Inquiry-Based Learning transforms education by encouraging students to actively explore questions and problems, fostering critical thinking and deeper understanding. This student-centered approach empowers Your curiosity and promotes engagement through hands-on activities and real-world applications. Discover how inquiry-based learning can revolutionize educational experiences by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
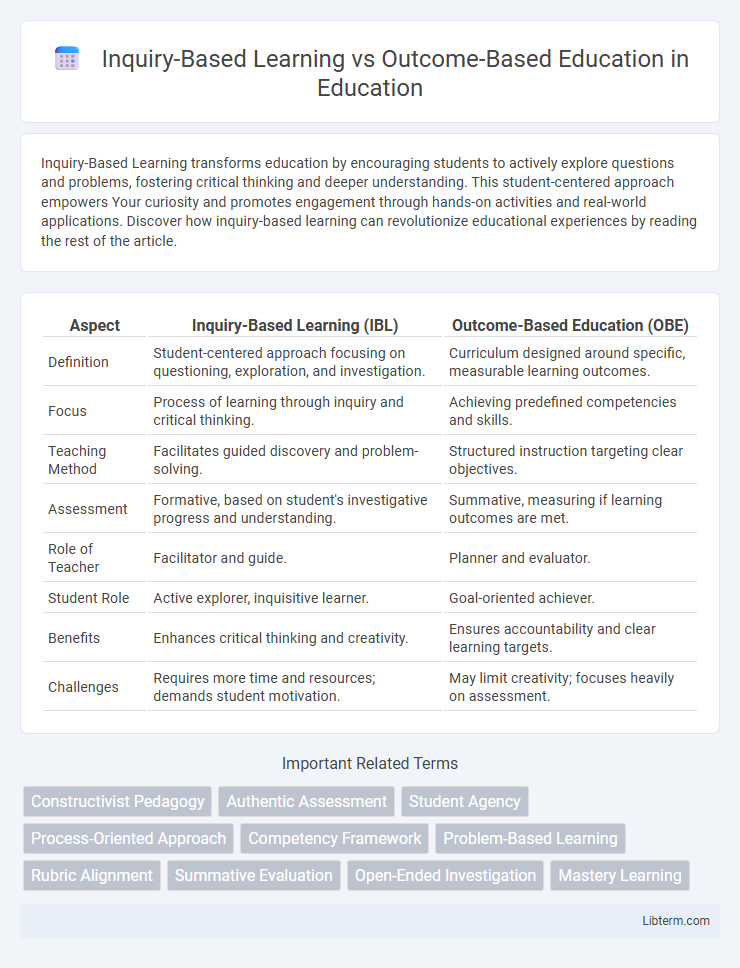
| Aspect | Inquiry-Based Learning (IBL) | Outcome-Based Education (OBE) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Student-centered approach focusing on questioning, exploration, and investigation. | Curriculum designed around specific, measurable learning outcomes. |
| Focus | Process of learning through inquiry and critical thinking. | Achieving predefined competencies and skills. |
| Teaching Method | Facilitates guided discovery and problem-solving. | Structured instruction targeting clear objectives. |
| Assessment | Formative, based on student's investigative progress and understanding. | Summative, measuring if learning outcomes are met. |
| Role of Teacher | Facilitator and guide. | Planner and evaluator. |
| Student Role | Active explorer, inquisitive learner. | Goal-oriented achiever. |
| Benefits | Enhances critical thinking and creativity. | Ensures accountability and clear learning targets. |
| Challenges | Requires more time and resources; demands student motivation. | May limit creativity; focuses heavily on assessment. |
Introduction to Inquiry-Based Learning and Outcome-Based Education
Inquiry-Based Learning (IBL) emphasizes student-centered exploration where learners engage in asking questions, investigating, and constructing knowledge through active participation. Outcome-Based Education (OBE) focuses on defining clear, measurable learning outcomes that guide curriculum design, instruction, and assessment to ensure students achieve specific competencies. Both approaches prioritize student achievement but differ as IBL fosters critical thinking and inquiry skills, while OBE targets mastery of predetermined educational objectives.
Core Principles of Inquiry-Based Learning
Inquiry-Based Learning centers on student-driven exploration, emphasizing questioning, investigation, and critical thinking as core principles. It fosters deeper understanding through active engagement with authentic problems and encourages learners to construct knowledge collaboratively. This approach contrasts Outcome-Based Education by prioritizing process and discovery over predefined learning outcomes and standardized assessments.
Foundations of Outcome-Based Education
Foundations of Outcome-Based Education (OBE) emphasize defining clear, measurable learning outcomes that guide curriculum design, assessment, and instruction to ensure students achieve specific competencies. Unlike Inquiry-Based Learning, which centers on student-driven exploration and questioning, OBE focuses on predetermined goals that align skills and knowledge with industry standards and societal needs. This results-oriented framework enhances accountability and provides a structured pathway for academic and career readiness.
Key Differences Between Inquiry-Based and Outcome-Based Approaches
Inquiry-Based Learning emphasizes student-driven exploration and critical thinking through questioning and investigation, fostering deeper understanding and problem-solving skills. Outcome-Based Education prioritizes clearly defined goals and measurable results, ensuring that specific competencies and learning objectives are achieved by all students. The key difference lies in Inquiry-Based Learning's process-oriented approach versus Outcome-Based Education's focus on predetermined outcomes and accountability metrics.
Advantages of Inquiry-Based Learning
Inquiry-Based Learning fosters critical thinking and problem-solving skills by encouraging students to explore questions and develop their understanding actively. This approach promotes deeper engagement and retention by allowing learners to construct knowledge through investigation and collaboration. Students gain adaptability and creativity, preparing them for real-world challenges beyond standardized assessment metrics.
Benefits of Outcome-Based Education
Outcome-Based Education (OBE) enhances student accountability by clearly defining expected competencies and learning outcomes, ensuring measurable academic progress. It promotes a structured curriculum design aligned with industry standards, facilitating the development of relevant skills for workforce readiness. OBE's focus on continuous assessment allows for targeted interventions, improving overall student performance and educational quality.
Challenges Faced in Inquiry-Based Learning
Inquiry-Based Learning faces challenges such as the demand for highly skilled educators capable of facilitating open-ended questioning and critical thinking, which can lead to inconsistent implementation across classrooms. Limited time and resources constrain the depth of inquiry possible, often resulting in superficial exploration rather than deep understanding. Furthermore, assessment methods in inquiry-based settings struggle to measure complex learning outcomes effectively, complicating the evaluation of student progress compared to the clearer benchmarks in Outcome-Based Education.
Limitations of Outcome-Based Education
Outcome-Based Education (OBE) often faces limitations such as a rigid focus on measurable outcomes that may overlook critical thinking and creativity development. This approach can lead to a narrow curriculum designed to satisfy specific standards, potentially restricting teacher autonomy and innovation. Furthermore, OBE's emphasis on standardized assessments may inadequately address individual student needs and diverse learning styles.
Effective Integration of Both Approaches in the Classroom
Effective integration of Inquiry-Based Learning (IBL) and Outcome-Based Education (OBE) in the classroom enhances student engagement and achievement by combining exploratory, student-centered inquiry with clearly defined learning outcomes and assessment criteria. Aligning inquiry activities with specific competencies and measurable outcomes ensures that students develop critical thinking skills while meeting academic standards and performance benchmarks. Educators can design curriculum frameworks that leverage IBL's emphasis on curiosity and problem-solving within the structured, goal-oriented approach of OBE to optimize both process and product of learning.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Approach for Student Success
Inquiry-Based Learning fosters critical thinking and deep understanding by encouraging students to explore and ask questions, while Outcome-Based Education prioritizes clear, measurable goals to ensure students achieve specific competencies. Selecting the right approach depends on balancing flexibility and structure, tailoring methods to student needs and educational contexts. Effective student success often emerges from integrating inquiry-driven exploration with targeted outcome assessments to create a comprehensive learning experience.
Inquiry-Based Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com