Departmentalized organizations divide tasks and responsibilities into specialized units to improve efficiency and focus. This structure enhances expert knowledge within departments, streamlining decision-making and communication. Discover how a departmentalized approach can transform your business operations by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
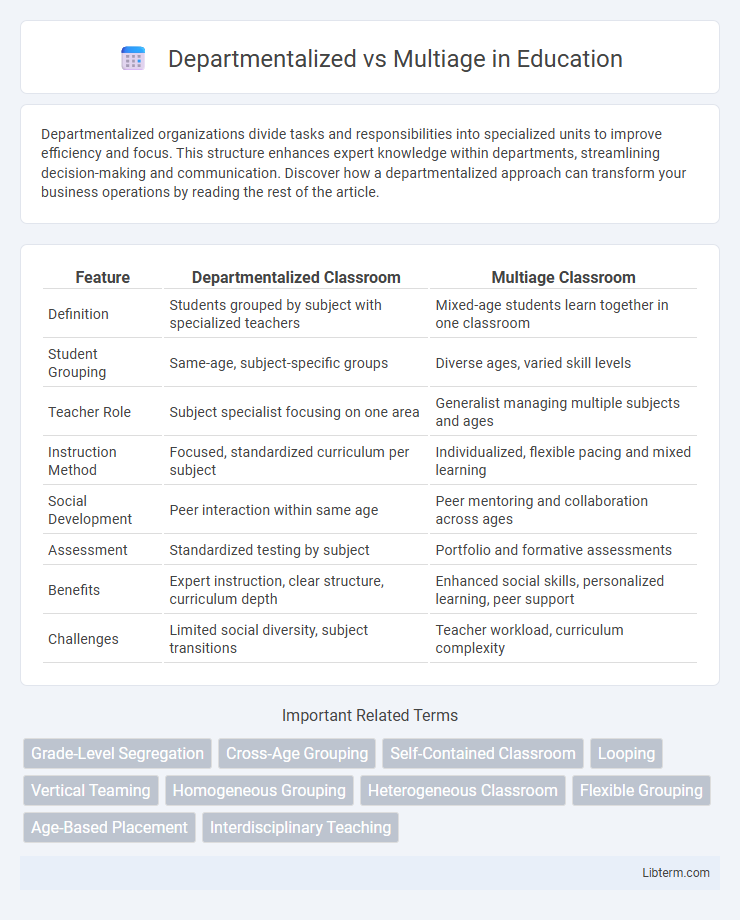
| Feature | Departmentalized Classroom | Multiage Classroom |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Students grouped by subject with specialized teachers | Mixed-age students learn together in one classroom |
| Student Grouping | Same-age, subject-specific groups | Diverse ages, varied skill levels |
| Teacher Role | Subject specialist focusing on one area | Generalist managing multiple subjects and ages |
| Instruction Method | Focused, standardized curriculum per subject | Individualized, flexible pacing and mixed learning |
| Social Development | Peer interaction within same age | Peer mentoring and collaboration across ages |
| Assessment | Standardized testing by subject | Portfolio and formative assessments |
| Benefits | Expert instruction, clear structure, curriculum depth | Enhanced social skills, personalized learning, peer support |
| Challenges | Limited social diversity, subject transitions | Teacher workload, curriculum complexity |
Understanding Departmentalized and Multiage Education
Departmentalized education organizes students by separate subject areas taught by specialized teachers, promoting subject expertise and structured learning environments. Multiage education groups students of different ages and abilities in the same classroom, encouraging personalized learning and peer collaboration across developmental stages. Understanding these models helps educators select approaches that best support diverse student needs and instructional goals.
Core Differences Between Departmentalized and Multiage Classrooms
Departmentalized classrooms separate students by subject area, allowing teachers to specialize and deliver focused, content-specific instruction, which enhances depth of knowledge in each discipline. Multiage classrooms group students of varying ages and abilities together, fostering peer learning, individualized pacing, and social-emotional development through mixed-age interactions. The core difference lies in the instructional structure: departmentalization emphasizes subject expertise and segmented learning, while multiage promotes integrated, flexible learning environments tailored to diverse developmental needs.
Benefits of Departmentalized Classrooms
Departmentalized classrooms enhance subject-specific expertise by allowing teachers to specialize in a particular content area, leading to deeper knowledge transfer and improved student outcomes. This structure facilitates efficient lesson planning and curriculum alignment, ensuring consistent delivery of standards-based instruction. Student engagement increases as learners receive targeted support tailored to each discipline, promoting mastery and academic growth across core subjects.
Advantages of Multiage Learning Environments
Multiage learning environments foster peer collaboration and mentorship, enhancing social skills and promoting individualized instruction tailored to diverse developmental stages. Students engage in flexible grouping that supports continuous progress and deeper understanding, reducing age-based competition and stress. This setting encourages a community atmosphere where mixed-age interactions build leadership abilities and reinforce empathy across different age groups.
Challenges Faced by Departmentalized Schools
Departmentalized schools face challenges such as reduced teacher collaboration due to subject specialization, leading to potential inconsistencies in student learning experiences. Scheduling complexities arise from coordinating multiple teachers and subjects, often resulting in fragmented instructional time. Student adjustment difficulties occur as learners navigate various classrooms and teaching styles, potentially impacting academic continuity and social-emotional development.
Obstacles in Multiage Classroom Implementation
Multiage classroom implementation faces obstacles such as curriculum alignment difficulties and managing diverse student needs simultaneously. Teachers must adapt instructional strategies to accommodate varying developmental stages, which can demand extensive professional development and time. Resource allocation often becomes challenging as materials and assessments may not fit traditional grade-level standards, complicating planning and evaluation.
Impact on Student Achievement and Social Skills
Departmentalized instruction allows teachers to specialize in specific subjects, often resulting in higher academic achievement through focused expertise and structured curriculum delivery. Multiage classrooms promote social development by fostering peer collaboration, leadership, and personalized learning, which can enhance students' social skills and adaptability. Research indicates that combining departmentalized subject mastery with multiage social dynamics can create balanced outcomes in both academic performance and interpersonal growth.
Teacher Roles in Departmentalized vs Multiage Settings
In departmentalized settings, teachers specialize in a specific subject, allowing for deep content expertise and focused lesson planning that caters to a narrower curriculum scope. Multiage classrooms require teachers to manage diverse age groups and learning levels simultaneously, emphasizing flexible instructional strategies and personalized learning to address varied developmental needs. The teacher's role in multiage environments centers on fostering collaborative learning communities and adapting curriculum pacing, contrasting with the compartmentalized, subject-specific responsibilities in departmentalized models.
Parental Perspectives on Educational Models
Parental perspectives on departmentalized versus multiage educational models often reflect concerns about student engagement and individualized learning. Departmentalized classrooms, where students switch between specialized teachers, appeal to parents valuing subject expertise and structured schedules. In contrast, parents favoring multiage settings emphasize social development and personalized instruction across age groups, seeing it as fostering collaboration and adaptability in diverse learning environments.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your School
Choosing between departmentalized and multiage approaches depends on your school's educational goals, student needs, and available resources. Departmentalized classrooms optimize subject-specific expertise and promote teacher collaboration, benefiting middle and high school settings, while multiage classrooms foster individualized learning, social development, and peer mentoring, ideal for elementary levels. Evaluate factors like curriculum complexity, student diversity, and teacher specialization to determine the most effective model for enhancing student engagement and academic growth.
Departmentalized Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com