Project-Based Learning enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills through hands-on experience. It encourages collaboration and real-world application, making education more engaging and effective for Your development. Discover how Project-Based Learning can transform your educational journey in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
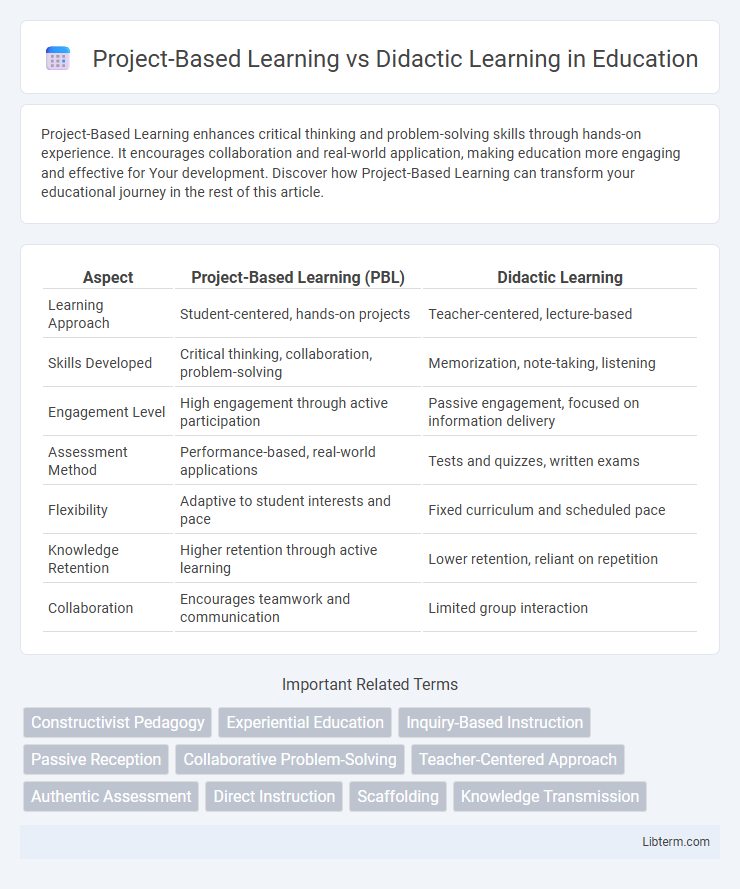
| Aspect | Project-Based Learning (PBL) | Didactic Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Learning Approach | Student-centered, hands-on projects | Teacher-centered, lecture-based |
| Skills Developed | Critical thinking, collaboration, problem-solving | Memorization, note-taking, listening |
| Engagement Level | High engagement through active participation | Passive engagement, focused on information delivery |
| Assessment Method | Performance-based, real-world applications | Tests and quizzes, written exams |
| Flexibility | Adaptive to student interests and pace | Fixed curriculum and scheduled pace |
| Knowledge Retention | Higher retention through active learning | Lower retention, reliant on repetition |
| Collaboration | Encourages teamwork and communication | Limited group interaction |
Introduction to Project-Based Learning and Didactic Learning
Project-Based Learning emphasizes student-centered exploration where learners actively engage in real-world projects to develop critical thinking, collaboration, and problem-solving skills. Didactic Learning relies on direct instruction with the teacher delivering structured content, focusing on memorization and mastery of specific knowledge. Combining both approaches can enhance educational outcomes by balancing experiential learning with foundational instruction.
Key Principles of Project-Based Learning
Project-Based Learning (PBL) emphasizes student-centered inquiry, real-world problem solving, and collaborative teamwork, engaging learners actively in constructing knowledge through meaningful projects. Key principles include authentic tasks that connect to students' interests, sustained inquiry that fosters critical thinking, and iterative reflection promoting deeper understanding and skill development. This approach contrasts with Didactic Learning's teacher-centered, fact-driven methods by prioritizing experiential learning and knowledge application over rote memorization.
Core Features of Didactic Learning
Didactic learning emphasizes structured, teacher-centered instruction where content is delivered through lectures, textbooks, and direct teaching methods. It prioritizes the transmission of factual knowledge with clearly defined objectives, standardized assessments, and a linear progression of topics. This approach ensures consistency in curriculum delivery but often limits student interaction and critical thinking opportunities compared to project-based learning.
Student Engagement: PBL vs Didactic Methods
Project-Based Learning (PBL) significantly increases student engagement by promoting active participation, collaboration, and critical thinking through real-world problem-solving tasks. In contrast, didactic learning often relies on passive absorption of information, leading to lower motivation and limited interaction. Studies show that PBL fosters deeper cognitive involvement and sustained interest compared to traditional lecture-based approaches.
Skill Development in Both Learning Approaches
Project-Based Learning fosters critical thinking, problem-solving, and collaboration skills through hands-on, real-world tasks, enhancing practical application and creativity. Didactic Learning strengthens foundational knowledge, memory retention, and systematic understanding, emphasizing structured content delivery and individual comprehension. Combining both methods can optimize skill development by balancing active engagement with theoretical mastery.
Teacher’s Role: Facilitator vs Instructor
In Project-Based Learning, the teacher acts as a facilitator who guides students through hands-on activities, encourages critical thinking, and fosters collaboration. In contrast, Didactic Learning positions the teacher as an instructor who delivers content through lectures and direct instruction, emphasizing knowledge transmission. This shift from instructor to facilitator transforms the classroom dynamic, promoting student autonomy and active engagement.
Assessment Strategies: Project-Based vs Traditional Testing
Project-Based Learning employs authentic assessment strategies such as portfolios, presentations, and real-world project evaluations that emphasize critical thinking, collaboration, and problem-solving skills. Traditional Testing in Didactic Learning relies heavily on standardized exams, quizzes, and multiple-choice tests designed to measure memorization and factual recall. The shift towards project-based assessments promotes deeper understanding and application of knowledge, contrasting with the conventional focus on individual performance metrics in traditional testing.
Advantages and Challenges of Project-Based Learning
Project-Based Learning (PBL) enhances critical thinking, collaboration, and real-world problem-solving skills by engaging students in hands-on projects that foster deeper understanding and retention of knowledge. Challenges of PBL include the need for extensive planning, resource allocation, and potential difficulties in assessing individual student performance within group work. Despite these obstacles, PBL's emphasis on experiential learning prepares students for complex, real-life situations more effectively than traditional didactic approaches.
Pros and Cons of Didactic Learning
Didactic learning offers structured content delivery and clear learning objectives, making it effective for acquiring foundational knowledge quickly and ensuring curriculum consistency. However, it often promotes passive student engagement and limits critical thinking opportunities, which can hinder the development of problem-solving skills and creativity. This traditional approach may not fully prepare learners for real-world applications requiring adaptive and collaborative abilities.
Choosing the Right Approach: Factors to Consider
Choosing between Project-Based Learning (PBL) and Didactic Learning depends on factors such as student engagement levels, the complexity of the subject matter, and available resources. PBL suits environments emphasizing critical thinking, collaboration, and real-world problem-solving, while Didactic Learning is effective for delivering foundational knowledge and structured content efficiently. Educators must evaluate learning objectives, student demographics, and assessment methods to determine the optimal approach.
Project-Based Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com