Cooperative education integrates academic learning with practical work experience, allowing students to apply classroom knowledge in real-world settings and develop professional skills. This approach enhances employability by providing hands-on training and networking opportunities within your chosen industry. Discover how cooperative education can transform your career prospects by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
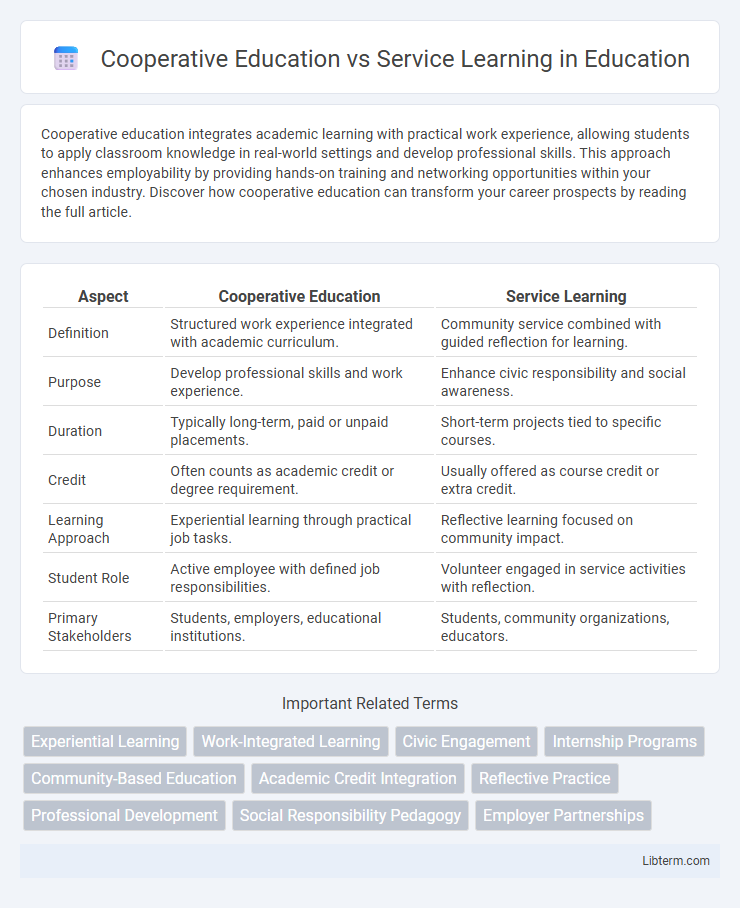
| Aspect | Cooperative Education | Service Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Structured work experience integrated with academic curriculum. | Community service combined with guided reflection for learning. |
| Purpose | Develop professional skills and work experience. | Enhance civic responsibility and social awareness. |
| Duration | Typically long-term, paid or unpaid placements. | Short-term projects tied to specific courses. |
| Credit | Often counts as academic credit or degree requirement. | Usually offered as course credit or extra credit. |
| Learning Approach | Experiential learning through practical job tasks. | Reflective learning focused on community impact. |
| Student Role | Active employee with defined job responsibilities. | Volunteer engaged in service activities with reflection. |
| Primary Stakeholders | Students, employers, educational institutions. | Students, community organizations, educators. |
Introduction to Experiential Learning Models
Experiential learning models such as Cooperative Education and Service Learning both emphasize practical, hands-on experiences that enhance academic knowledge through real-world application. Cooperative Education integrates structured workplace experiences directly related to a student's academic program, fostering professional skills and industry connections. Service Learning combines community service with coursework, promoting civic responsibility and social awareness while reinforcing academic objectives.
Defining Cooperative Education
Cooperative education integrates structured work experience with academic coursework, allowing students to apply theoretical knowledge in real-world employment settings. It typically involves paid internships or work placements directly related to a student's field of study, fostering professional skill development and workplace readiness. This model emphasizes a formal partnership between educational institutions and employers to enhance career opportunities and experiential learning outcomes.
Understanding Service Learning
Service Learning integrates community service with academic learning, emphasizing real-world applications and civic responsibility. Unlike Cooperative Education, which primarily focuses on career-related work experience, Service Learning fosters personal growth, social awareness, and active citizenship. This experiential approach deepens students' understanding by connecting classroom concepts with meaningful community engagement.
Key Objectives of Cooperative Education
Cooperative Education aims to integrate academic learning with practical work experience to enhance students' professional skills and career readiness. It focuses on developing discipline-specific competencies, fostering workplace adaptability, and promoting a deeper understanding of industry standards. This experiential learning model prioritizes long-term employment outcomes and strong partnerships between educational institutions and employers.
Primary Goals of Service Learning
Service learning primarily aims to integrate meaningful community service with academic learning, enhancing students' civic responsibility and social awareness. It focuses on fostering critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and a deeper understanding of societal issues through active engagement with diverse communities. Unlike cooperative education, which centers on practical job training and career development, service learning emphasizes reciprocal benefits for both students and the community.
Differences in Structure and Implementation
Cooperative education integrates structured, paid work experiences directly related to students' academic programs, emphasizing long-term employment placements with clearly defined learning objectives and employer supervision. Service learning combines community service activities with academic coursework, focusing on addressing societal needs through reflective practice and often involves short-term, volunteer-based projects without formal employment contracts. The implementation of cooperative education relies on established partnerships with industry for credit-bearing internships, while service learning is embedded within curriculum design to foster civic responsibility and enhance academic understanding.
Academic and Career Benefits
Cooperative education integrates structured work experiences directly related to academic curricula, enhancing practical skills and boosting career readiness through real-world application. Service learning combines community service with academic instruction, fostering critical thinking, civic responsibility, and social awareness alongside academic achievement. Both approaches improve employability, but cooperative education emphasizes professional skill development, whereas service learning strengthens interpersonal and ethical competencies.
Community Impact and Student Engagement
Cooperative education integrates structured work experiences with academic learning, enhancing community impact by addressing local industry needs while fostering practical skills in students. Service learning emphasizes direct community involvement, cultivating social responsibility and civic engagement through volunteer activities linked to coursework. Both approaches boost student engagement by connecting theoretical knowledge to real-world applications, though cooperative education tends to focus more on career readiness and service learning on community development.
Challenges and Limitations
Cooperative Education faces challenges such as securing meaningful placements and balancing academic requirements with work responsibilities, which can limit student engagement and skill development. Service Learning encounters limitations including inconsistent quality of community partnerships and difficulty in measuring impact on student learning and community benefit. Both models must address these issues to maximize experiential learning outcomes and foster sustainable community relationships.
Choosing the Right Approach: Factors to Consider
Choosing between cooperative education and service learning requires evaluating educational goals, desired skill development, and community engagement levels. Cooperative education emphasizes structured work experience with employer partnerships, enhancing career readiness through practical application of academic knowledge. Service learning prioritizes social responsibility and civic engagement, integrating meaningful community service with reflection to foster personal growth and societal impact.
Cooperative Education Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com