A paper-based portfolio offers a tangible way to showcase your work, allowing for easy organization and personalized presentation. It serves as a reliable tool during interviews or meetings, providing a physical representation of your skills and accomplishments. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to create an effective paper-based portfolio that highlights your strengths.
Table of Comparison
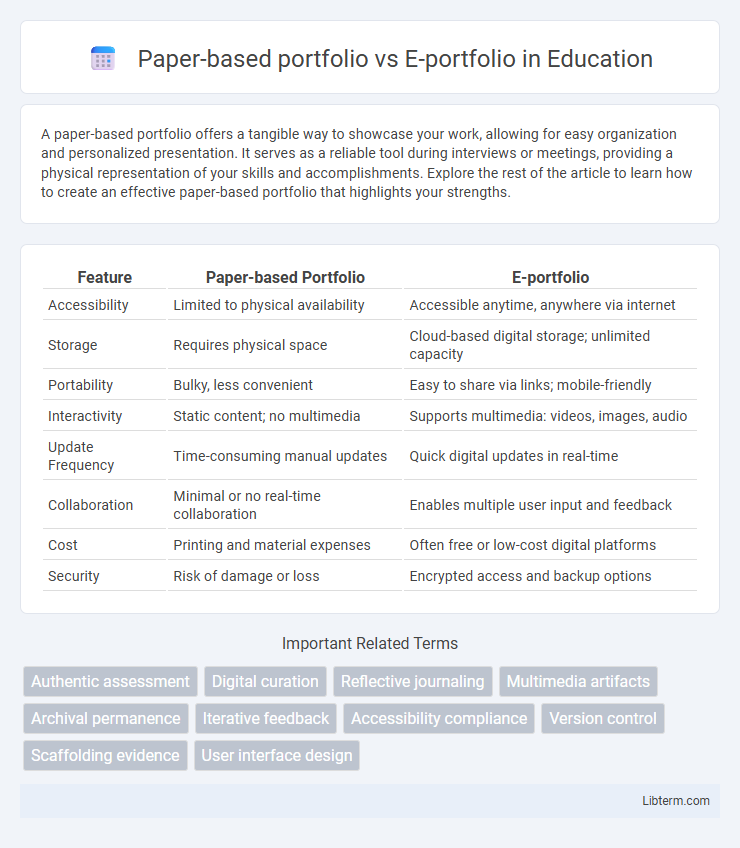
| Feature | Paper-based Portfolio | E-portfolio |
|---|---|---|
| Accessibility | Limited to physical availability | Accessible anytime, anywhere via internet |
| Storage | Requires physical space | Cloud-based digital storage; unlimited capacity |
| Portability | Bulky, less convenient | Easy to share via links; mobile-friendly |
| Interactivity | Static content; no multimedia | Supports multimedia: videos, images, audio |
| Update Frequency | Time-consuming manual updates | Quick digital updates in real-time |
| Collaboration | Minimal or no real-time collaboration | Enables multiple user input and feedback |
| Cost | Printing and material expenses | Often free or low-cost digital platforms |
| Security | Risk of damage or loss | Encrypted access and backup options |
Introduction to Portfolio Assessment
Portfolio assessment evaluates a collection of student work to measure learning progress and achievements. Paper-based portfolios consist of physical documents, sketches, and printed assignments, offering tangible evidence but limiting accessibility and ease of updates. E-portfolios leverage digital platforms to organize multimedia artifacts, enabling interactive presentation, instant sharing, and continuous reflection across different learning environments.
Defining Paper-Based and E-Portfolios
Paper-based portfolios consist of physical documents, photographs, and printed work samples compiled manually in binders or folders, offering tangible evidence of skills and achievements. E-portfolios are digital collections of multimedia artifacts, including text, images, videos, and hyperlinks, hosted on online platforms for easy access, sharing, and updating. These digital portfolios enhance interactivity and integration with other digital tools, contrasting with the static nature of paper-based formats.
Organization and Accessibility
Paper-based portfolios rely on physical documents, which can lead to challenges in organization and limited accessibility due to their bulk and the need for manual sorting. E-portfolios utilize digital platforms that enable efficient organization through tagging, categorization, and quick search functions, allowing users to access their work anytime, anywhere via internet-enabled devices. The enhanced flexibility and scalability of e-portfolios significantly improve ease of management and accessibility compared to traditional paper-based systems.
Customization and Creativity
Paper-based portfolios offer limited customization, typically constrained by physical materials and layout options, reducing the scope for dynamic creativity. E-portfolios enable extensive customization through multimedia integration, interactive elements, and real-time updates, fostering greater creative expression and personalization. Digital tools allow users to tailor content with diverse formats such as videos, animations, and hyperlinks, enhancing engagement and showcasing unique skills effectively.
Assessment and Feedback Opportunities
Paper-based portfolios limit timely assessment and feedback due to physical constraints and manual review processes. E-portfolios enhance assessment opportunities with real-time access for educators, enabling immediate, detailed feedback through multimedia integration. Digital platforms support continuous tracking of progress and interactive evaluations, improving the overall quality of learner assessment.
Security and Privacy Concerns
Paper-based portfolios offer tangible control over content, reducing risks of digital breaches but are vulnerable to physical theft or loss. E-portfolios implement advanced encryption, secure cloud storage, and authentication protocols to protect data, yet remain susceptible to cyberattacks and unauthorized access. Ensuring privacy in e-portfolios requires robust cybersecurity measures, regular software updates, and user awareness to mitigate potential vulnerabilities.
Environmental Impact
Paper-based portfolios contribute significantly to deforestation, increased carbon emissions, and waste accumulation due to the production, printing, and disposal processes. E-portfolios minimize environmental impact by utilizing digital storage and reducing paper consumption, leading to lower carbon footprints and decreased resource use over time. Organizations adopting e-portfolios support sustainability initiatives by promoting eco-friendly alternatives that align with global efforts to reduce environmental degradation.
Cost and Resource Considerations
Paper-based portfolios often incur ongoing costs for printing, storage, and physical materials, making them less scalable and more resource-intensive over time compared to e-portfolios. E-portfolios reduce expenses by leveraging digital platforms that enable easy updates, centralized storage, and minimal material use, significantly lowering both financial and environmental costs. Investing in e-portfolio technology also enhances accessibility and sustainability, optimizing resource management across educational and professional environments.
Future Trends in Portfolio Management
Paper-based portfolios face declining use as digital transformation drives the adoption of e-portfolios, which offer enhanced accessibility, real-time updates, and multimedia integration. Future trends emphasize AI-powered analytics and blockchain technology to improve security, authenticity, and personalized learning pathways within e-portfolio platforms. Institutions increasingly prioritize sustainable, cloud-based solutions that support seamless sharing, collaboration, and lifelong career development.
Choosing the Right Portfolio for Your Needs
Choosing the right portfolio depends on your specific goals, target audience, and convenience preferences. Paper-based portfolios offer tangible, professional presentation suitable for interviews or physical reviews, while e-portfolios provide dynamic, easily shareable content with multimedia integration for digital platforms. Assess the balance between traditional professionalism and innovative accessibility to determine which format best enhances your portfolio's impact.
Paper-based portfolio Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com