Mastering task management is crucial for boosting productivity and reducing stress in both personal and professional life. Prioritizing, breaking down complex projects, and setting realistic deadlines help ensure consistent progress and goal achievement. Explore the following insights to enhance your efficiency and get your tasks done with confidence.
Table of Comparison
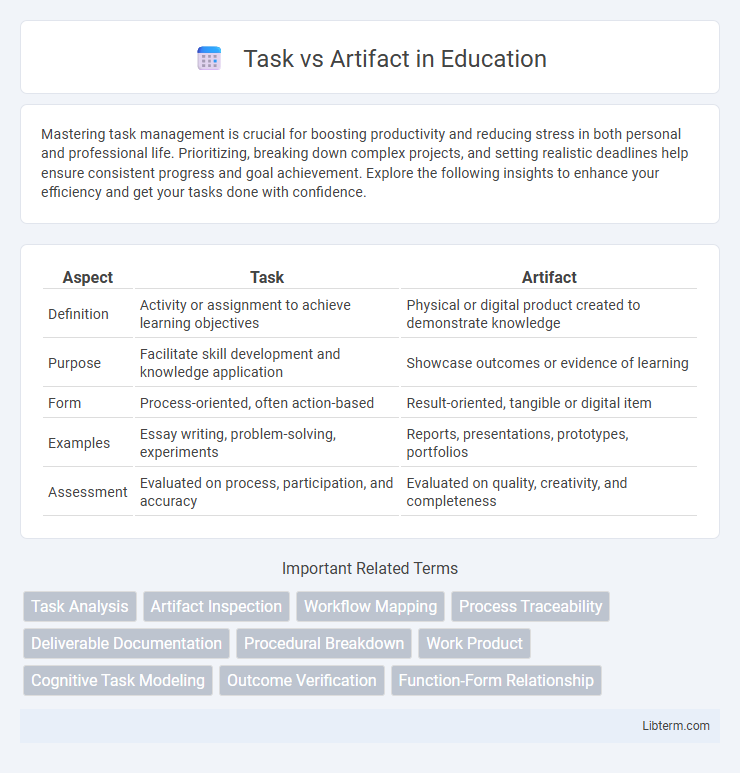
| Aspect | Task | Artifact |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Activity or assignment to achieve learning objectives | Physical or digital product created to demonstrate knowledge |
| Purpose | Facilitate skill development and knowledge application | Showcase outcomes or evidence of learning |
| Form | Process-oriented, often action-based | Result-oriented, tangible or digital item |
| Examples | Essay writing, problem-solving, experiments | Reports, presentations, prototypes, portfolios |
| Assessment | Evaluated on process, participation, and accuracy | Evaluated on quality, creativity, and completeness |
Understanding the Concepts: Task and Artifact
A task represents a specific action or set of actions aimed at achieving a particular goal within a process or project, often defined by clear objectives and deliverables. An artifact refers to any tangible by-product or item produced during the execution of tasks, such as documents, models, or diagrams, serving as evidence or support for the work performed. Understanding the distinction between tasks and artifacts is crucial for effective workflow management, ensuring that each task contributes to the creation or refinement of relevant artifacts that advance project goals.
Key Differences Between Task and Artifact
Task refers to a specific unit of work or activity performed to achieve a goal, while Artifact is a tangible byproduct or output produced as a result of completing a task. Tasks are action-oriented and dynamic, involving processes or steps, whereas Artifacts are static and serve as evidence or documentation of the work completed. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for effective project management and workflow optimization.
Defining Task: Purpose and Scope
A task represents a discrete unit of work designed to achieve a specific goal within a project, defined by clear objectives and boundaries that guide its execution. Its purpose centers on breaking down complex projects into manageable actions to enhance focus and productivity. The scope delineates the task's limits, specifying inputs, required resources, expected outputs, and dependencies to ensure alignment with overall project goals.
Defining Artifact: Characteristics and Role
An artifact is a tangible or digital object produced or utilized during a project, serving as concrete evidence of work progress and deliverables. Key characteristics of artifacts include documentation, models, designs, or code that capture knowledge, requirements, or decisions, enabling communication and traceability. Artifacts play a critical role in ensuring project consistency, quality assurance, and facilitating collaboration among stakeholders.
How Tasks Lead to Artifacts
Tasks represent specific actions or processes undertaken by individuals or teams to achieve project objectives, driving the creation of tangible or intangible artifacts. These artifacts include documents, models, designs, or software components that embody the deliverables resulting from task execution. The systematic completion of tasks ensures artifact development aligns with project requirements, facilitating progress tracking and quality control.
Artifact Types: Examples Across Domains
Artifact types vary significantly across domains, including physical artifacts like tools and machinery in manufacturing, digital artifacts such as code repositories and software documentation in software development, and cultural artifacts like manuscripts and artworks in anthropology. Each artifact type serves as a tangible or intangible product resulting from specific tasks, enabling analysis, replication, or preservation within its respective field. Understanding these diverse artifact types enhances task management and outcome evaluation by aligning resources with domain-specific requirements.
The Lifecycle: From Task Initiation to Artifact Creation
The lifecycle from task initiation to artifact creation involves defining a task with clear objectives, executing it through organized workflows, and producing a tangible or digital artifact that documents the outcomes or supports further project phases. Effective task management ensures each step is meticulously tracked, enabling seamless transition from conceptual stages to artifact development. Artifacts serve as critical deliverables or documentation, capturing the results and decisions made during the task lifecycle for future reference and quality assurance.
Task vs Artifact: Impacts on Workflow Optimization
Task represents specific actions or processes that need completion within a workflow, while an Artifact refers to the digital or physical outputs produced by these tasks. Understanding the distinction between Task and Artifact is crucial for workflow optimization, as it enables precise identification of bottlenecks and resource allocation. Prioritizing task efficiency alongside artifact quality enhances overall productivity and facilitates seamless process automation.
Common Misconceptions About Tasks and Artifacts
Tasks are often mistakenly viewed as standalone actions, but they are part of a broader workflow that includes inputs, processes, and outputs. Artifacts, frequently confused with mere documents, represent tangible or digital work products that serve as evidence of task completion and project progress. Understanding that tasks drive the creation of artifacts clarifies their distinct yet interdependent roles in project management and software development.
Best Practices for Managing Tasks and Artifacts
Effective management of tasks and artifacts involves clearly defining task objectives and linking artifacts as supporting documentation to enhance traceability and accountability. Employing task management tools that integrate artifact storage ensures seamless collaboration and version control, promoting real-time updates and reducing redundancy. Regular reviews and updates of both tasks and artifacts optimize workflow efficiency and maintain project alignment with business goals.
Task Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com