Summative assessment evaluates student learning by measuring their understanding at the end of an instructional unit, providing a clear picture of overall achievement. This process typically involves exams, projects, or papers designed to assess knowledge comprehensively. Discover how summative assessment can enhance your educational outcomes by reading further.
Table of Comparison
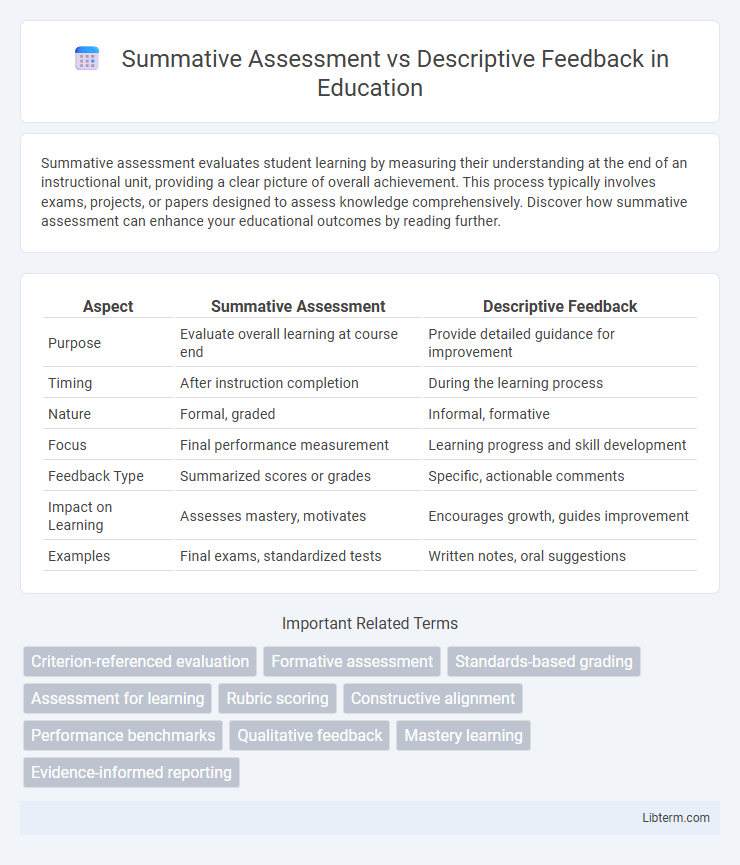
| Aspect | Summative Assessment | Descriptive Feedback |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Evaluate overall learning at course end | Provide detailed guidance for improvement |
| Timing | After instruction completion | During the learning process |
| Nature | Formal, graded | Informal, formative |
| Focus | Final performance measurement | Learning progress and skill development |
| Feedback Type | Summarized scores or grades | Specific, actionable comments |
| Impact on Learning | Assesses mastery, motivates | Encourages growth, guides improvement |
| Examples | Final exams, standardized tests | Written notes, oral suggestions |
Introduction to Summative Assessment and Descriptive Feedback
Summative assessment evaluates student learning by measuring performance against predefined standards at the end of an instructional period, providing a cumulative score or grade. Descriptive feedback offers detailed, specific information aimed at improving student understanding and skills through qualitative comments rather than numerical results. Both approaches serve distinct purposes in education, with summative assessment focusing on accountability and descriptive feedback emphasizing formative growth.
Defining Summative Assessment
Summative assessment evaluates student learning at the end of an instructional period by measuring achievement against predefined standards or learning objectives. It typically takes the form of final exams, standardized tests, or end-of-term projects that provide a summary judgment of performance. This assessment type is primarily used for grading, accountability, and determining overall proficiency rather than ongoing instructional guidance.
Understanding Descriptive Feedback
Descriptive feedback provides specific, actionable insights that help learners understand their strengths and areas for improvement, enhancing deeper comprehension and skill development. Unlike summative assessment, which evaluates overall performance at the end of a learning period, descriptive feedback supports ongoing learning by guiding students through detailed observations and constructive suggestions. This targeted communication fosters motivation and encourages self-regulation, making it an essential tool in formative educational practices.
Key Differences Between Summative Assessment and Descriptive Feedback
Summative assessment evaluates student learning at the end of an instructional period using grades or scores to measure overall performance, while descriptive feedback provides detailed, qualitative information aimed at guiding improvement during the learning process. Summative assessments are often standardized and formal, emphasizing accountability and final outcomes, whereas descriptive feedback is formative, personalized, and focuses on specific strengths and areas for growth. The key difference lies in summative assessment's role in certifying achievement versus descriptive feedback's function in enhancing ongoing learning.
Purposes and Goals in Education
Summative assessment primarily aims to evaluate student learning by measuring achievement against standardized benchmarks, providing a quantifiable summary of performance at the end of an instructional period. Descriptive feedback focuses on guiding student improvement through detailed, constructive commentary on specific aspects of their work, promoting ongoing learning and skill development. The goal of summative assessment is accountability and certification, while descriptive feedback targets personalized growth and deeper understanding.
Impact on Student Learning and Motivation
Summative assessment provides a comprehensive evaluation of student learning at the end of an instructional period, often influencing final grades and academic progression, but may limit ongoing motivation due to its evaluative nature. Descriptive feedback, by offering specific, actionable insights during the learning process, fosters a growth mindset and enhances student engagement, leading to improved academic performance. Research indicates that integrating descriptive feedback with summative assessment creates a balanced approach, positively impacting both motivation and mastery of content.
Examples in Classroom Practice
Summative assessment examples in classroom practice include final exams, standardized tests, and end-of-unit quizzes that evaluate student learning outcomes against set benchmarks. Descriptive feedback examples involve teachers providing specific comments on students' work, such as highlighting strengths, identifying areas for improvement, and suggesting actionable steps to enhance understanding. Incorporating descriptive feedback alongside summative assessments fosters continuous learning and supports student growth throughout the instructional process.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Summative assessment offers clear, quantifiable data on student performance, making it useful for grading and evaluating overall achievement but often lacks detailed insights for improvement. Descriptive feedback provides personalized, actionable guidance that fosters learning and skill development, though it can be time-consuming to produce and may challenge standardization in large classrooms. Balancing summative assessments with descriptive feedback promotes a comprehensive understanding of student progress and supports tailored instructional strategies.
Integrating Both Approaches for Effective Assessment
Integrating summative assessment and descriptive feedback enhances educational outcomes by combining final evaluation with actionable insights for improvement. Summative assessments provide a comprehensive measure of student achievement at the end of a learning cycle, while descriptive feedback offers detailed, formative guidance that supports ongoing development. Implementing both approaches enables educators to accurately assess performance and foster continuous learning, leading to more personalized and effective instructional strategies.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Assessment Strategy
Selecting the right assessment strategy depends on the educational goals and context, with summative assessments measuring overall learning outcomes and descriptive feedback fostering ongoing student growth. Effective educators balance these approaches by using summative assessments to evaluate achievement and descriptive feedback to guide improvement and deepen understanding. Integrating both methods maximizes student development and ensures comprehensive evaluation of learning progress.
Summative Assessment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com