Performance-based assessment evaluates your skills through practical tasks rather than traditional tests, offering a more accurate reflection of your abilities. This method emphasizes real-world application, making it highly relevant across educational and professional settings. Explore the rest of the article to understand how performance-based assessments can enhance your evaluation process.
Table of Comparison
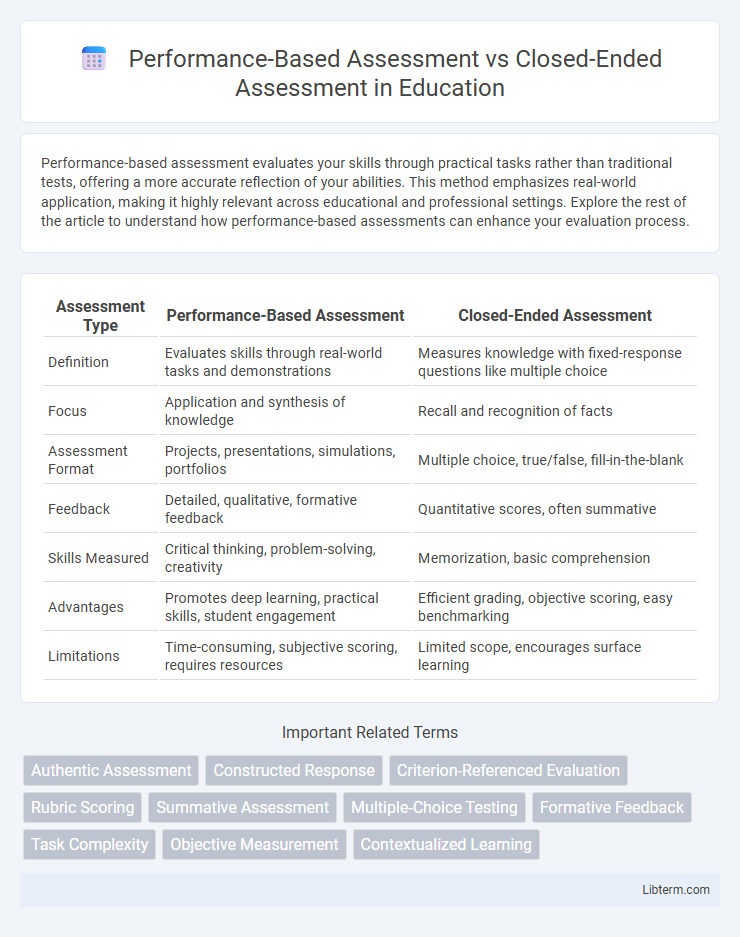
| Assessment Type | Performance-Based Assessment | Closed-Ended Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Evaluates skills through real-world tasks and demonstrations | Measures knowledge with fixed-response questions like multiple choice |
| Focus | Application and synthesis of knowledge | Recall and recognition of facts |
| Assessment Format | Projects, presentations, simulations, portfolios | Multiple choice, true/false, fill-in-the-blank |
| Feedback | Detailed, qualitative, formative feedback | Quantitative scores, often summative |
| Skills Measured | Critical thinking, problem-solving, creativity | Memorization, basic comprehension |
| Advantages | Promotes deep learning, practical skills, student engagement | Efficient grading, objective scoring, easy benchmarking |
| Limitations | Time-consuming, subjective scoring, requires resources | Limited scope, encourages surface learning |
Introduction to Assessment Types
Performance-based assessment evaluates students through tasks that require applying skills and knowledge in real-world scenarios, promoting critical thinking and practical understanding. Closed-ended assessment relies on fixed-response formats like multiple-choice or true/false questions, facilitating objective scoring and efficient data analysis. Both assessment types serve distinct educational purposes, supporting diverse learning and evaluation strategies.
Defining Performance-Based Assessment
Performance-based assessment evaluates learners through real-world tasks that demonstrate their knowledge, skills, and abilities in practical contexts, emphasizing application and critical thinking. Unlike closed-ended assessments that rely on fixed responses such as multiple-choice or true/false questions, performance-based assessments require students to create, perform, or produce tangible outputs. This approach provides a deeper understanding of competency by assessing higher-order cognitive skills and authentic problem-solving capabilities.
Understanding Closed-Ended Assessment
Closed-ended assessment involves questions with predetermined answers, such as multiple-choice or true/false formats, enabling quick and objective grading. This type of evaluation effectively measures factual knowledge and specific skills by restricting responses to fixed options. While efficient for large-scale testing, closed-ended assessments may limit the scope of critical thinking and deeper comprehension compared to performance-based methods.
Key Differences Between the Two Approaches
Performance-based assessment evaluates learners through real-world tasks, measuring critical thinking, problem-solving, and application of knowledge, whereas closed-ended assessment relies on fixed-response formats like multiple-choice or true/false questions. The former emphasizes authentic demonstration of skills and deeper understanding, while the latter focuses on recall, recognition, and efficient grading. Performance-based assessments offer richer, qualitative data on learner abilities; closed-ended assessments provide quantitative, easily comparable results.
Advantages of Performance-Based Assessment
Performance-based assessment enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills by requiring learners to demonstrate knowledge through real-world tasks and projects. It provides a more accurate measurement of student competencies and practical abilities by evaluating complex, authentic performances rather than selecting from predetermined answers. This method also encourages deeper engagement and retention of material, fostering creativity and adaptability essential for success in dynamic environments.
Benefits of Closed-Ended Assessment
Closed-ended assessments offer clear, objective scoring that enhances reliability and consistency across test takers, making them ideal for large-scale standardized testing. Their structured format allows for quick analysis and efficient grading, saving time and resources for educators and institutions. This type of assessment also facilitates easy comparison of student performance data, providing actionable insights to inform curriculum adjustments and teaching strategies.
Limitations of Performance-Based Assessment
Performance-Based Assessment often faces limitations such as subjectivity in scoring, lengthy administration time, and challenges in ensuring standardization across different assessors and contexts. These assessments may struggle with scalability and reliability compared to Closed-Ended Assessments, which offer clear, objective grading but less insight into complex skills. Constraints in resource allocation and evaluator expertise further impact the consistency and fairness of Performance-Based Assessment outcomes.
Drawbacks of Closed-Ended Assessment
Closed-ended assessments often limit students' ability to demonstrate higher-order thinking skills, as they primarily assess rote memorization and recall rather than critical analysis or creativity. These assessments provide little insight into a learner's problem-solving process, making it difficult to evaluate depth of understanding or reasoning abilities. Furthermore, closed-ended tests can lead to guessing, which may distort true performance and hinder accurate measurement of knowledge mastery.
Choosing the Right Assessment Method
Choosing the right assessment method depends on the learning objectives and the skills being evaluated. Performance-based assessments provide an authentic measure of students' abilities to apply knowledge through real-world tasks, promoting critical thinking and problem-solving. Closed-ended assessments efficiently gauge foundational knowledge and recall through multiple-choice or true/false questions, offering quick, objective scoring.
Impact on Student Learning Outcomes
Performance-based assessments enhance student learning outcomes by promoting critical thinking, problem-solving, and application of knowledge in real-world contexts. Closed-ended assessments primarily measure recall and recognition, which may limit deeper understanding and skill development. Research shows performance-based tasks lead to higher engagement and better retention of material, directly impacting academic achievement and long-term learning.
Performance-Based Assessment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com