Lecture-based teaching offers a structured way to deliver information efficiently to large groups, emphasizing clear explanations and expert knowledge. This method supports your ability to grasp complex concepts through focused listening and note-taking. Explore the rest of the article to understand how lecture-based teaching can enhance your learning experience.
Table of Comparison
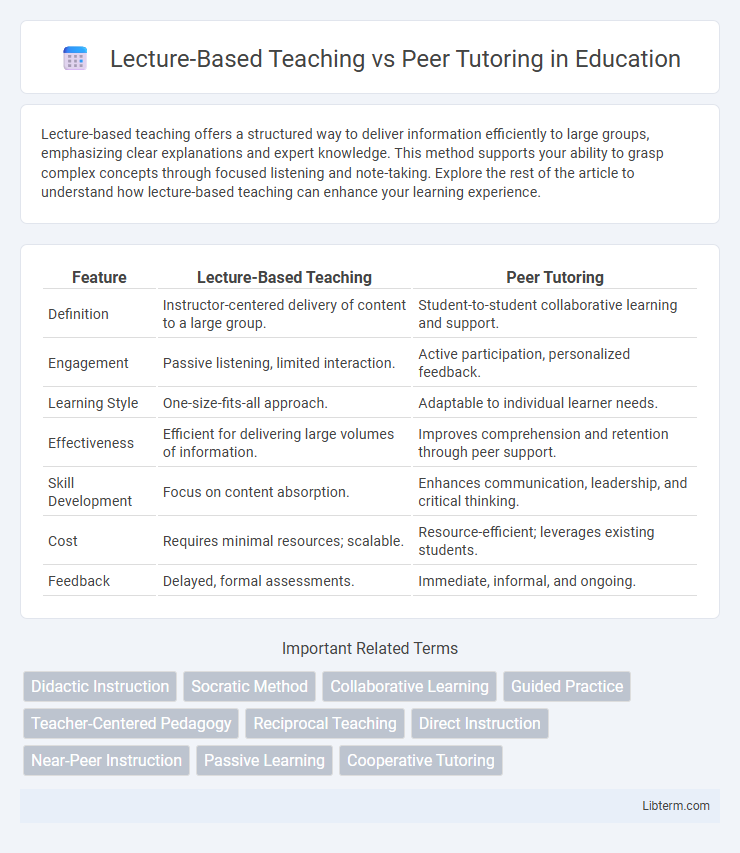
| Feature | Lecture-Based Teaching | Peer Tutoring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Instructor-centered delivery of content to a large group. | Student-to-student collaborative learning and support. |
| Engagement | Passive listening, limited interaction. | Active participation, personalized feedback. |
| Learning Style | One-size-fits-all approach. | Adaptable to individual learner needs. |
| Effectiveness | Efficient for delivering large volumes of information. | Improves comprehension and retention through peer support. |
| Skill Development | Focus on content absorption. | Enhances communication, leadership, and critical thinking. |
| Cost | Requires minimal resources; scalable. | Resource-efficient; leverages existing students. |
| Feedback | Delayed, formal assessments. | Immediate, informal, and ongoing. |
Introduction to Lecture-Based Teaching and Peer Tutoring
Lecture-based teaching primarily involves an instructor delivering content directly to students, emphasizing structured information transfer and standardized assessment. Peer tutoring engages students collaboratively, where learners actively support each other's understanding through dialogue and personalized feedback. Both methods influence cognitive engagement, with lecture-based teaching fostering foundational knowledge acquisition and peer tutoring enhancing critical thinking and social learning skills.
Historical Background of Teaching Methods
Lecture-based teaching originated in ancient Greece, notably at Plato's Academy, where knowledge was primarily transmitted through oratory and formal speeches. Peer tutoring has roots in the medieval university system, where older or more knowledgeable students guided their peers in scholastic learning. Both methods evolved over centuries, reflecting shifts from authoritative dissemination to collaborative learning models in educational history.
Defining Lecture-Based Teaching
Lecture-based teaching is an instructional method where the educator delivers content directly to students, typically in a structured format emphasizing information transmission. This approach prioritizes clarity, organization, and expert knowledge dissemination, often relying on verbal communication and multimedia aids to enhance understanding. Its effectiveness depends on the lecturer's ability to engage students and present material in a comprehensible and memorable way.
Understanding Peer Tutoring
Peer tutoring enhances comprehension by promoting active engagement and personalized feedback, which contrasts with the passive reception often found in lecture-based teaching. Students in peer tutoring settings benefit from collaborative learning, where explaining concepts to peers reinforces their own understanding and critical thinking skills. Research shows peer tutoring improves retention and motivates learners through social interaction, making it a powerful complement to traditional lectures.
Effectiveness in Knowledge Retention
Peer tutoring significantly enhances knowledge retention by promoting active engagement and personalized feedback, as supported by numerous educational studies revealing improved recall and comprehension rates. Lecture-based teaching, while efficient for delivering large volumes of information, often results in lower retention due to passive learning and limited interaction. Combining both methods can optimize retention by balancing structured content delivery with collaborative reinforcement.
Engagement Levels: Passive vs. Active Learning
Lecture-based teaching often results in passive learning, where students primarily listen and absorb information with limited interaction. Peer tutoring encourages active learning by involving students in discussions, problem-solving, and teaching peers, which boosts engagement and retention. Studies show active participation in peer tutoring significantly enhances comprehension and critical thinking compared to traditional lectures.
Impact on Critical Thinking and Problem Solving
Peer tutoring significantly enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills by encouraging active engagement and collaborative learning, which promotes deeper understanding and application of concepts. Lecture-based teaching, while effective for delivering foundational knowledge, often limits opportunities for interactive problem-solving and real-time critical analysis. Research shows learners in peer tutoring environments demonstrate higher retention rates and improved ability to tackle complex problems through discussion and feedback.
Social and Emotional Benefits
Lecture-based teaching often limits student interaction, which can constrain the development of social and emotional skills such as empathy and collaboration. Peer tutoring fosters a supportive learning environment where students build communication, teamwork, and confidence through active engagement. Research highlights that peer tutoring not only enhances academic performance but also improves emotional intelligence and social connectedness among participants.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Method
Lecture-based teaching often struggles with limited student engagement and passive learning, leading to lower retention rates and reduced critical thinking development. Peer tutoring faces challenges such as inconsistent tutor quality, potential for misinformation, and dependence on student motivation and communication skills. Both methods may encounter difficulties in addressing diverse learning styles and providing personalized feedback effectively.
Choosing the Right Approach: Factors to Consider
Choosing between lecture-based teaching and peer tutoring depends on factors such as class size, learning objectives, and student engagement levels. Lecture-based teaching suits large groups needing structured content delivery, while peer tutoring benefits smaller groups requiring personalized support and active collaboration. Considering the diversity of student learning styles and resource availability ensures the most effective instructional approach is selected.
Lecture-Based Teaching Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com