Task-Based Instruction focuses on learning through engaging in meaningful tasks that simulate real-life situations, enhancing practical language use and problem-solving skills. This approach prioritizes active participation and contextual learning, making the educational experience more relevant and effective for learners. Discover how Task-Based Instruction can transform Your teaching methods by exploring key strategies and benefits in the full article.
Table of Comparison
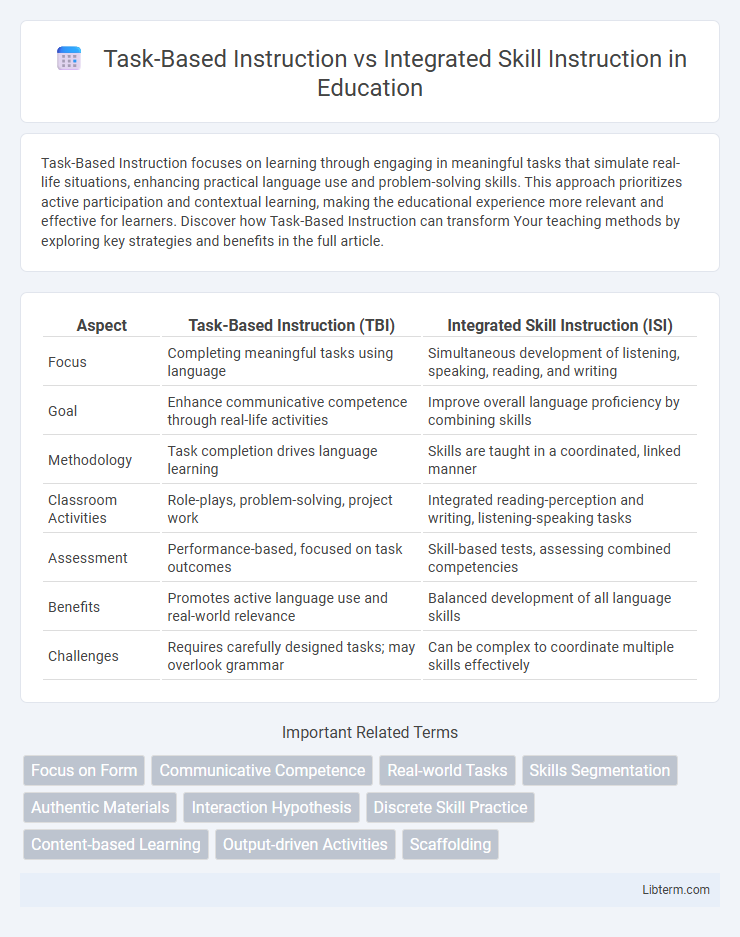
| Aspect | Task-Based Instruction (TBI) | Integrated Skill Instruction (ISI) |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Completing meaningful tasks using language | Simultaneous development of listening, speaking, reading, and writing |
| Goal | Enhance communicative competence through real-life activities | Improve overall language proficiency by combining skills |
| Methodology | Task completion drives language learning | Skills are taught in a coordinated, linked manner |
| Classroom Activities | Role-plays, problem-solving, project work | Integrated reading-perception and writing, listening-speaking tasks |
| Assessment | Performance-based, focused on task outcomes | Skill-based tests, assessing combined competencies |
| Benefits | Promotes active language use and real-world relevance | Balanced development of all language skills |
| Challenges | Requires carefully designed tasks; may overlook grammar | Can be complex to coordinate multiple skills effectively |
Introduction to Teaching Approaches
Task-Based Instruction emphasizes real-world language use by engaging learners in meaningful tasks that promote practical communication and problem-solving skills. Integrated Skill Instruction combines listening, speaking, reading, and writing activities to develop language proficiency holistically, enhancing learner interaction and comprehension. Both approaches address different aspects of language acquisition, influenced by communicative language teaching theories and learner-centered pedagogy.
Defining Task-Based Instruction
Task-Based Instruction (TBI) centers on using authentic tasks as the primary unit of learning, emphasizing real-world communication over isolated language drills. It engages learners in meaningful activities that require practical language use, such as problem-solving, information exchange, or project completion. This approach fosters language acquisition through active participation and contextualized practice, enhancing fluency and comprehension skills.
Understanding Integrated Skill Instruction
Integrated Skill Instruction combines listening, speaking, reading, and writing tasks to promote holistic language acquisition, enhancing learners' communicative competence in authentic contexts. It emphasizes the simultaneous development of multiple skills through meaningful activities, increasing learner engagement and retention. This approach contrasts with Task-Based Instruction, which isolates specific tasks to target individual language functions sequentially.
Key Principles of Task-Based Instruction
Task-Based Instruction centers on using authentic tasks that require meaningful language use, promoting learner autonomy and interaction for effective language acquisition. It emphasizes real-world relevance, where learners complete tasks that mirror practical communication, enhancing fluency and problem-solving skills. This approach contrasts with Integrated Skill Instruction, which combines listening, speaking, reading, and writing without necessarily focusing on task authenticity or completion.
Core Components of Integrated Skill Instruction
Integrated Skill Instruction combines listening, speaking, reading, and writing to enhance overall language proficiency through interconnected activities. Core components include authentic materials, meaningful communication, contextualized tasks, and feedback mechanisms that support simultaneous development of multiple skills. This approach promotes cognitive engagement and real-world applicability, contrasting with task-based instruction's focus on discrete tasks.
Benefits of Task-Based Instruction
Task-Based Instruction enhances language acquisition by promoting authentic communication through real-life tasks, which improves learners' practical speaking and listening skills. It fosters learner motivation and engagement by emphasizing meaningful interaction and problem-solving rather than rote memorization. This approach also adapts well to diverse proficiency levels, allowing personalized learning experiences that boost confidence and fluency.
Advantages of Integrated Skill Instruction
Integrated Skill Instruction enhances language acquisition by combining listening, speaking, reading, and writing skills in meaningful contexts, promoting real-world communication competence. It fosters cognitive connections among skills, leading to greater retention and transferability of language use. This holistic approach accommodates diverse learning styles and supports authentic interaction, improving overall language proficiency more effectively than isolated task-based activities.
Challenges in Implementation
Task-Based Instruction faces challenges in implementation due to the need for carefully designed authentic tasks that require significant teacher preparation and appropriate classroom resources. Integrated Skill Instruction encounters difficulties in balancing the simultaneous development of listening, speaking, reading, and writing skills, often demanding complex lesson planning and assessment strategies. Both approaches struggle with aligning instructional methods to diverse learner proficiency levels and maintaining student engagement throughout the instructional process.
Classroom Applications and Examples
Task-Based Instruction enhances language learning by engaging students in real-world tasks such as planning a trip or conducting interviews, which promotes practical communication skills and learner autonomy. Integrated Skill Instruction combines reading, writing, listening, and speaking activities within a single lesson, like analyzing a news article followed by group discussions and writing exercises to reinforce language comprehension and production. Both approaches improve language proficiency but Task-Based Instruction emphasizes meaningful output through authentic tasks, whereas Integrated Skill Instruction focuses on simultaneous development of multiple language skills.
Choosing the Right Approach for Learners
Task-Based Instruction emphasizes real-world tasks that promote active language use and practical communication skills, ideal for learners seeking functional proficiency. Integrated Skill Instruction combines reading, writing, listening, and speaking to develop balanced language competence, suitable for learners needing comprehensive skill development. Selecting the right approach depends on learners' goals, proficiency levels, and contextual needs to maximize effective language acquisition.
Task-Based Instruction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com