Social sciences explore human behavior, societies, and social relationships through disciplines like sociology, anthropology, and political science. This field combines qualitative and quantitative methods to analyze cultural, economic, and psychological factors shaping communities. Discover how understanding social sciences can enrich your perspective by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
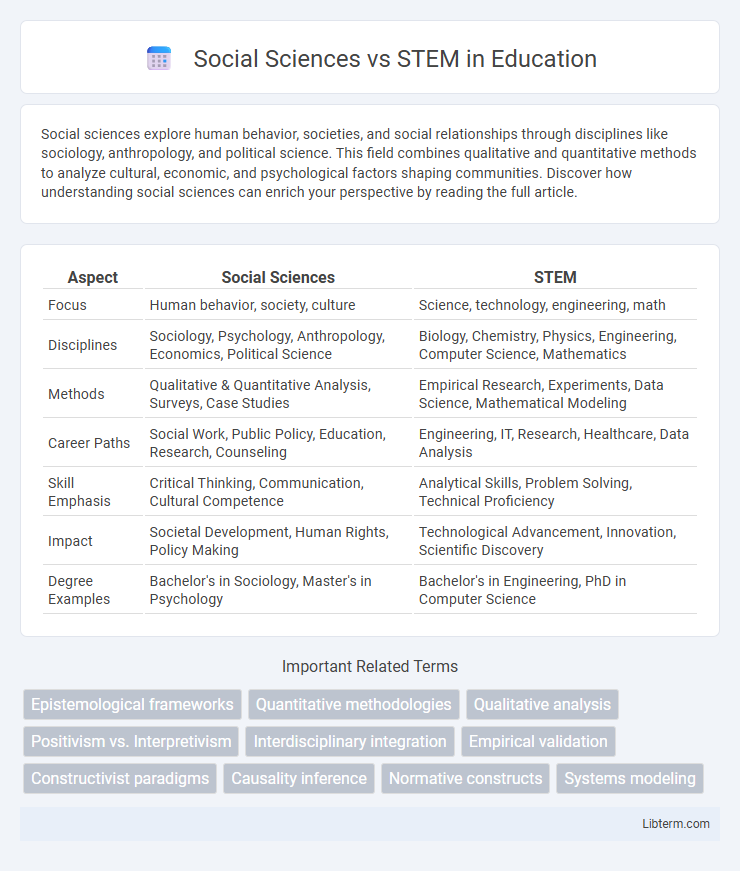
| Aspect | Social Sciences | STEM |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Human behavior, society, culture | Science, technology, engineering, math |
| Disciplines | Sociology, Psychology, Anthropology, Economics, Political Science | Biology, Chemistry, Physics, Engineering, Computer Science, Mathematics |
| Methods | Qualitative & Quantitative Analysis, Surveys, Case Studies | Empirical Research, Experiments, Data Science, Mathematical Modeling |
| Career Paths | Social Work, Public Policy, Education, Research, Counseling | Engineering, IT, Research, Healthcare, Data Analysis |
| Skill Emphasis | Critical Thinking, Communication, Cultural Competence | Analytical Skills, Problem Solving, Technical Proficiency |
| Impact | Societal Development, Human Rights, Policy Making | Technological Advancement, Innovation, Scientific Discovery |
| Degree Examples | Bachelor's in Sociology, Master's in Psychology | Bachelor's in Engineering, PhD in Computer Science |
Understanding Social Sciences and STEM
Social Sciences encompass disciplines like sociology, psychology, and anthropology that study human behavior, societies, and social relationships through qualitative and quantitative research methods. STEM fields--science, technology, engineering, and mathematics--focus on empirical, data-driven approaches to solving technical and scientific problems using logic, experimentation, and mathematical modeling. Understanding both Social Sciences and STEM provides a comprehensive perspective, combining insights into human behavior with technological innovation and analytical precision.
Core Differences in Methodologies
Social Sciences rely primarily on qualitative methods such as ethnography, case studies, and surveys to explore human behavior and societal patterns, emphasizing context and interpretation. STEM fields prioritize quantitative methodologies including experiments, mathematical modeling, and statistical analysis to produce reproducible and measurable results. The core difference lies in Social Sciences' focus on subjectivity and complexity versus STEM's emphasis on objectivity and empirical validation.
Key Areas of Study in Each Field
Social Sciences primarily explore human behavior, societies, and cultural dynamics, with key areas including psychology, sociology, anthropology, economics, and political science. STEM fields concentrate on science, technology, engineering, and mathematics, emphasizing subjects such as biology, chemistry, physics, computer science, and engineering disciplines. Both domains utilize distinct methodologies tailored to their focus, with Social Sciences often employing qualitative and quantitative research, while STEM prioritizes empirical, experimental, and computational techniques.
Career Opportunities: Social Sciences vs STEM
Career opportunities in STEM fields such as engineering, computer science, and biotechnology typically offer higher starting salaries and strong job market growth driven by technological innovation and digital transformation. Social sciences careers, including psychology, sociology, and economics, provide diverse paths in education, government, and non-profits but often exhibit slower salary growth and more competitive job markets. STEM roles consistently show high demand in sectors like healthcare, finance, and information technology, whereas social science graduates benefit from roles emphasizing critical thinking, communication, and policy development.
Skills Developed in Social Sciences and STEM
Social Sciences cultivate critical thinking, qualitative analysis, and strong communication skills through the study of human behavior and society, fostering empathy and ethical reasoning. STEM disciplines develop quantitative reasoning, problem-solving abilities, and technical proficiency in fields like engineering, computer science, and mathematics, emphasizing data-driven solutions. Both areas enhance research capabilities and adaptability, preparing students for diverse professional challenges.
Impact on Society: Comparing Contributions
Social Sciences analyze human behavior, social systems, and cultural dynamics to inform policies that improve education, healthcare, and governance, directly shaping societal well-being. STEM fields drive technological innovation, scientific discoveries, and infrastructure development, fostering economic growth and enhancing quality of life through advancements like renewable energy and medical technologies. Both domains contribute significantly to societal progress by addressing distinct but complementary challenges in human development and environmental sustainability.
The Interdisciplinary Connection
The interdisciplinary connection between social sciences and STEM fields fosters innovative problem-solving by integrating qualitative insights with quantitative methods. Social sciences contribute critical understanding of human behavior and societal impacts, enriching STEM disciplines like data science, artificial intelligence, and environmental studies. Collaborative research across these domains drives advancements in technology while addressing ethical, cultural, and social dimensions essential for sustainable development.
Common Misconceptions and Stereotypes
Social Sciences are often mistakenly perceived as less rigorous or less valuable than STEM fields, despite their critical role in understanding human behavior, society, and cultural dynamics. STEM disciplines are frequently stereotyped as exclusively technical and objective, ignoring the significant ethical, social, and psychological considerations they entail. Both Social Sciences and STEM are essential, complementary domains that contribute to solving complex global challenges through diverse methodologies and interdisciplinary approaches.
Academic and Research Approaches
Social Sciences emphasize qualitative research methods such as ethnography, case studies, and participant observation to explore human behavior and societal structures, while STEM fields prioritize quantitative approaches, including experiments, simulations, and statistical modeling, to analyze natural phenomena and technological processes. Academic programs in Social Sciences often incorporate interdisciplinary frameworks and critical theory to interpret social dynamics, whereas STEM disciplines focus on empirical validation and reproducibility through controlled experiments and data-driven innovation. Research in Social Sciences seeks to understand complex social contexts and cultural patterns, contrasting with STEM's objective to develop predictive models and technological solutions grounded in natural sciences.
Choosing the Right Path: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right path between social sciences and STEM depends on factors such as career goals, personal interests, and job market demand. Social sciences emphasize understanding human behavior, societies, and cultural dynamics, while STEM focuses on technology, engineering, and scientific innovation. Evaluating one's strengths, potential earning power, and the long-term impact of each field is crucial for making an informed decision.
Social Sciences Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com