Competency-Based Education focuses on mastering specific skills and knowledge at your own pace, ensuring practical understanding over traditional time-based learning. This approach tailors education to individual needs, promoting deeper engagement and real-world application. Explore the rest of the article to discover how Competency-Based Education can transform your learning experience.
Table of Comparison
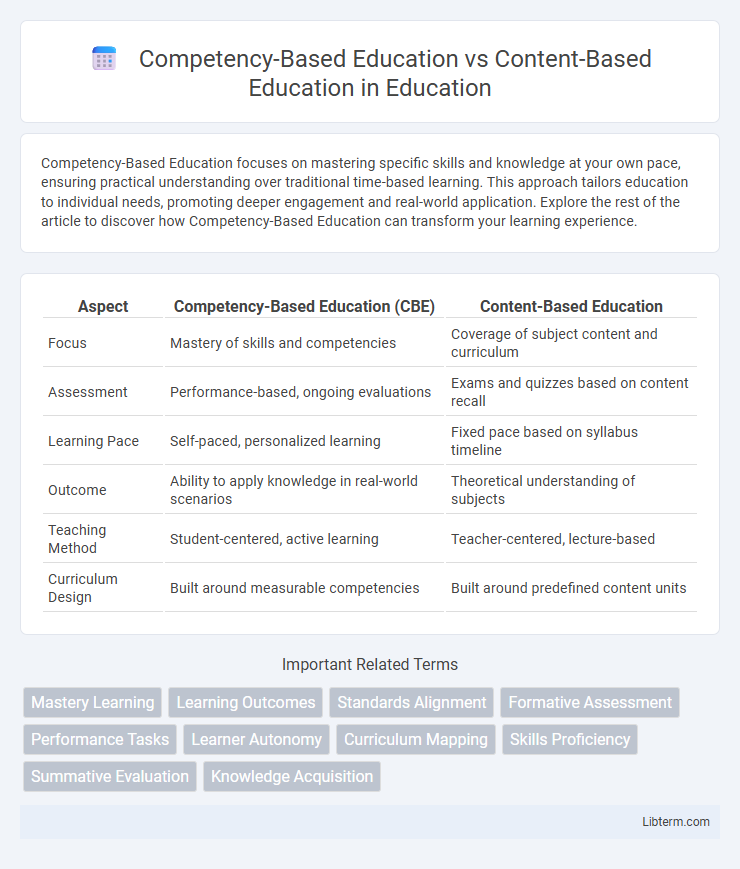
| Aspect | Competency-Based Education (CBE) | Content-Based Education |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Mastery of skills and competencies | Coverage of subject content and curriculum |
| Assessment | Performance-based, ongoing evaluations | Exams and quizzes based on content recall |
| Learning Pace | Self-paced, personalized learning | Fixed pace based on syllabus timeline |
| Outcome | Ability to apply knowledge in real-world scenarios | Theoretical understanding of subjects |
| Teaching Method | Student-centered, active learning | Teacher-centered, lecture-based |
| Curriculum Design | Built around measurable competencies | Built around predefined content units |
Understanding Competency-Based Education
Competency-Based Education (CBE) emphasizes mastery of specific skills and abilities, allowing students to progress at their own pace once they demonstrate proficiency. Unlike Content-Based Education, which focuses on the delivery of subject matter regardless of individual understanding, CBE prioritizes measurable outcomes and real-world application. This approach enhances personalized learning by aligning educational goals with workforce demands and critical competencies.
What Defines Content-Based Education?
Content-Based Education centers on delivering subject matter knowledge through structured curricula focused on specific topics, facts, and theories. It emphasizes mastery of predefined content standards and assessments designed to measure retention and comprehension of the material. This approach prioritizes linear progression through educational content, ensuring students acquire essential information aligned with academic benchmarks.
Key Differences Between Competency and Content Approaches
Competency-based education emphasizes mastery of specific skills and real-world application, while content-based education focuses on the absorption of information and subject matter knowledge. Competency approaches allow for personalized pacing and assessment based on demonstrated abilities, whereas content approaches typically follow a fixed curriculum and time schedule. The key difference lies in outcome orientation: competencies measure what learners can do, whereas content measures what learners know.
Goals and Outcomes of Competency-Based Education
Competency-Based Education (CBE) emphasizes mastering specific skills and knowledge applicable to real-world tasks, aiming to develop measurable competencies rather than simply covering course content. The primary goal of CBE is to ensure learners attain demonstrable proficiency and practical abilities that align with industry standards and workforce demands. Outcomes focus on personalized learning paths, faster progression based on skill mastery, and readiness for professional challenges.
Learning Objectives in Content-Based Education
Learning objectives in content-based education emphasize the mastery of specific subject matter and knowledge acquisition, guiding students to understand and recall key concepts within a discipline. These objectives are structured to cover comprehensive content coverage, often aligned with standardized curricula or textbooks. The focus remains on delivering information and ensuring that learners can demonstrate familiarity with defined content areas.
Assessment Methods: Competency vs Content
Competency-Based Education (CBE) utilizes performance-based assessments that measure students' ability to demonstrate specific skills and real-world applications, ensuring mastery of competencies before progression. Content-Based Education primarily relies on traditional exams and quizzes that evaluate the retention and recall of subject matter knowledge without necessarily assessing practical proficiency. CBE assessments often include portfolios, practical tasks, and simulations, which provide a deeper insight into learner capabilities compared to the standardized testing methods commonly used in content-based frameworks.
Student Engagement and Personalization
Competency-Based Education (CBE) enhances student engagement by allowing learners to progress upon mastering specific skills, creating a more personalized learning experience tailored to individual strengths and needs. In contrast, Content-Based Education emphasizes standardized curriculum delivery, which may limit personalization and reduce active student involvement. CBE's focus on real-world application and mastery promotes deeper understanding, motivating students through relevant and adaptive pathways.
Challenges in Implementing Both Models
Competency-based education faces challenges such as accurately assessing skill mastery, ensuring personalized pacing, and aligning curriculum with industry standards, often requiring extensive faculty training and resource allocation. Content-based education struggles with engaging diverse learners due to rigid curriculum structures, inconsistent knowledge retention, and the difficulty of updating teaching materials to keep pace with rapid advancements. Both models require substantial institutional support to overcome obstacles related to assessment methods, curriculum design, and scalability in diverse educational environments.
Impact on Teachers and Curriculum Design
Competency-Based Education (CBE) shifts focus from traditional content delivery to mastering skills and abilities, requiring teachers to act as facilitators and assess student progress through practical application rather than exams. This approach demands curriculum redesign to integrate real-world competencies, personalized learning pathways, and flexible pacing, contrasting with Content-Based Education's standardized syllabi and uniform assessment methods. The impact on teachers involves continuous professional development to support individualized instruction, while curriculum design prioritizes skill acquisition aligned with labor market needs and student readiness.
Future Trends in Educational Approaches
Competency-Based Education (CBE) is rapidly gaining traction due to its focus on mastery of specific skills and personalized learning paths, aligning with workforce demands and lifelong learning trends. Content-Based Education remains foundational but is evolving by integrating digital tools and adaptive technologies to enhance engagement and retention. Future educational approaches emphasize hybrid models that blend competency mastery with content knowledge, supported by AI-driven analytics to tailor instruction and assessment in real-time.
Competency-Based Education Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com