Criterion-referenced assessment evaluates a learner's performance against a fixed set of standards or criteria, rather than comparing results to other students. This method focuses on what You have achieved and helps identify specific areas for improvement, promoting targeted learning outcomes. Explore the rest of the article to understand how criterion-referenced assessment can enhance educational practices.
Table of Comparison
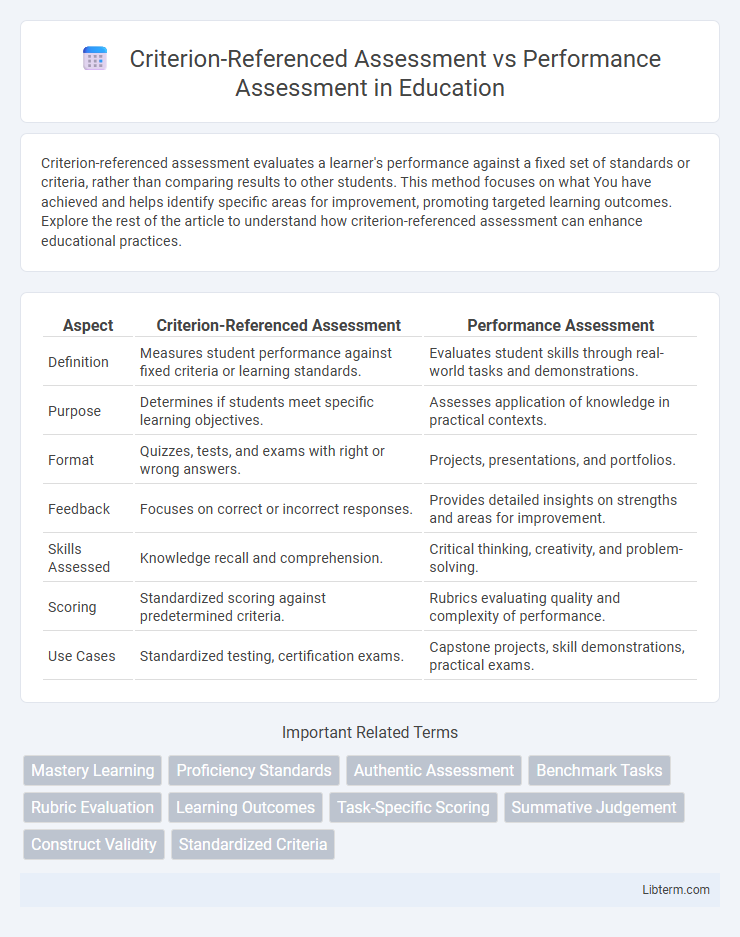
| Aspect | Criterion-Referenced Assessment | Performance Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measures student performance against fixed criteria or learning standards. | Evaluates student skills through real-world tasks and demonstrations. |
| Purpose | Determines if students meet specific learning objectives. | Assesses application of knowledge in practical contexts. |
| Format | Quizzes, tests, and exams with right or wrong answers. | Projects, presentations, and portfolios. |
| Feedback | Focuses on correct or incorrect responses. | Provides detailed insights on strengths and areas for improvement. |
| Skills Assessed | Knowledge recall and comprehension. | Critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving. |
| Scoring | Standardized scoring against predetermined criteria. | Rubrics evaluating quality and complexity of performance. |
| Use Cases | Standardized testing, certification exams. | Capstone projects, skill demonstrations, practical exams. |
Introduction to Assessment Types
Criterion-referenced assessment evaluates student performance based on predefined learning standards or criteria, providing clear benchmarks for mastery. Performance assessment requires students to demonstrate skills through real-world tasks, emphasizing practical application and critical thinking. These assessment types complement each other by measuring both knowledge acquisition and the ability to apply that knowledge effectively.
Defining Criterion-Referenced Assessment
Criterion-referenced assessment evaluates a student's performance based on specific learning objectives or criteria, measuring mastery of predefined skills without comparing to other students. It allows educators to determine whether each learner has achieved established competencies, facilitating targeted instruction and feedback. This type of assessment is essential for identifying individual strengths and areas needing improvement according to curriculum standards.
Understanding Performance Assessment
Performance assessment evaluates a student's ability to apply skills and knowledge in real-world or practical tasks, emphasizing authentic demonstrations rather than selecting correct answers. Unlike criterion-referenced assessment, which measures performance against predetermined standards or criteria, performance assessments provide rich insights into critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity. These assessments typically involve projects, presentations, or experiments, offering educators detailed evidence of student competencies and skill mastery.
Key Differences Between the Two Assessments
Criterion-referenced assessment measures student performance against a set standard or specific learning objectives, providing clear benchmarks for mastery of content. Performance assessment evaluates students' ability to apply skills and knowledge through real-world tasks, emphasizing practical application and higher-order thinking. Key differences include criterion-referenced assessments' focus on predetermined criteria and objective scoring versus performance assessments' reliance on holistic, subjective evaluation of complex tasks.
Advantages of Criterion-Referenced Assessment
Criterion-referenced assessment offers clear advantages by measuring student performance against predetermined standards, ensuring objective evaluation of specific skills and knowledge. This approach facilitates targeted instruction and personalized feedback, helping educators identify individual learning gaps accurately. Criterion-referenced assessments promote consistent benchmarking, enabling reliable tracking of student progress over time.
Benefits of Performance Assessment
Performance assessment offers a practical evaluation method by measuring a student's ability to apply skills and knowledge in real-world or simulated tasks, promoting deeper understanding and retention. It enhances critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity, which are essential skills beyond rote memorization tested in criterion-referenced assessments. This assessment type provides educators with detailed insights into student progress and instructional effectiveness through authentic demonstrations of competence.
Challenges and Limitations
Criterion-referenced assessments face challenges such as limited scope in measuring complex skills and potential bias due to rigid performance benchmarks. Performance assessments often encounter issues with subjectivity in scoring, time-consuming administration, and difficulty ensuring reliability and validity across diverse learners. Both assessment types require careful design and consistent calibration to address limitations in accurately reflecting student learning and abilities.
Appropriate Uses in Education
Criterion-referenced assessment is appropriate for measuring students' mastery of specific learning objectives or skills, providing clear benchmarks for proficiency and guiding targeted instruction. Performance assessment is suitable for evaluating complex, real-world tasks that require higher-order thinking, problem-solving, and application of knowledge. Both methods are essential in education to balance standardized knowledge checks with authentic demonstrations of student abilities.
Assessment Examples and Case Studies
Criterion-referenced assessment evaluates student performance against predefined learning standards, often seen in standardized tests like the SAT or state proficiency exams. Performance assessment requires students to demonstrate skills through tasks such as presentations, portfolios, or projects, exemplified by case studies in medical education where practical competencies are assessed. Research comparing both methods highlights case studies in K-12 education illustrating improved student engagement and deeper understanding with performance assessments, while criterion-referenced tests provide reliable benchmarking for mastery of specific standards.
Choosing the Right Assessment Method
Choosing the right assessment method depends on the learning objectives and the skills being measured; Criterion-Referenced Assessment evaluates whether students meet specific learning standards, making it ideal for mastery of defined content. Performance Assessment requires students to demonstrate skills through real-world tasks, providing a more authentic measure of applied knowledge and critical thinking. Selecting between these methods hinges on whether the goal is to assess knowledge acquisition or practical ability in context.
Criterion-Referenced Assessment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com