Kinesthetic instruction engages learners through hands-on activities, allowing them to physically interact with the material to enhance understanding and retention. This method is particularly effective for those who learn best by doing and moving, as it taps into the body's natural ability to process information kinesthetically. Discover how incorporating kinesthetic instruction can transform Your learning experience by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
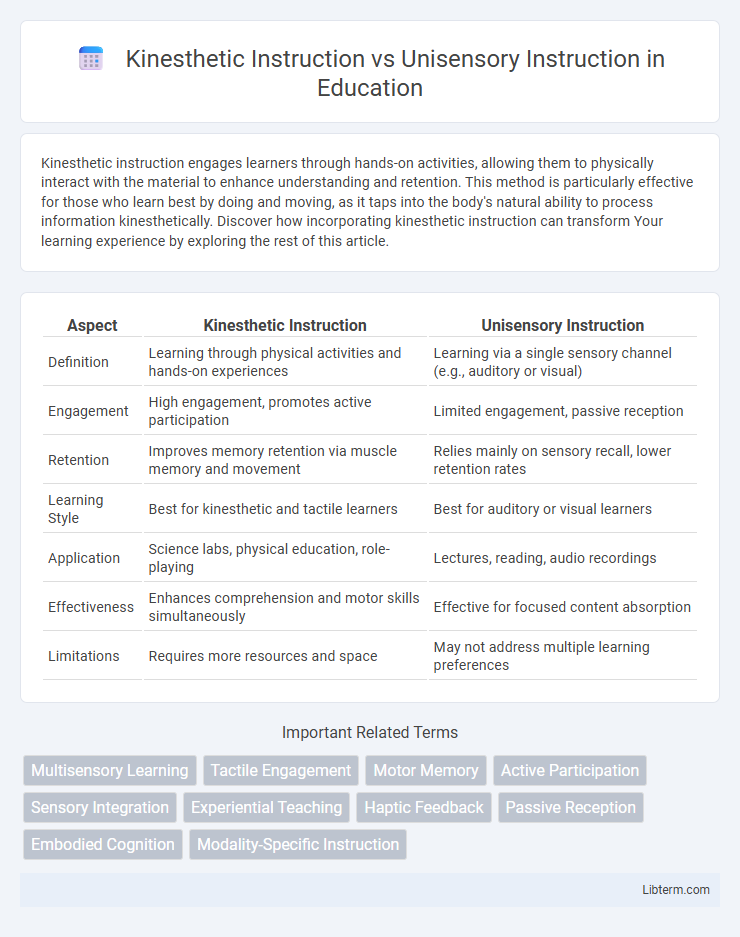
| Aspect | Kinesthetic Instruction | Unisensory Instruction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Learning through physical activities and hands-on experiences | Learning via a single sensory channel (e.g., auditory or visual) |
| Engagement | High engagement, promotes active participation | Limited engagement, passive reception |
| Retention | Improves memory retention via muscle memory and movement | Relies mainly on sensory recall, lower retention rates |
| Learning Style | Best for kinesthetic and tactile learners | Best for auditory or visual learners |
| Application | Science labs, physical education, role-playing | Lectures, reading, audio recordings |
| Effectiveness | Enhances comprehension and motor skills simultaneously | Effective for focused content absorption |
| Limitations | Requires more resources and space | May not address multiple learning preferences |
Introduction to Kinesthetic and Unisensory Instruction
Kinesthetic instruction engages learners through physical activities, enhancing memory retention and motor skills by involving multiple muscle groups. Unisensory instruction relies on a single sensory modality, typically visual or auditory, which can limit multisensory integration and reduce learning effectiveness for some students. Research shows that combining kinesthetic experiences with traditional unisensory methods supports deeper cognitive processing and improved educational outcomes.
Defining Kinesthetic Instruction
Kinesthetic instruction emphasizes hands-on learning through physical activities and movement, enhancing memory retention and comprehension by engaging the body's sensory systems. It contrasts with unisensory instruction, which relies on a single sensory modality, typically auditory or visual, limiting the learner's experiential depth. Incorporating kinesthetic strategies supports diverse learning styles by stimulating motor skills alongside cognitive processes, promoting active participation and deeper understanding.
Understanding Unisensory Instruction
Unisensory instruction focuses on engaging a single sense, such as auditory or visual, to facilitate learning by isolating sensory input for clearer information processing. This method challenges students to develop specific sensory pathways and can strengthen targeted cognitive skills related to the chosen sense. Understanding unisensory instruction helps educators tailor lesson plans to individual learning preferences or needs, making it a valuable strategy for specialized educational environments.
Key Differences Between Kinesthetic and Unisensory Methods
Kinesthetic instruction engages multiple senses through physical movement and hands-on activities, promoting active learning and muscle memory retention, while unisensory instruction relies on a single sensory channel, such as auditory or visual input, limiting engagement to one modality. Kinesthetic methods enhance cognitive connections by integrating tactile, proprioceptive, and motor experiences, whereas unisensory approaches often focus on passive reception of information. The key difference lies in kinesthetic learning's emphasis on bodily interaction to reinforce concepts, contrasting with the sensory restriction of unisensory instruction.
Cognitive Benefits of Kinesthetic Learning
Kinesthetic instruction enhances cognitive functions by engaging the motor system, which improves memory retention and spatial awareness. This learning approach promotes active participation, increasing neural connections related to problem-solving and critical thinking. In contrast, unisensory instruction limits cognitive engagement by relying predominantly on a single sensory modality, often resulting in lower information processing efficiency.
Advantages and Limitations of Unisensory Instruction
Unisensory instruction focuses on engaging a single sense, such as visual or auditory, which can simplify the learning process and allow for targeted skill development. It offers clear, manageable input that benefits learners with specific sensory strengths but may limit engagement and retention for those who need multimodal stimuli. The major limitation of unisensory instruction is its reduced effectiveness in accommodating diverse learning preferences, potentially leading to decreased motivation and slower comprehension compared to kinesthetic or multisensory approaches.
Impact on Student Engagement and Retention
Kinesthetic instruction, which incorporates physical activity and hands-on learning, significantly enhances student engagement and retention by stimulating multiple sensory pathways and promoting active participation. In contrast, unisensory instruction, relying primarily on a single sensory modality like auditory or visual input, often results in lower engagement and reduced information retention due to passive learning. Research shows that kinesthetic learning strategies improve memory retention by up to 40% and increase student motivation and attentiveness in classroom settings.
Practical Classroom Strategies for Each Approach
Kinesthetic instruction enhances learning through hands-on activities, movement-based tasks, and physical engagement, encouraging students to grasp concepts via doing, such as role-playing or building models. Unisensory instruction targets a single sense, often visual or auditory, emphasizing focused practice through methods like lectures, reading, or listening exercises to strengthen comprehension in a specific sensory channel. Effective classroom strategies include integrating tactile manipulatives and interactive simulations for kinesthetic learners, while unisensory learners benefit from structured note-taking and repetitive auditory drills tailored to their dominant sensory preference.
Research Findings Comparing Both Instructional Styles
Research findings highlight that kinesthetic instruction, which engages multiple senses through physical movement, enhances memory retention and comprehension more effectively than unisensory instruction, which relies on a single sensory modality. Studies demonstrate that learners exposed to kinesthetic methods show improved attention, deeper cognitive processing, and higher motivation compared to those receiving unisensory instruction. Neuroeducational research indicates that multisensory integration in kinesthetic instruction activates broader neural networks, supporting enhanced learning outcomes.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Instructional Method
Selecting the appropriate instructional method depends on learners' needs and learning objectives, with kinesthetic instruction offering hands-on engagement that enhances memory and skill acquisition. Unisensory instruction, focusing on a single sensory channel, can streamline learning for specific tasks but may limit multisensory integration. Educators should consider cognitive load, learner preferences, and the complexity of content when deciding between kinesthetic and unisensory approaches to maximize educational outcomes.
Kinesthetic Instruction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com