Crossdisciplinary approaches integrate knowledge and methods from multiple disciplines to solve complex problems more effectively. This strategy enhances innovation by combining diverse perspectives and expertise, leading to more comprehensive solutions. Explore the full article to discover how crossdisciplinary collaboration can benefit your projects and research.
Table of Comparison
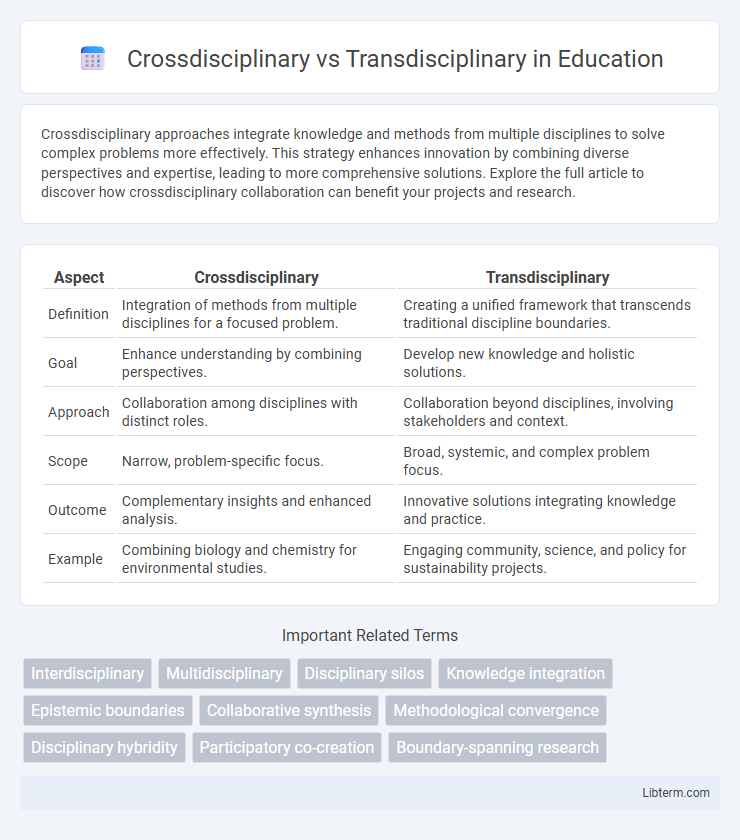
| Aspect | Crossdisciplinary | Transdisciplinary |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integration of methods from multiple disciplines for a focused problem. | Creating a unified framework that transcends traditional discipline boundaries. |
| Goal | Enhance understanding by combining perspectives. | Develop new knowledge and holistic solutions. |
| Approach | Collaboration among disciplines with distinct roles. | Collaboration beyond disciplines, involving stakeholders and context. |
| Scope | Narrow, problem-specific focus. | Broad, systemic, and complex problem focus. |
| Outcome | Complementary insights and enhanced analysis. | Innovative solutions integrating knowledge and practice. |
| Example | Combining biology and chemistry for environmental studies. | Engaging community, science, and policy for sustainability projects. |
Introduction to Crossdisciplinary and Transdisciplinary Approaches
Crossdisciplinary approaches integrate methods and insights from multiple disciplines to address complex problems by combining their perspectives while maintaining disciplinary boundaries. Transdisciplinary approaches transcend individual disciplines by creating new frameworks and knowledge that unify and synthesize diverse expertise for holistic problem-solving. These approaches are crucial in fields like environmental science, healthcare, and education for fostering innovation and comprehensive understanding.
Defining Crossdisciplinary: Meaning and Characteristics
Crossdisciplinary approaches integrate methods and perspectives from multiple academic disciplines to address a common problem without fully merging the disciplines. This approach maintains distinct disciplinary boundaries while promoting collaboration, often involving shared terminology or conceptual frameworks. Key characteristics of crossdisciplinary work include the combination of expertise from fields such as biology, engineering, or sociology to create more comprehensive solutions while preserving the unique methodologies of each discipline.
Understanding Transdisciplinary: A Semantic Overview
Transdisciplinary approaches transcend traditional academic boundaries by integrating knowledge from multiple disciplines and non-academic sources to address complex real-world problems. Unlike crossdisciplinary methods that juxtapose perspectives without full integration, transdisciplinary research fosters a holistic synthesis, emphasizing collaboration among stakeholders, including practitioners and community members. This paradigm shift promotes the co-creation of solutions that are context-specific, socially relevant, and sustainable, reflecting a deeper understanding of interconnected systems and diverse knowledge forms.
Key Differences Between Crossdisciplinary and Transdisciplinary
Crossdisciplinary approaches integrate methods and insights from multiple disciplines while maintaining the boundaries of each field, promoting collaboration without fully merging knowledge domains. Transdisciplinary approaches transcend traditional disciplinary boundaries by creating a unity of intellectual frameworks, leading to the development of new paradigms and innovative problem-solving strategies. The key difference lies in crossdisciplinary work combining perspectives alongside existing disciplines, whereas transdisciplinary work synthesizes and transforms them to address complex, real-world challenges.
Historical Evolution of Crossdisciplinary and Transdisciplinary Methods
Crossdisciplinary methods emerged in the mid-20th century as academic fields sought to collaborate while retaining their disciplinary boundaries, promoting knowledge exchange without fully integrating methodologies. Transdisciplinary approaches evolved later, particularly in the 1990s, emphasizing the integration of academic and non-academic knowledge to address complex societal problems through unified frameworks. The historical progression from crossdisciplinary to transdisciplinary reflects a shift from cooperation among disciplines to the creation of holistic, boundary-transcending paradigms.
Benefits and Challenges of Crossdisciplinary Collaboration
Crossdisciplinary collaboration leverages diverse expertise to solve complex problems by integrating knowledge from multiple disciplines, enhancing innovation and creativity through varied perspectives. Benefits include improved problem-solving capabilities and accelerated learning, while challenges involve communication barriers, conflicting methodologies, and difficulty in aligning goals across different fields. Effective crossdisciplinary teamwork requires strong coordination, mutual respect, and adaptive leadership to bridge disciplinary gaps and harness collective strengths.
Advantages and Limitations of Transdisciplinary Teams
Transdisciplinary teams integrate knowledge across disciplines to solve complex problems, fostering innovation through holistic perspectives and collaborative expertise. Advantages include enhanced creativity, improved problem-solving capacity, and the ability to address real-world challenges that exceed traditional disciplinary boundaries. Limitations involve potential communication barriers, time-intensive collaboration processes, and difficulties in aligning diverse disciplinary methodologies.
Real-World Applications: Crossdisciplinary vs Transdisciplinary Projects
Crossdisciplinary projects integrate methods and perspectives from different disciplines to address specific real-world problems, fostering collaboration without fully merging disciplinary boundaries. Transdisciplinary projects transcend traditional academic frameworks, creating holistic solutions by co-producing knowledge with stakeholders, including communities and policymakers. Real-world applications of transdisciplinary approaches often result in innovative, sustainable outcomes, especially in complex societal challenges like climate change or public health.
Selecting the Right Approach: Factors for Decision-Making
Selecting the right approach between crossdisciplinary and transdisciplinary methods depends on project goals, stakeholder involvement, and desired outcomes. Crossdisciplinary approaches integrate perspectives from multiple disciplines without fully merging them, ideal for targeted problem-solving within defined boundaries. Transdisciplinary approaches transcend traditional disciplinary limits, fostering collaboration and knowledge co-creation among diverse stakeholders to address complex, real-world challenges comprehensively.
Conclusion: The Future of Interdisciplinary Collaboration
Crossdisciplinary approaches integrate methods from multiple disciplines to enhance problem-solving within existing boundaries, while transdisciplinary collaboration transcends traditional fields by creating unified frameworks and shared goals. The future of interdisciplinary collaboration lies in embracing transdisciplinary models that foster innovation through holistic problem-solving and stakeholder inclusion beyond academia. Advancements in digital communication and complex global challenges will increasingly drive the adoption of transdisciplinary networks for impactful, sustainable solutions.
Crossdisciplinary Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com