Baseline data establishes a critical starting point for measuring progress and evaluating outcomes in any project or study. Accurate baseline data enables you to identify trends, set realistic goals, and make informed decisions. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to collect, analyze, and effectively utilize baseline data for your success.
Table of Comparison
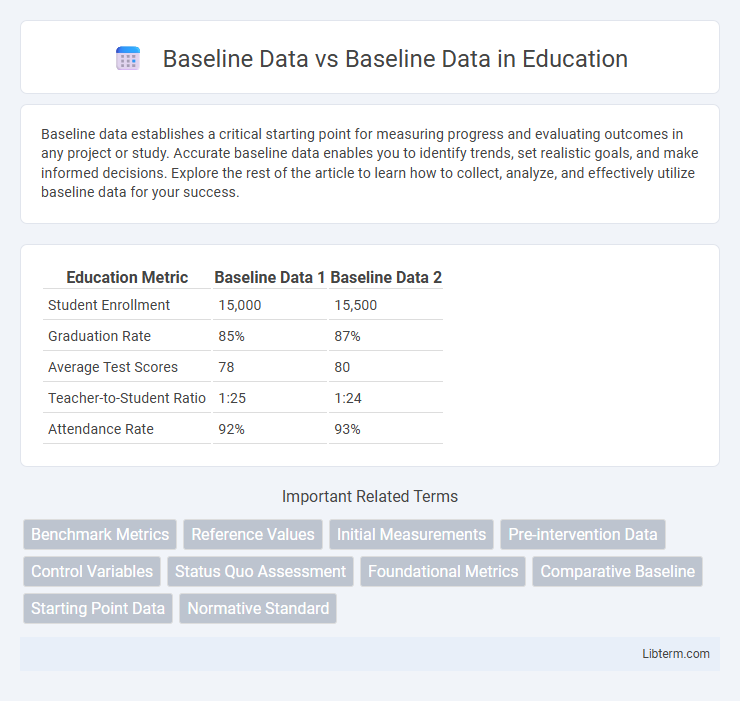
| Education Metric | Baseline Data 1 | Baseline Data 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Student Enrollment | 15,000 | 15,500 |
| Graduation Rate | 85% | 87% |
| Average Test Scores | 78 | 80 |
| Teacher-to-Student Ratio | 1:25 | 1:24 |
| Attendance Rate | 92% | 93% |
Understanding Baseline Data: An Overview
Baseline data represents the initial set of measurements collected before a project or intervention begins, serving as a critical reference point for future comparisons. Accurate understanding of baseline data enables effective tracking of progress, assessment of impacts, and identification of trends over time. Properly defined baseline data ensures that subsequent changes in variables are attributable to specific actions rather than external factors.
Defining Baseline Data in Different Contexts
Baseline data represents initial measurements collected at the start of a study or project to establish a reference point for future comparison. In healthcare, baseline data may include patient health metrics before treatment, while in environmental science, it refers to pre-intervention ecosystem conditions. Accurate baseline data is crucial for assessing changes, measuring progress, and validating outcomes across diverse fields.
Importance of Baseline Data in Research
Baseline data serves as a critical reference point in research, enabling precise measurement of changes and effects by providing initial conditions before intervention. It allows researchers to establish validity and reliability of study outcomes through consistent comparisons across time, population, or experimental groups. Accurate baseline data collection minimizes confounding variables and enhances the ability to attribute observed results directly to the intervention or treatment applied.
Baseline Data in Clinical Trials vs. Observational Studies
Baseline data in clinical trials consists of controlled and precisely measured variables such as patient demographics, biomarkers, and clinical outcomes collected before intervention, ensuring comparability between randomized groups. In observational studies, baseline data often include broader, real-world patient information like medical history, lifestyle factors, and baseline health status, recorded without intervention control, reflecting natural patient variation. The accuracy and consistency of baseline data directly impact the validity of conclusions regarding treatment effects or associations in both study types.
Common Methods for Collecting Baseline Data
Common methods for collecting baseline data include surveys, interviews, direct observations, and existing records analysis, each designed to provide accurate initial measurements for comparison. Surveys offer standardized data collection across large populations, while interviews allow for in-depth understanding of individual or group perspectives. Direct observations capture real-time behaviors, and analyzing existing records leverages historical data to establish pre-intervention benchmarks.
Analyzing Baseline Data: Techniques and Tools
Analyzing baseline data involves techniques such as descriptive statistics, trend analysis, and regression modeling to identify patterns and establish benchmarks for future comparisons. Tools like Excel, SPSS, and Tableau facilitate data visualization, cleaning, and statistical analysis, enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of baseline data interpretation. Employing automation with Python libraries such as Pandas and NumPy accelerates data processing and supports in-depth baseline data analysis for informed decision-making.
Interpreting Baseline Data for Decision Making
Interpreting baseline data involves analyzing initial measurements or conditions that serve as a reference point for future comparisons, enabling informed decision making. Accurate assessment of baseline data helps identify trends, deviations, and areas needing improvement, which supports strategic planning and resource allocation. Effective use of baseline data enhances the ability to monitor progress, evaluate outcomes, and make evidence-based decisions in various fields such as healthcare, education, and business.
Challenges in Comparing Baseline Data Sets
Challenges in comparing baseline data sets often arise from variations in data collection methods, definitions, and timeframes, leading to inconsistencies that hinder accurate analysis. Differences in sample size, population characteristics, and measurement tools further complicate direct comparisons between baseline datasets. Harmonizing these data sets requires standardized protocols and advanced statistical techniques to address bias and ensure valid, reliable conclusions.
Ensuring Accuracy and Reliability of Baseline Data
Ensuring accuracy and reliability of baseline data involves rigorous data validation, consistent measurement techniques, and comprehensive documentation. Reliable baseline data serves as a critical reference point for monitoring progress, identifying trends, and making informed decisions in various fields like environmental studies and clinical trials. Implementing quality control protocols and periodic data audits enhances data integrity and minimizes errors or biases in baseline datasets.
Best Practices for Reporting Baseline Data
Effective reporting of baseline data involves accurately capturing initial conditions using standardized metrics and ensuring data consistency for reliable comparisons. Best practices emphasize transparent documentation of data collection methods, clear definition of variables, and inclusion of contextual factors to enhance data interpretability. Utilizing visualization tools and maintaining data quality controls further support meaningful analysis and informed decision-making.
Baseline Data Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com