressing Bias: Inclusion and Exclusion in Curricula
Phantom Curriculum refers to the hidden biases embedded in educational content that subtly reinforce exclusionary narratives, while Null Curriculum highlights the topics purposefully omitted, leading to marginalization of certain groups or perspectives. Addressing bias requires an intentional inclusion of diverse voices and subjects, ensuring curricula represent varied cultural, social, and historical experiences to foster equity. Strategies include critical curriculum review, inclusive content development, and active engagement with underrepresented communities to dismantle systemic exclusion in education.
Strategies for Educators: Recognizing Unseen Curricula
Educators can implement reflective practices and curriculum audits to identify Phantom and Null Curricula by examining content gaps and implicit messages students receive. Using qualitative methods like student feedback and classroom observations helps uncover hidden knowledge exclusions affecting learner outcomes. Strategically addressing these unseen curricula ensures comprehensive educational equity and promotes inclusive learning environments.
Building Awareness: Towards a More Comprehensive Curriculum
Phantom Curriculum refers to the implicit lessons students learn indirectly through school culture and hidden messages, while Null Curriculum encompasses topics that are deliberately excluded from the formal syllabus. Building awareness of these curricula encourages educators to create more comprehensive learning environments by identifying and addressing gaps between official content and student experiences. Emphasizing inclusivity and transparency enhances curriculum design, fostering well-rounded knowledge acquisition beyond traditional boundaries.
Phantom Curriculum Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com