Experiential learning enhances your understanding by engaging directly with real-world experiences, facilitating deeper retention and practical application of knowledge. This hands-on approach not only improves critical thinking and problem-solving skills but also fosters personal growth and adaptability. Discover how integrating experiential learning can transform your educational journey by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
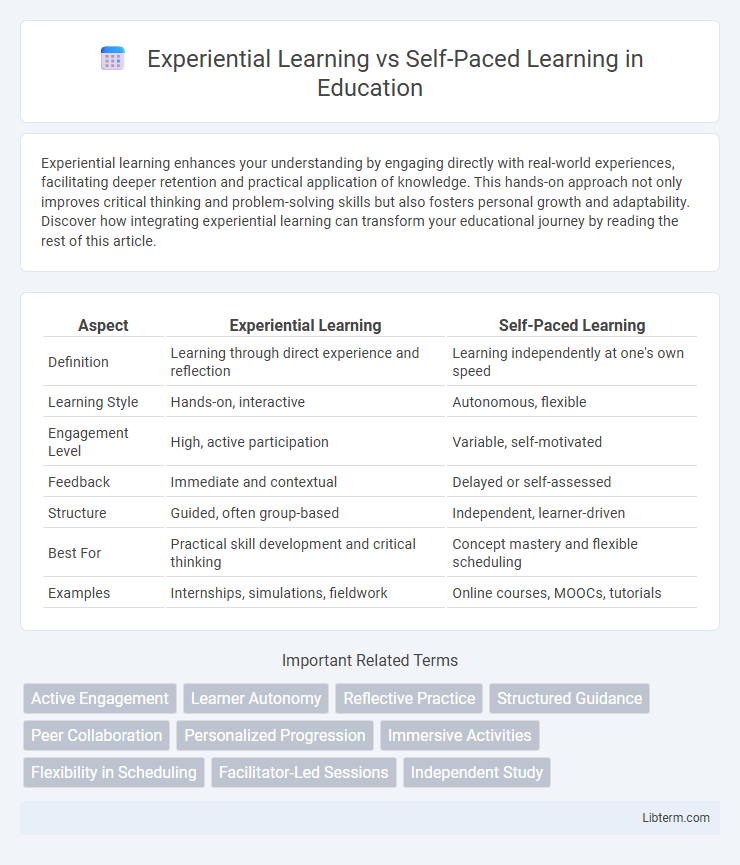
| Aspect | Experiential Learning | Self-Paced Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Learning through direct experience and reflection | Learning independently at one's own speed |
| Learning Style | Hands-on, interactive | Autonomous, flexible |
| Engagement Level | High, active participation | Variable, self-motivated |
| Feedback | Immediate and contextual | Delayed or self-assessed |
| Structure | Guided, often group-based | Independent, learner-driven |
| Best For | Practical skill development and critical thinking | Concept mastery and flexible scheduling |
| Examples | Internships, simulations, fieldwork | Online courses, MOOCs, tutorials |
Introduction to Experiential and Self-Paced Learning
Experiential learning emphasizes learning through direct experience, reflection, and active engagement, enabling learners to apply concepts in real-world contexts for deeper understanding. Self-paced learning allows individuals to control the timing and speed of their educational journey, offering flexibility and autonomy to accommodate diverse learning styles. Both methodologies support personalized education but differ fundamentally in their approach to interaction and learner control.
Defining Experiential Learning
Experiential learning is an educational approach where learners gain knowledge and skills through direct experience, reflection, and real-world application, emphasizing active participation over passive absorption. This method contrasts with self-paced learning, which allows individuals to progress through material independently at their own speed, often relying on pre-designed content without immediate practical engagement. Experiential learning prioritizes hands-on activities, problem-solving, and collaborative projects to foster deeper understanding and retention.
Understanding Self-Paced Learning
Self-paced learning allows learners to control the timing, speed, and sequence of their educational activities, fostering autonomy and personalized study habits. This method leverages digital platforms and resources, enabling access to diverse materials anytime and anywhere, which enhances flexibility and accommodates individual learning styles. Emphasizing mastery, self-paced learning supports continuous assessment and revision, promoting deeper understanding and long-term retention of knowledge.
Key Differences Between the Two Approaches
Experiential learning emphasizes active engagement through hands-on activities and real-world experiences, fostering practical skill development and deep understanding. Self-paced learning allows learners to control the timing and pace of their study, promoting flexibility and individualized progress without immediate external interaction. The key difference lies in experiential learning's reliance on direct experience and reflection, whereas self-paced learning prioritizes autonomy and time management.
Benefits of Experiential Learning
Experiential learning enhances skill retention and critical thinking by engaging learners directly in real-world tasks, creating practical knowledge that transcends traditional theoretical methods. This approach fosters adaptability and problem-solving abilities, improving performance in dynamic environments. Immersive experiences also boost motivation and confidence, leading to deeper learning and long-term application of skills.
Advantages of Self-Paced Learning
Self-paced learning offers the advantage of flexibility, allowing learners to progress according to their own schedules and comprehension speeds, which enhances retention and reduces stress. It provides personalized learning paths tailored to individual needs, improving engagement and motivation through adaptive content and resources. This method also promotes autonomy, encouraging learners to take responsibility for their progress and develop critical time-management skills.
Challenges of Experiential Learning
Experiential learning presents challenges such as the requirement for substantial resources, including time, materials, and facilitation expertise, to effectively simulate real-world scenarios. Learners may encounter difficulties in reflecting on experiences critically and transferring insights to broader contexts without guided support. Furthermore, assessing outcomes in experiential learning can be complex due to its subjective and dynamic nature, complicating standardized evaluation compared to self-paced learning models.
Limitations of Self-Paced Learning
Self-paced learning often lacks real-time interaction and immediate feedback, which can hinder the development of practical skills and critical thinking. The absence of structured guidance may lead to decreased motivation and inconsistent progress, making it challenging to master complex concepts. This learning mode may also result in isolation, reducing opportunities for collaboration and experiential engagement critical for deeper understanding.
Choosing the Right Learning Approach
Experiential learning enhances skill retention through hands-on activities and real-world problem-solving, making it ideal for learners seeking practical application and immediate feedback. In contrast, self-paced learning offers flexibility and autonomy, allowing individuals to progress based on personal schedules and learning speeds. Selecting the right approach depends on goals such as skill acquisition, available time, and preferred learning style, with experiential methods benefiting those needing immersive experience and self-paced formats suiting independent, time-constrained learners.
Conclusion: Balancing Experiential and Self-Paced Learning
Balancing experiential learning and self-paced learning maximizes educational outcomes by combining hands-on practice with flexible, individualized study. Experiential learning enhances skill application and retention through real-world engagement, while self-paced learning supports personalized progress and deeper conceptual understanding. Integrating both approaches fosters a comprehensive learning environment that adapts to diverse learner needs and promotes continuous development.
Experiential Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com