Cognitive development encompasses the progression of mental processes such as thinking, problem-solving, and memory from infancy through adulthood. Understanding these stages can help you support learning and adaptation more effectively in everyday situations. Explore the rest of this article to discover key milestones and strategies for enhancing cognitive growth.
Table of Comparison
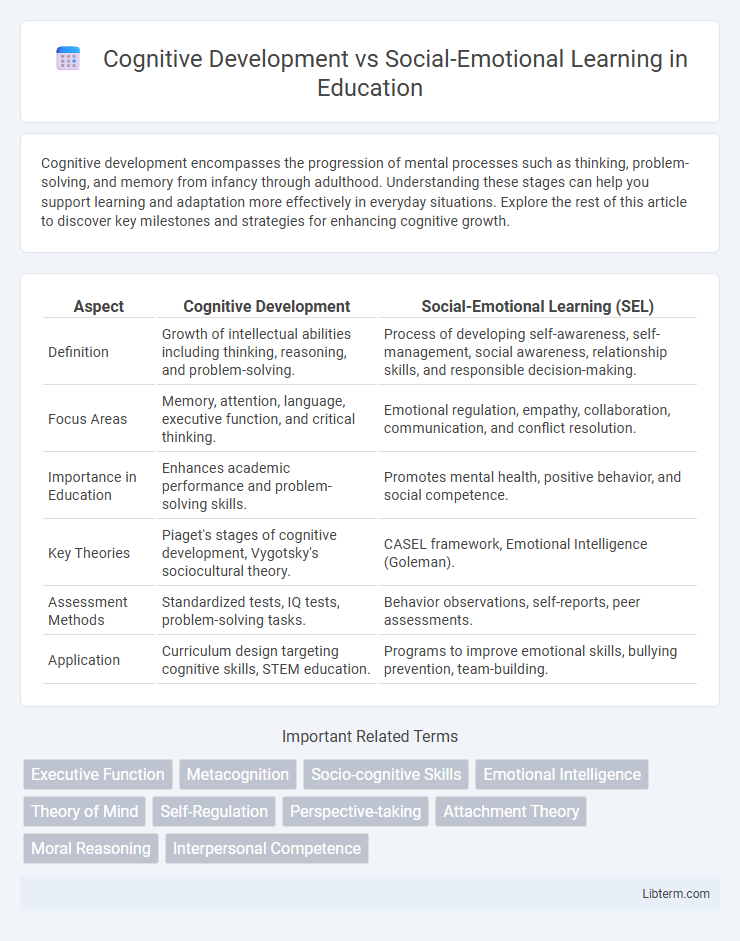
| Aspect | Cognitive Development | Social-Emotional Learning (SEL) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Growth of intellectual abilities including thinking, reasoning, and problem-solving. | Process of developing self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, relationship skills, and responsible decision-making. |
| Focus Areas | Memory, attention, language, executive function, and critical thinking. | Emotional regulation, empathy, collaboration, communication, and conflict resolution. |
| Importance in Education | Enhances academic performance and problem-solving skills. | Promotes mental health, positive behavior, and social competence. |
| Key Theories | Piaget's stages of cognitive development, Vygotsky's sociocultural theory. | CASEL framework, Emotional Intelligence (Goleman). |
| Assessment Methods | Standardized tests, IQ tests, problem-solving tasks. | Behavior observations, self-reports, peer assessments. |
| Application | Curriculum design targeting cognitive skills, STEM education. | Programs to improve emotional skills, bullying prevention, team-building. |
Introduction to Cognitive Development and Social-Emotional Learning
Cognitive development encompasses the processes through which individuals acquire knowledge, think critically, and solve problems, forming the foundation for learning and decision-making. Social-emotional learning (SEL) involves understanding and managing emotions, establishing positive relationships, and making responsible choices, essential for personal and social well-being. Both frameworks support holistic growth, with cognitive development enhancing intellectual abilities while SEL fosters emotional intelligence and interpersonal skills.
Defining Cognitive Development: Core Concepts
Cognitive development encompasses the growth of mental processes such as perception, memory, reasoning, and problem-solving from infancy through adulthood. Key theories by Jean Piaget outline stages where children progress from sensory-motor experiences to abstract thinking, emphasizing assimilation and accommodation mechanisms. Understanding these core concepts is essential for differentiating cognitive growth from social-emotional learning, which centers on interpersonal skills and emotional regulation.
Understanding Social-Emotional Learning (SEL)
Social-Emotional Learning (SEL) encompasses skills such as emotional regulation, empathy, relationship-building, and responsible decision-making, which are crucial for personal and academic success. Unlike cognitive development that primarily targets intellectual abilities like memory and problem-solving, SEL focuses on understanding and managing emotions and social interactions. Research shows integrating SEL into education promotes mental well-being, improves classroom behavior, and enhances students' ability to collaborate effectively.
Key Differences Between Cognitive Development and SEL
Cognitive development focuses on the growth of mental processes such as thinking, problem-solving, memory, and language acquisition, while social-emotional learning (SEL) emphasizes skills related to self-awareness, emotion regulation, empathy, and relationship-building. Key differences include cognitive development's emphasis on intellectual capabilities and information processing, contrasted with SEL's concentration on managing emotions, social interactions, and ethical decision-making. Understanding these distinctions helps educators tailor approaches that foster both intellectual growth and social competence in children.
The Role of Cognitive Skills in Academic Achievement
Cognitive skills such as attention, memory, and problem-solving play a crucial role in academic achievement by enabling students to process information effectively and apply knowledge across subjects. Strong cognitive development supports critical thinking and reasoning, essential for understanding complex concepts and completing academic tasks. Research consistently shows that enhanced cognitive abilities correlate with higher academic performance and improved learning outcomes.
How Social-Emotional Skills Impact Learning Outcomes
Social-emotional skills such as self-regulation, empathy, and effective communication significantly enhance cognitive development by fostering a positive learning environment and improving students' ability to focus and persist through challenges. Research indicates that students with strong social-emotional competencies exhibit higher academic achievement, better problem-solving skills, and increased motivation. Integrating social-emotional learning (SEL) into educational curricula supports improved behavioral outcomes and cognitive growth by promoting emotional intelligence and interpersonal skills essential for lifelong learning.
Integrating Cognitive and SEL Approaches in Education
Integrating cognitive development with social-emotional learning (SEL) enhances educational outcomes by fostering critical thinking alongside emotional regulation and interpersonal skills. Research shows that combining cognitive strategies, such as problem-solving and memory enhancement, with SEL competencies like empathy and self-awareness promotes holistic student growth and academic resilience. Educational frameworks that blend these approaches support adaptable learners equipped for complex real-world challenges and collaborative environments.
Challenges in Balancing Cognitive and Emotional Growth
Balancing cognitive development and social-emotional learning poses challenges such as integrating academic skills with emotional intelligence, which requires tailored educational approaches to meet diverse student needs. Educators often struggle to foster critical thinking and problem-solving while simultaneously promoting empathy, self-regulation, and interpersonal skills. Effective strategies must address these dual demands to support holistic child development in dynamic learning environments.
Effective Strategies for Supporting Both Areas in the Classroom
Implementing project-based learning and collaborative group activities enhances cognitive development by promoting critical thinking and problem-solving skills while simultaneously fostering social-emotional learning through teamwork, communication, and empathy. Using role-playing exercises and reflective journaling supports students in understanding emotions, developing self-regulation, and improving interpersonal relationships, which are crucial for social-emotional growth. Incorporating mindfulness practices and individualized feedback creates an environment conducive to focused attention and emotional well-being, effectively bridging cognitive and social-emotional domains in classroom instruction.
Future Trends in Cognitive and Social-Emotional Learning Research
Future trends in cognitive development and social-emotional learning research emphasize the integration of artificial intelligence and neuroimaging technologies to personalize learning experiences and assess developmental progress more accurately. Emerging studies prioritize the role of executive functions, such as working memory and cognitive flexibility, alongside emotional regulation and empathy in fostering holistic growth in educational settings. Cross-disciplinary collaborations increasingly explore how virtual reality and gamification can enhance both cognitive skills and social-emotional competencies in diverse populations.
Cognitive Development Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com