Norm-referenced assessments compare an individual's performance to a larger group, providing insight into relative standing rather than absolute mastery. These evaluations help identify how Your skills measure up against peers, often used in educational settings to guide instruction. Explore the rest of the article to understand the implications and uses of norm-referenced tests in more detail.
Table of Comparison
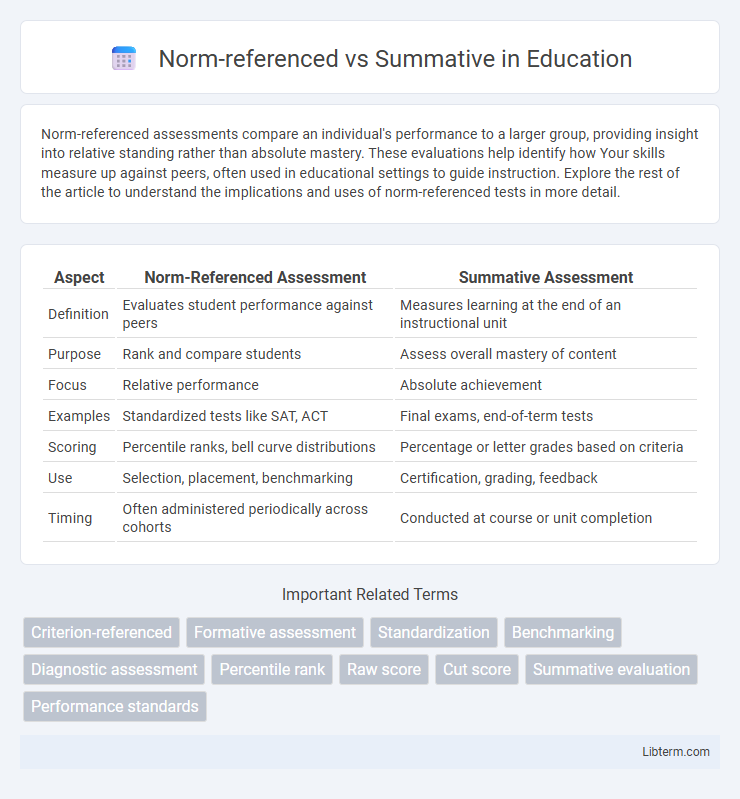
| Aspect | Norm-Referenced Assessment | Summative Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Evaluates student performance against peers | Measures learning at the end of an instructional unit |
| Purpose | Rank and compare students | Assess overall mastery of content |
| Focus | Relative performance | Absolute achievement |
| Examples | Standardized tests like SAT, ACT | Final exams, end-of-term tests |
| Scoring | Percentile ranks, bell curve distributions | Percentage or letter grades based on criteria |
| Use | Selection, placement, benchmarking | Certification, grading, feedback |
| Timing | Often administered periodically across cohorts | Conducted at course or unit completion |
Introduction to Assessment Types
Norm-referenced assessment compares a student's performance against a predefined group, highlighting relative standing within a cohort, while summative assessment evaluates overall learning outcomes at the end of an instructional period to determine mastery of specific content. Both types play critical roles in educational settings, with norm-referenced tests often used for selection or placement and summative assessments guiding final grading and curriculum effectiveness. Understanding these distinctions is essential for educators to design balanced evaluation strategies that align with learning objectives.
Defining Norm-Referenced Assessment
Norm-referenced assessment evaluates student performance by comparing individual scores to a statistically derived group average, identifying relative rankings within a peer group. It focuses on percentile ranks, standard scores, and normal distribution to discern how well a student performs against a norm group. This contrasts with summative assessments, which measure mastery of specific curriculum standards without direct comparison to others.
Understanding Summative Assessment
Summative assessment evaluates student learning by measuring mastery of content at the end of an instructional period, providing a clear snapshot of achievement against predetermined standards. Unlike norm-referenced assessments that rank students relative to their peers, summative assessments focus on whether each student meets specific learning objectives. This data-driven approach helps educators determine curriculum effectiveness and guide future instruction.
Key Differences Between Norm-Referenced and Summative Assessments
Norm-referenced assessments compare a student's performance to that of a peer group, emphasizing relative ranking and percentile scores, while summative assessments evaluate student learning against predefined curriculum standards to determine mastery. Norm-referenced tests often include standardized exams like IQ tests, whereas summative assessments encompass final exams or end-of-unit tests designed to measure comprehensive knowledge. The key difference lies in purpose: norm-referenced assesses comparative performance, and summative assesses overall achievement at a specific point in time.
Purposes and Objectives
Norm-referenced assessments aim to compare a student's performance against a peer group, identifying relative rankings and percentile ranks to inform placement or selection decisions. Summative assessments evaluate student learning at the end of an instructional period, measuring mastery of specific content standards or learning objectives to determine overall achievement. Both serve distinct educational purposes: norm-referenced tests prioritize comparative interpretation, while summative tests focus on measuring competency and instructional effectiveness.
Evaluation Methods and Scoring
Norm-referenced evaluation methods compare individual performance against a predefined group, using percentile ranks or standard scores to indicate relative standing. Summative evaluation methods assess overall achievement at the end of a course or unit, typically assigning scores based on predetermined criteria or mastery levels. Scoring in norm-referenced assessments emphasizes ranking, while summative assessments focus on measuring competency and content mastery.
Advantages of Norm-Referenced Assessments
Norm-referenced assessments provide a clear benchmark by comparing an individual's performance against a broader population, enabling educators to identify relative strengths and weaknesses efficiently. These assessments facilitate targeted intervention by highlighting percentile ranks, which help prioritize resource allocation for students needing additional support. Norm-referenced tests also promote standardization and consistency across diverse educational settings, ensuring equitable measurement of student achievement.
Benefits of Summative Assessments
Summative assessments provide a comprehensive evaluation of student learning by measuring mastery of specific content at the end of instructional units, offering clear data for curriculum effectiveness and student progress. These assessments enable educators to identify knowledge gaps and inform instructional decisions by delivering standardized scores that facilitate comparisons across different cohorts. The results from summative assessments support accountability, guide grade assignments, and assist in monitoring long-term educational outcomes.
Common Challenges and Limitations
Norm-referenced assessments often face challenges related to cultural and socioeconomic biases, which can skew comparisons among diverse student populations. Summative assessments may have limitations in capturing a student's comprehensive learning progress due to their focus on final outcomes rather than ongoing development. Both assessment types struggle with providing actionable feedback for personalized instruction, limiting their effectiveness in supporting individualized learning trajectories.
Choosing the Right Assessment Approach
Choosing the right assessment approach depends on the specific educational goal and context, with norm-referenced tests comparing student performance against a peer group to identify relative ranking, whereas summative assessments evaluate student learning at the end of an instructional period to measure mastery of content. Norm-referenced assessments are ideal for selection and placement decisions, while summative assessments provide critical data for determining overall achievement and guiding curriculum improvements. Understanding the purpose, stakeholders' needs, and desired outcomes ensures the effective selection between norm-referenced and summative assessments.
Norm-referenced Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com